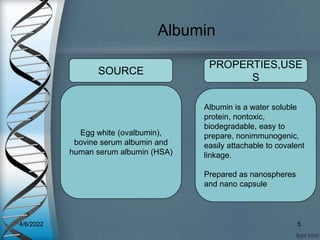
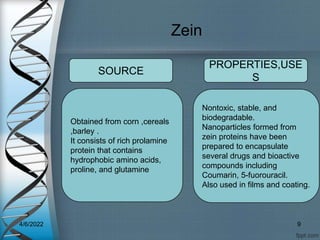
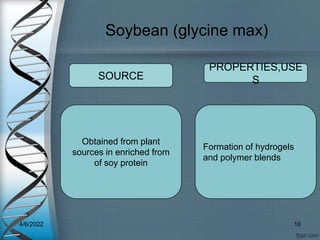
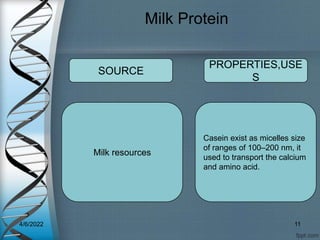
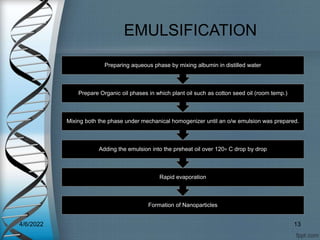
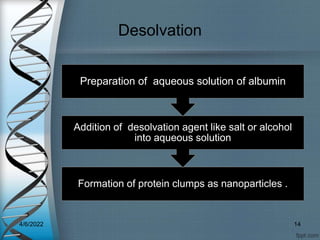
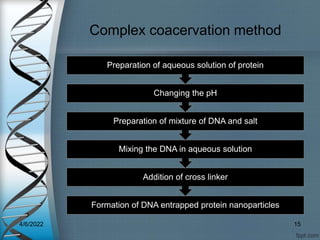
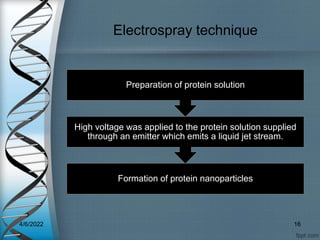
Protein-based nanostructures have revolutionized nanomedicine, offering enhanced biocompatibility and targeted drug delivery options, particularly in pharmaceuticals for various therapies. Different protein nanoparticles such as albumin, gelatin, and zein exhibit unique properties and advantages, including improved bioavailability and reduced toxicity. Their applications span drug delivery, immunological adjuvants, and treatment of diseases like cancer and tuberculosis.