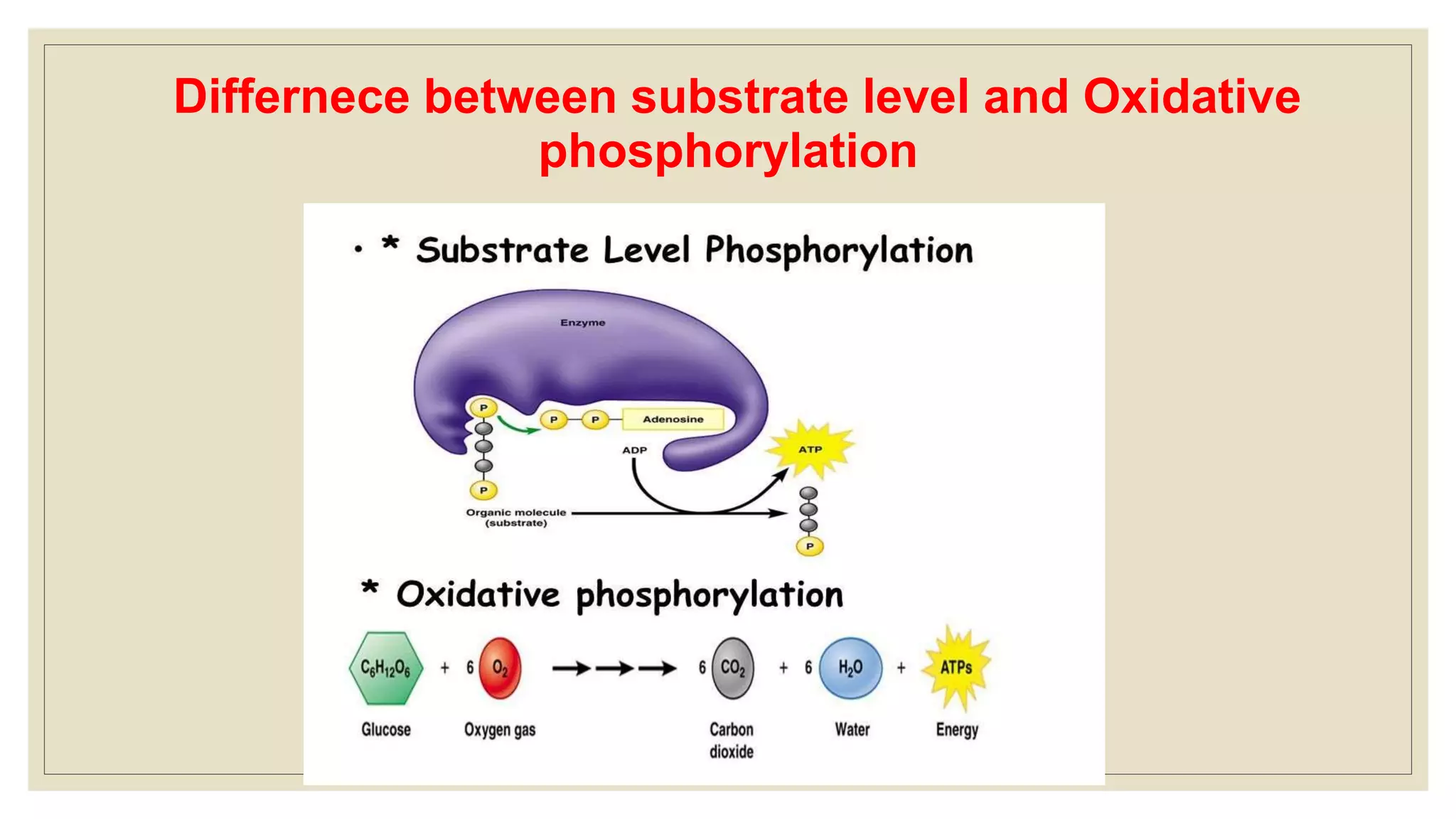
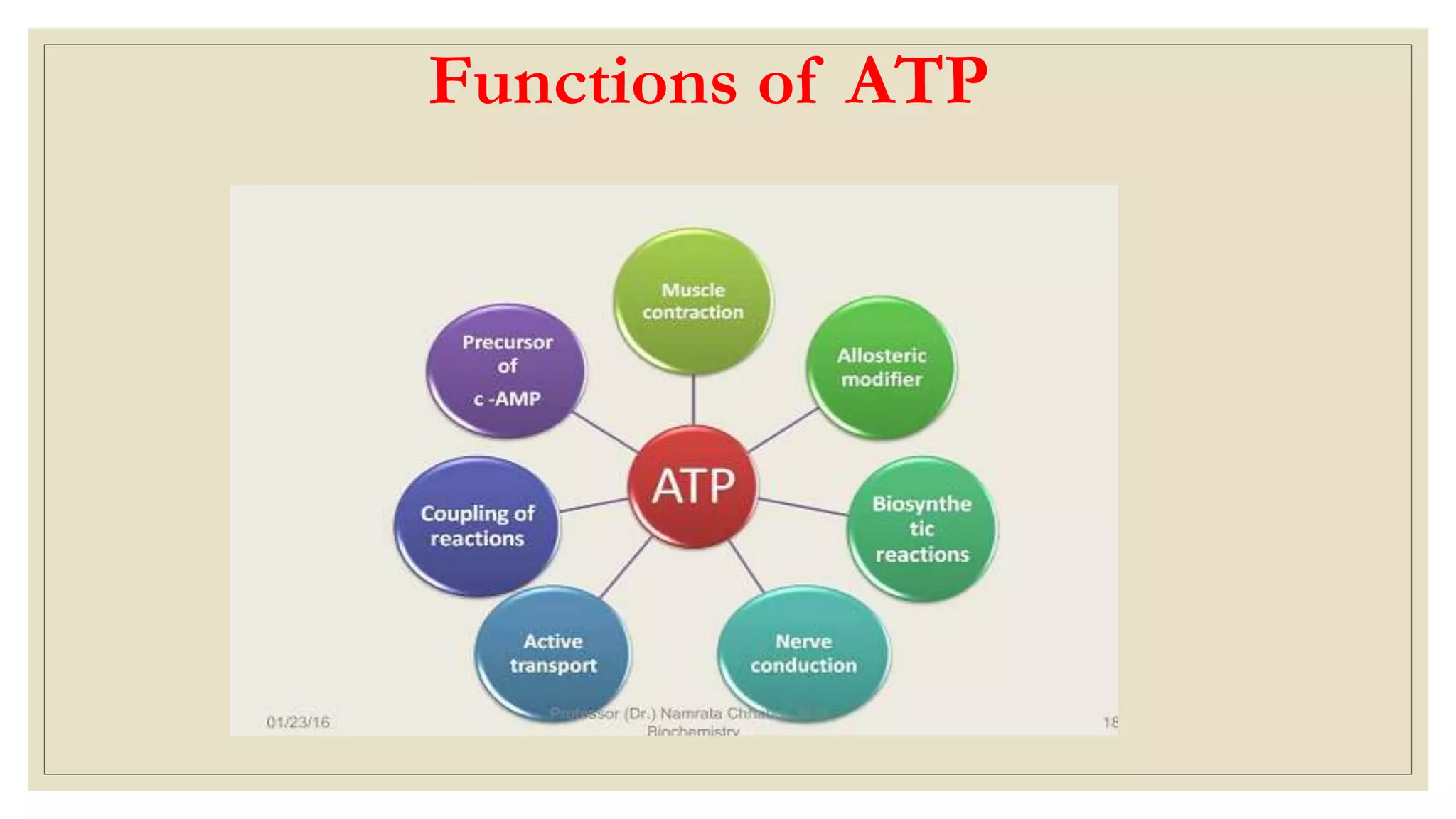
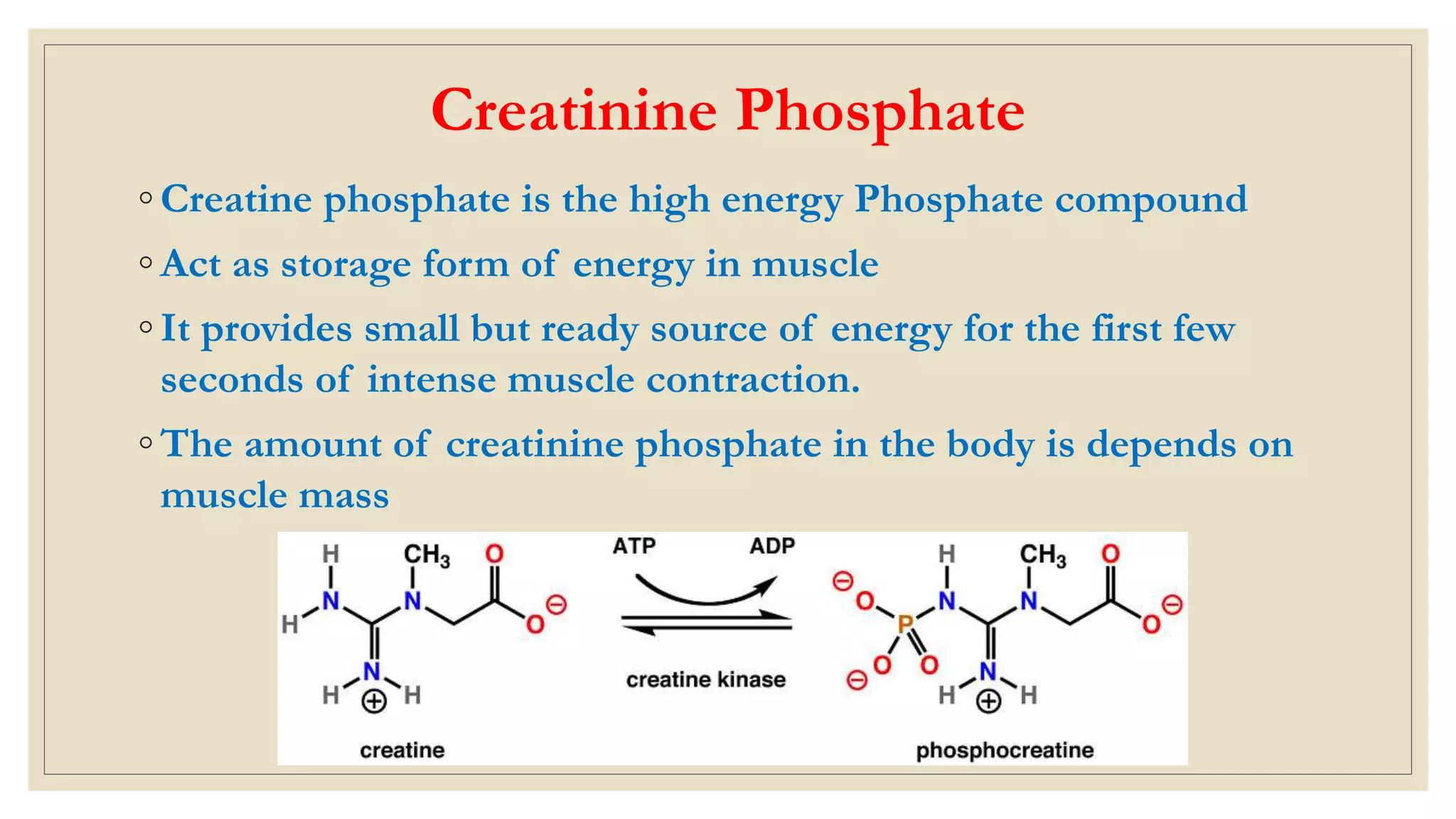
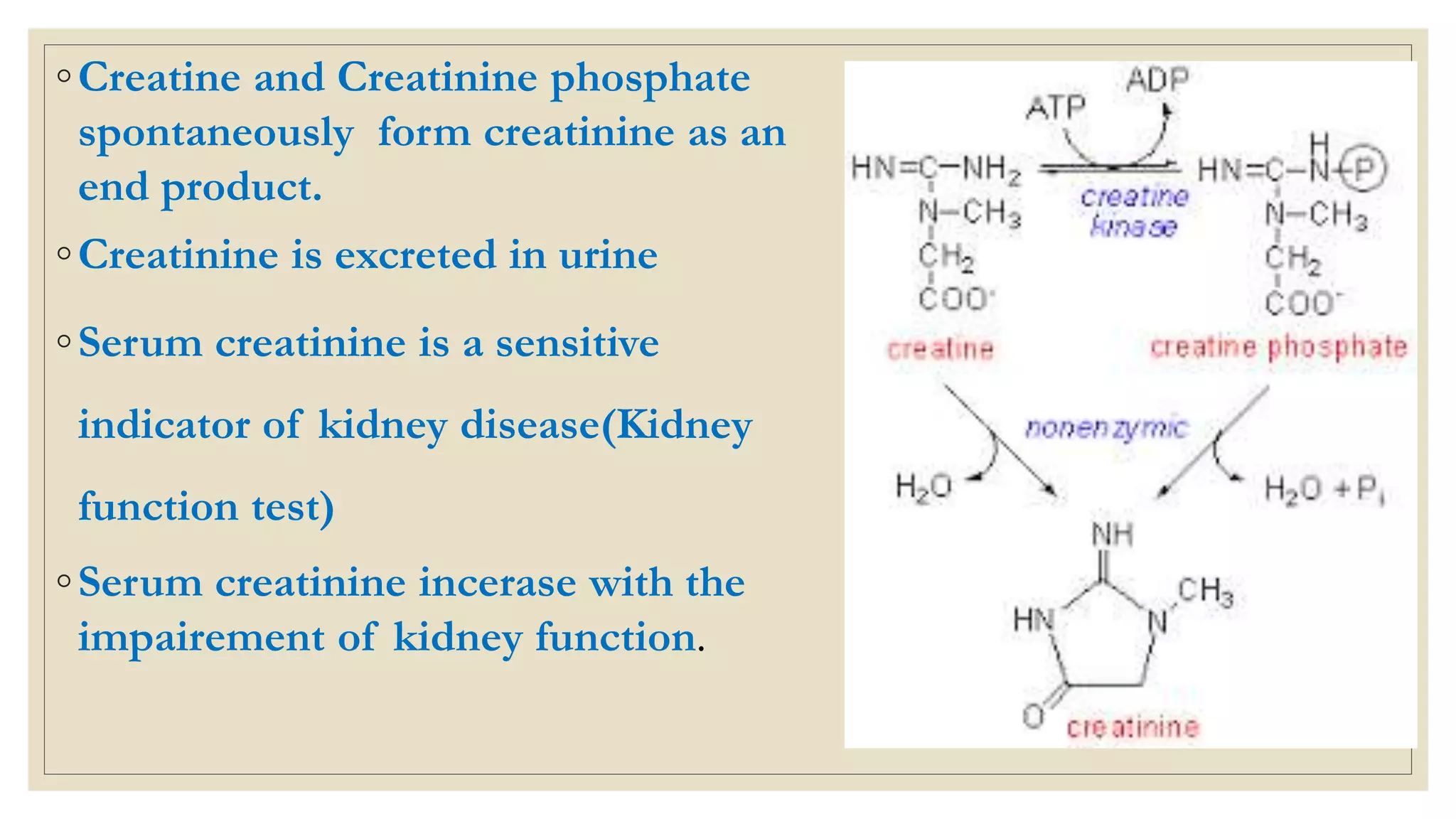
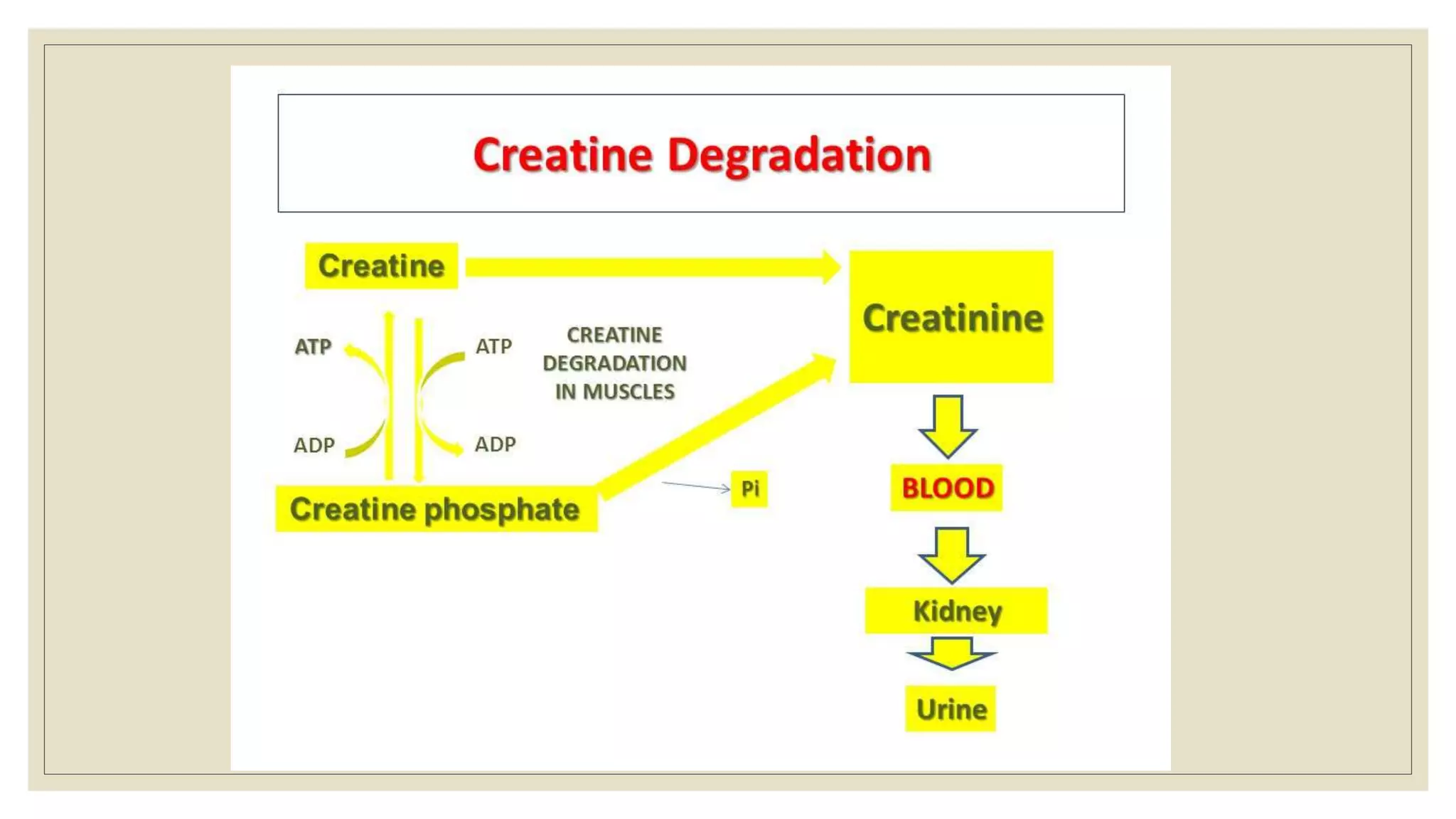
This document summarizes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and creatine phosphate. It discusses that ATP is an organic compound that provides energy for many cellular processes through substrate-level phosphorylation, which forms 10% of ATP, and oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria, which forms 90% of ATP. Creatine phosphate acts as a storage form of energy in muscles, providing a ready source of energy for intense muscle contraction in the first few seconds before oxidative phosphorylation can produce more ATP. The document also notes that creatinine is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate and creatine in muscles that is excreted in the urine, with serum creatinine levels indicating kidney function.