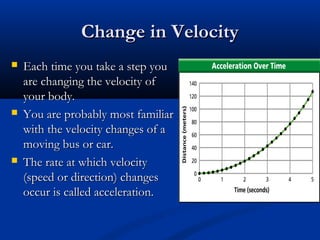
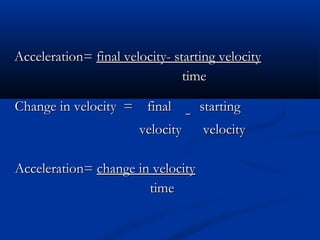
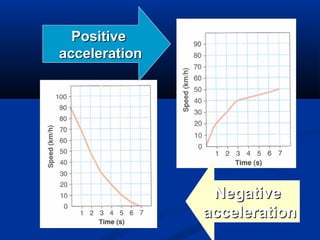
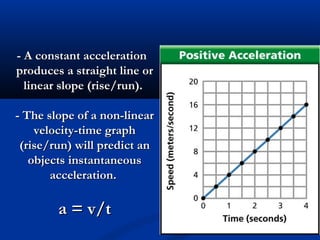
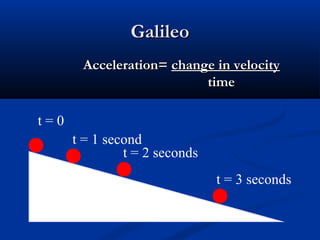
This document discusses acceleration and how it relates to changes in an object's velocity over time. It defines acceleration as the rate of change of velocity, whether that means changing speed or direction. Acceleration is calculated by finding the change in velocity divided by the time taken. Positive acceleration increases velocity while negative acceleration decreases velocity. The constant acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 10 m/s2. Free falling objects experience this acceleration and will fall at increasing speeds over time if air resistance is negligible. Galileo was one of the first scientists to study acceleration from gravity by rolling objects down inclined planes and observing their increasing speed over time.