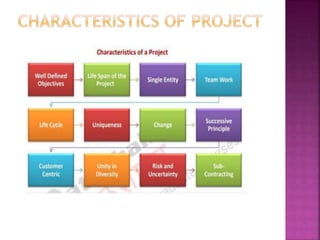
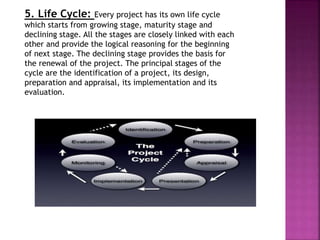
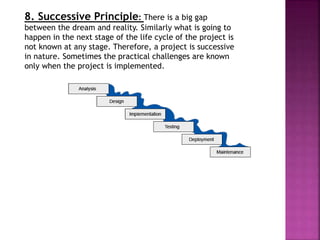
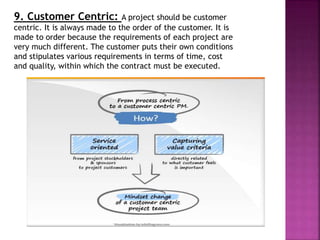
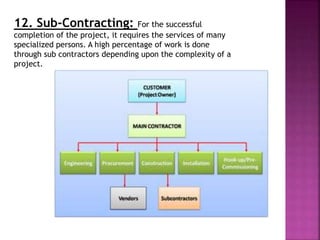
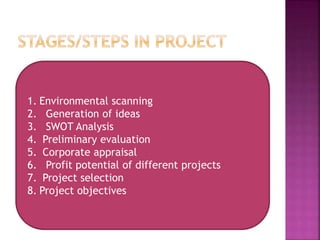
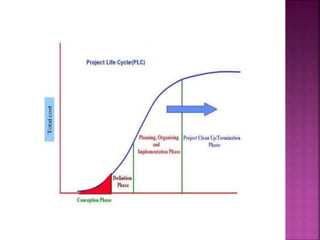
This document discusses the stages in a project life cycle. It outlines 5 stages: 1) Conception/identification, 2) Definition/formulation, 3) Planning and organizing, 4) Implementation, and 5) Project clean-up/termination. The conception stage involves generating project ideas. Definition involves developing the idea and collecting relevant facts. Planning and organizing deals with creating an execution plan and preparing for implementation. Implementation involves carrying out the planned work. Clean-up/termination wraps up the project upon completion of objectives. Proper execution of each stage is important for the successful management of a project over its life cycle.