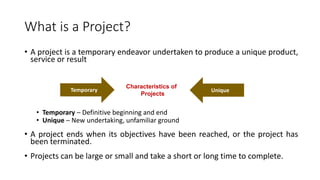
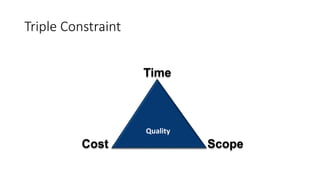
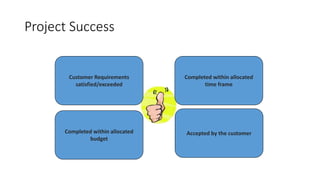
This document provides an overview of project planning and control concepts including the key elements of a project management syllabus. It discusses project definition, identification, feasibility analysis, location, layout, scheduling, cost control, quality control, financing, budgeting, and organization. It defines projects as temporary endeavors with unique goals and characteristics such as objectives, life cycles, uniqueness, teamwork, complexity, risk, customer focus, and changes. Project management is described as applying skills and techniques to meet stakeholder needs and expectations by planning, organizing, controlling, and measuring activities to balance scope, time and cost constraints.