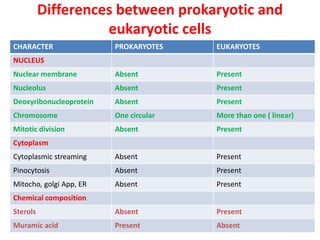
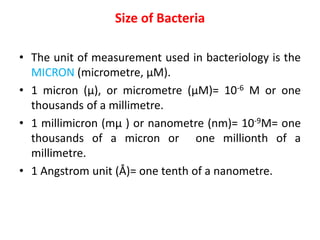
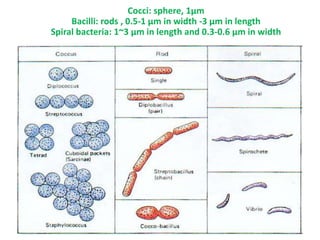
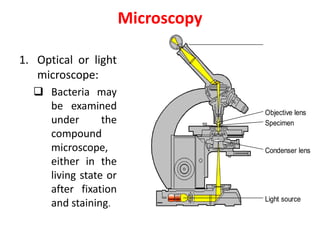
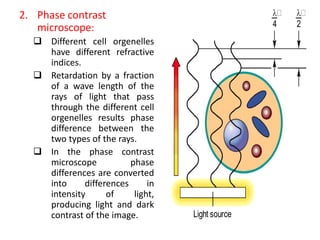
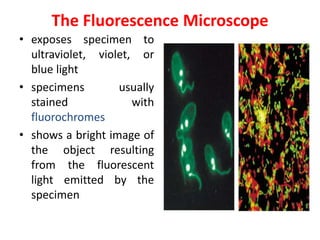
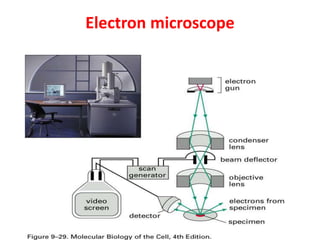
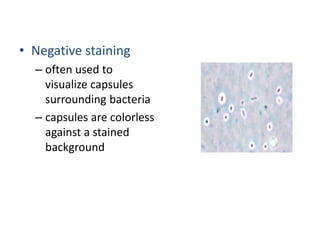
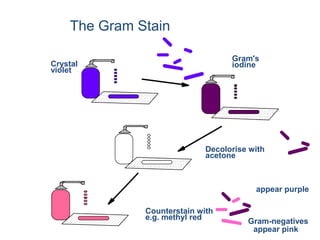
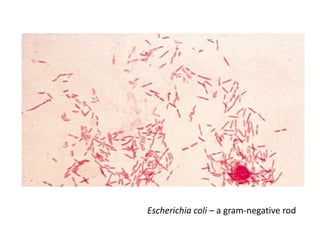
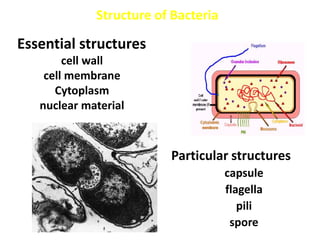
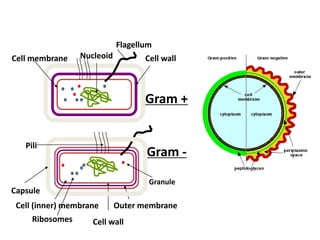
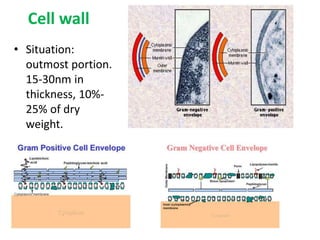
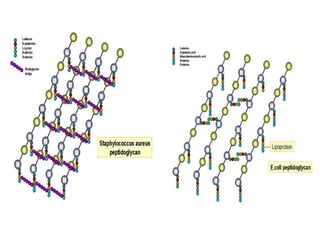
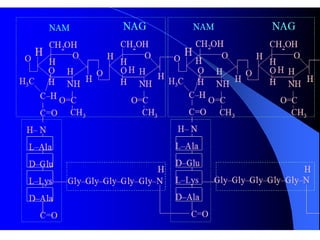
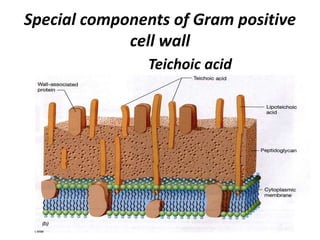
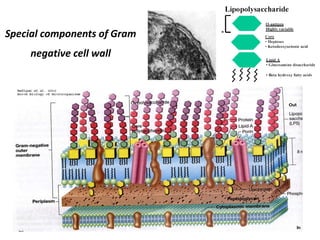
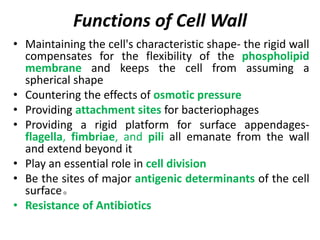
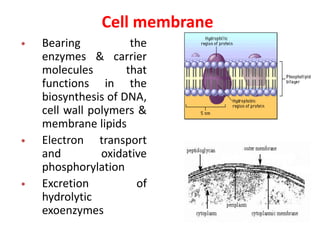
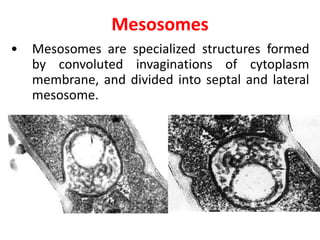
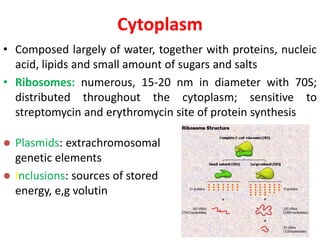
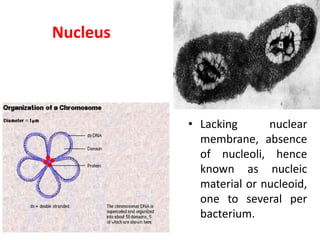
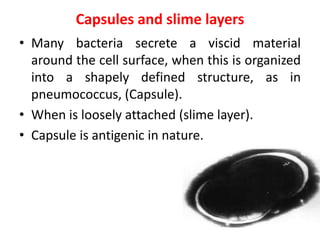
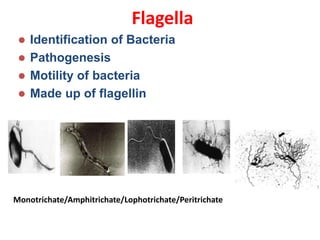
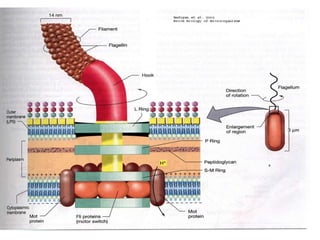
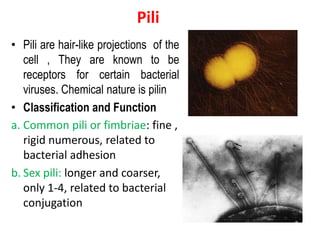
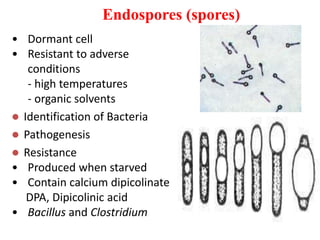
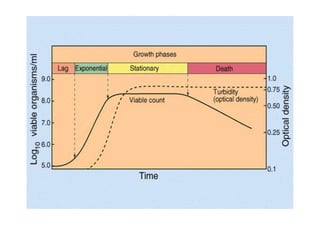
Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic organisms that are studied in medical microbiology. They have distinct cell structures including a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleic material. Bacteria can be visualized under light, phase contrast, or electron microscopes and stained using simple, differential, or acid-fast staining techniques. Gram staining divides bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative categories based on cell wall structure. Bacteria exhibit a variety of external structures such as flagella, pili, capsules, and endospores, and follow a defined growth curve with lag, log, stationary, and death phases.