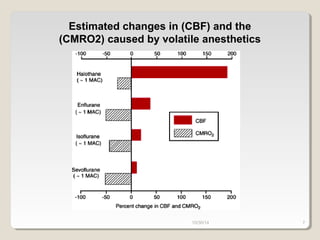
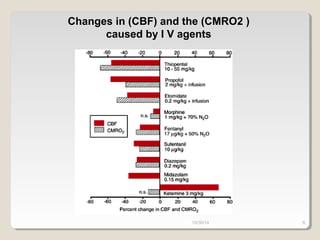
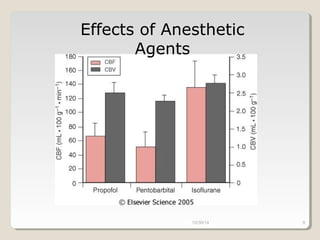
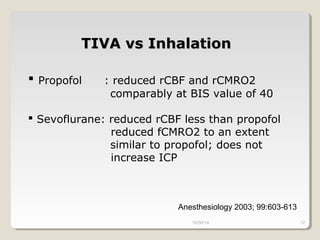
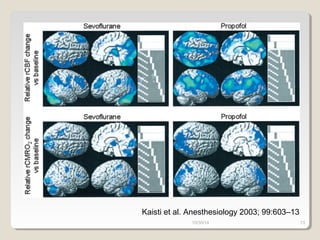
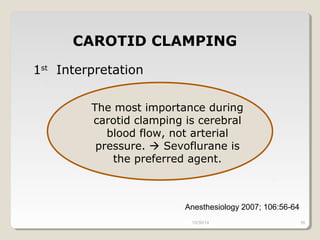
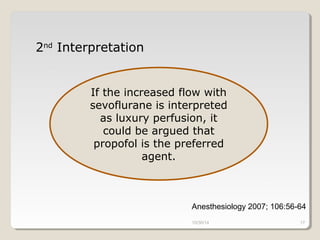
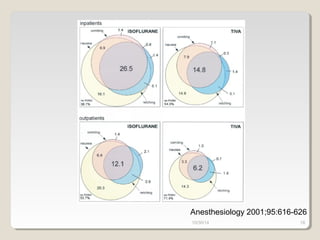
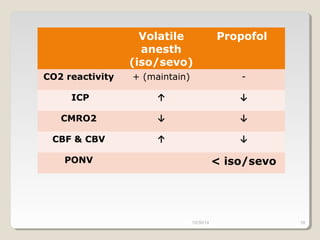
This document compares total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) and inhalation agents for brain surgery, emphasizing the importance of hemodynamic stability and cerebral protection. While specific anesthetic choices may be less crucial in elective surgeries, propofol is highlighted as beneficial for reducing intracranial pressure in patients with severe brain trauma, whereas inhalation agents like sevoflurane maintain CO2 reactivity. The findings suggest TIVA is preferable until the dura is opened, while inhalation anesthesia is favored during brain tumor surgeries due to its effects on CO2 reactivity.