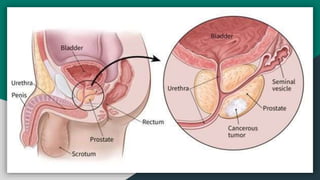
The document provides information about benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate vaporization surgery. It defines BPH and discusses its causes, signs and symptoms, and complications. It then describes the anatomy of the prostate gland and different types of prostate laser surgery procedures. The advantages and disadvantages of prostate vaporization are outlined. Pre-operative, intra-operative, and post-operative nursing care are also summarized.