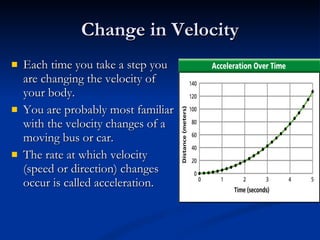
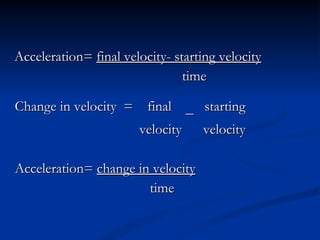
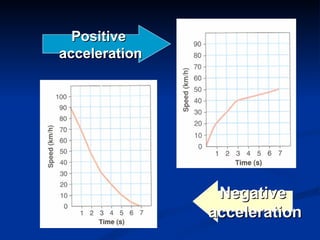
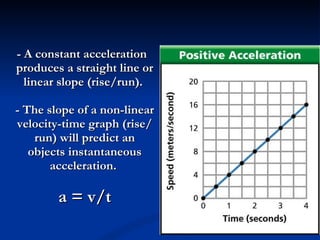
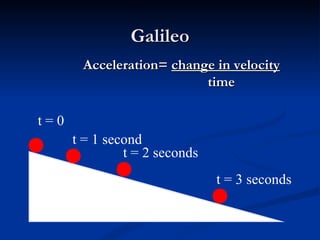
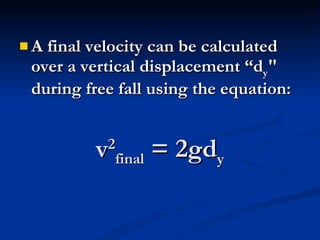Acceleration describes how an object's velocity changes over time. An object accelerates when its speed changes, its direction changes, or both its speed and direction change. Acceleration is calculated by taking the change in velocity and dividing by the time elapsed. Common examples of acceleration include objects falling due to gravity, objects moving in circles due to centripetal force, and vehicles changing speed.