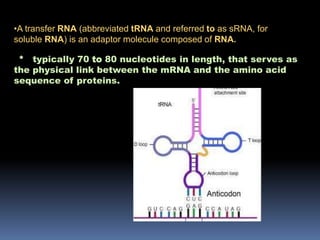
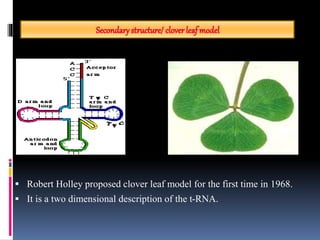
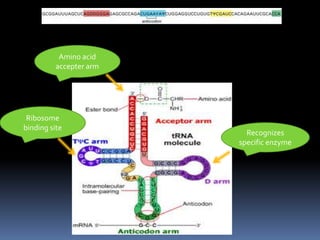
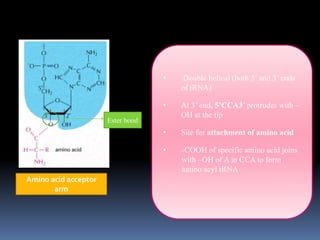
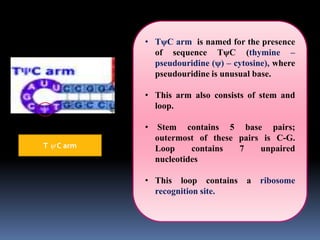
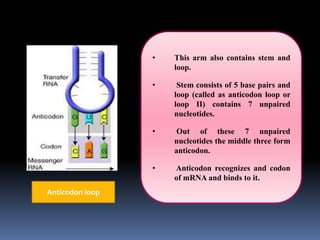
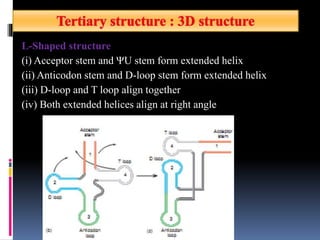
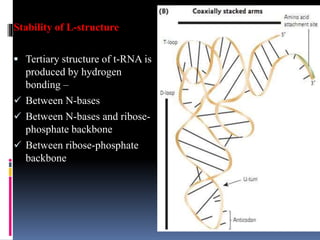
tRNA is a small RNA molecule that serves as the physical link between mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins during protein synthesis. It has a specific three-dimensional structure and performs several important functions. tRNA has a cloverleaf secondary structure and an L-shaped tertiary structure that allows it to interact with mRNA and transfer the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain. tRNA plays key roles in translation, regulation of enzyme synthesis, and some viruses use tRNAs as primers for reverse transcription.