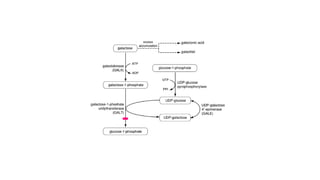
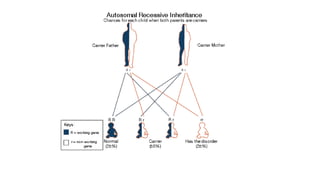
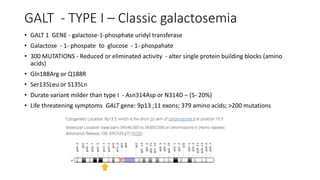
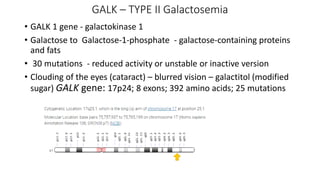
Galactosemia is a genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of enzymes involved in galactose metabolism, leading to an accumulation of galactose and its metabolites in the body. There are three main types caused by deficiencies in galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (GALT), galactokinase (GALK), or galactose-4-epimerase (GALE). Symptoms include jaundice, poor feeding, vomiting, and long term issues such as speech delays, intellectual disability, and ovarian dysfunction. Treatment requires strict lifelong avoidance of galactose in the diet through exclusion of milk and milk products, along with calcium and soy or hydrolyzed protein formula supplementation.