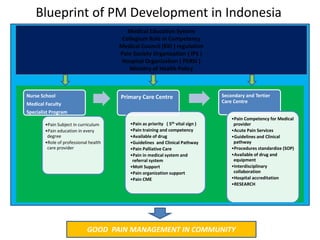
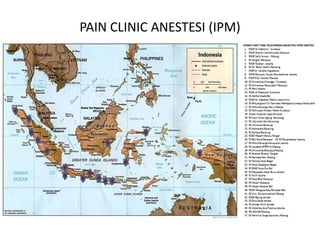
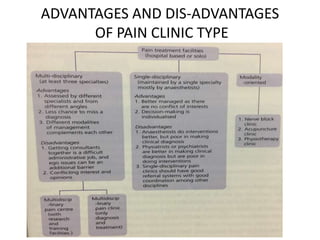
The document outlines the establishment and operation of pain clinics in Indonesia, emphasizing the need for interventional pain management, multidisciplinary approaches, and proper resources. It discusses the preparation of pain clinics, including human resources, systems, and facilities, advocating for a holistic view on pain management and training for medical professionals. Additionally, it highlights the importance of collaboration between various specialties, guidelines for clinical practices, and the challenges faced in pain management.