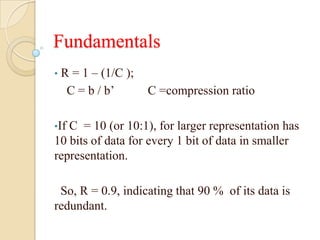
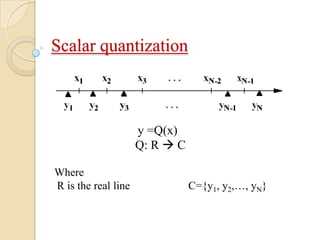
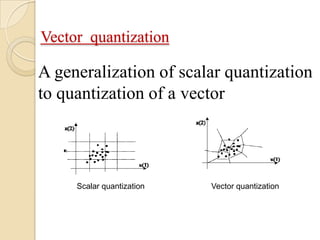
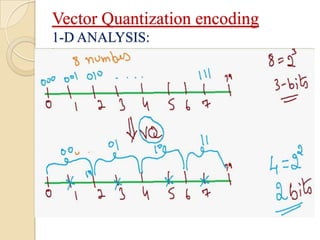
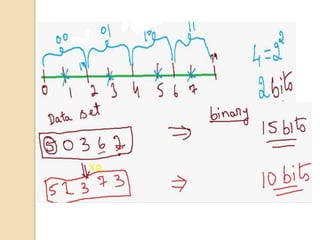
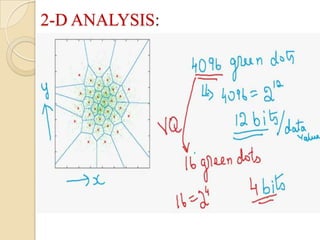
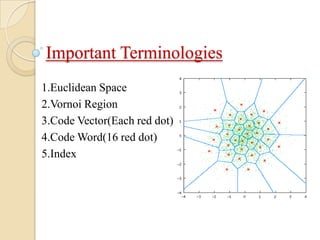
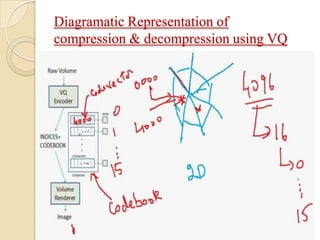
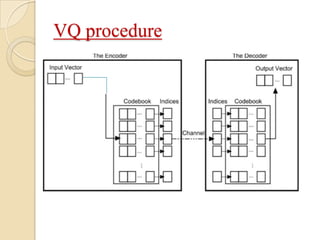
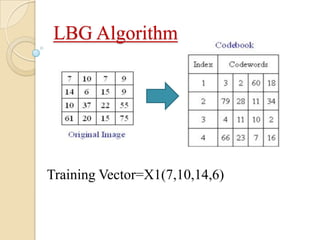
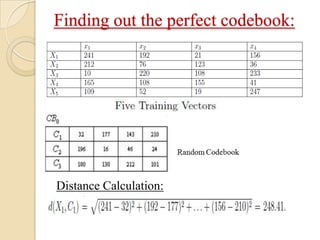
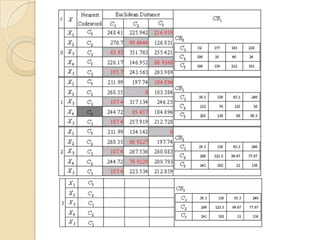
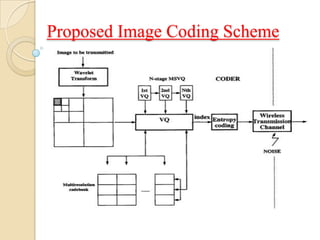
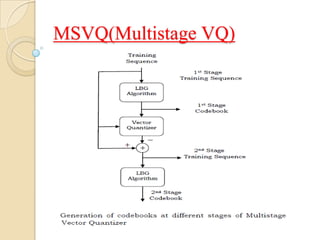
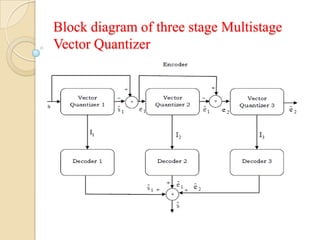
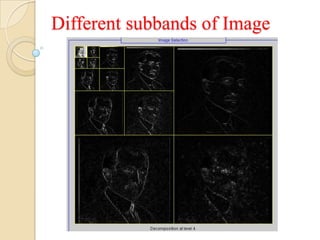
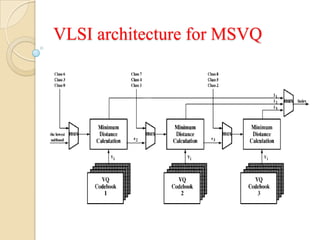
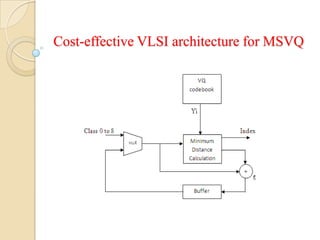
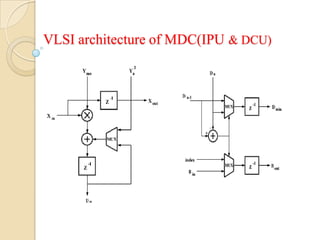
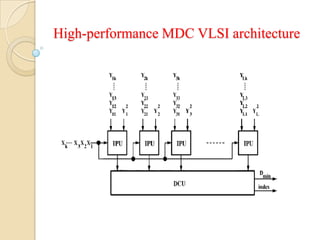
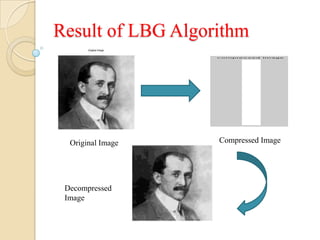
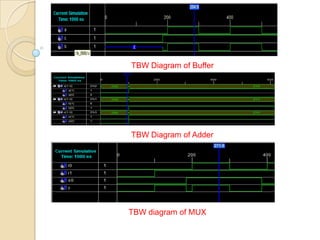
This document presents a VLSI architecture for an image compression system using vector quantization. It discusses motivation, objectives, and provides an introduction to image compression techniques including scalar and vector quantization. It describes the LBG algorithm for generating codebooks and proposes a multistage vector quantization approach. A cost-effective VLSI architecture for multistage vector quantization is presented, including the design of individual components like the image processing unit and decompression control unit. Results show the proposed architecture can compress images with good quality while maintaining low hardware complexity.