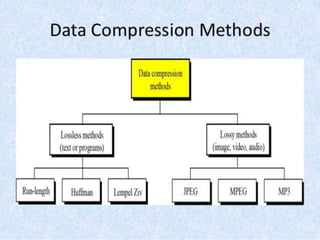
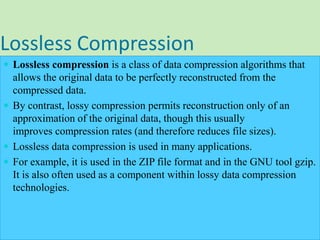
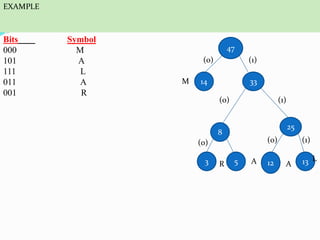
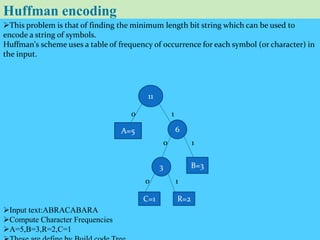
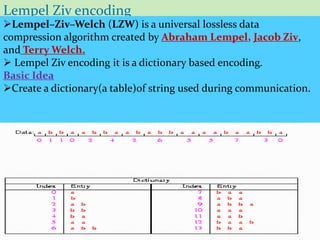
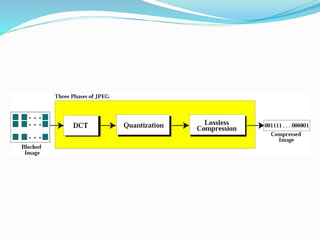
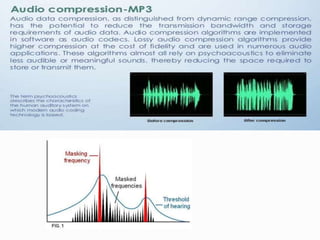
This document discusses data compression algorithms including lossless and lossy methods. It defines lossless compression as allowing perfect reconstruction of the original data and lossy compression as permitting only approximate reconstruction. Specific lossless methods covered are run-length encoding, Huffman coding, and Lempel-Ziv encoding. Lossy methods discussed are JPEG compression for images, discrete cosine transform, and MPEG video compression. The document concludes that the presented approach of using the Hartley transform for image compression with separate magnitude and phase processing achieved good performance.