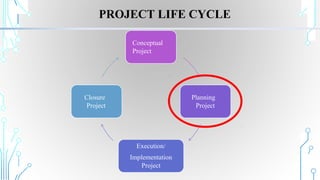
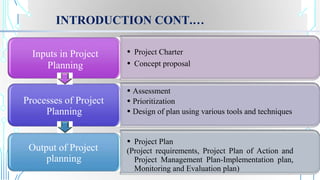
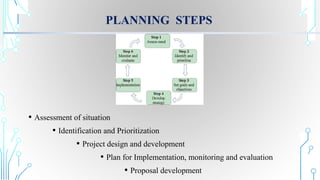
Project planning involves establishing the scope, aims, and objectives of a project. It includes assessing the situation, identifying and prioritizing problems and strategies, designing the project, and planning for implementation, monitoring, and evaluation. The output of project planning is a project plan that outlines the project requirements, plan of action, and management plan. Commonly used tools for project planning include Gantt charts, problem tree analysis, SWOT analysis, logical framework analysis, and project management software.