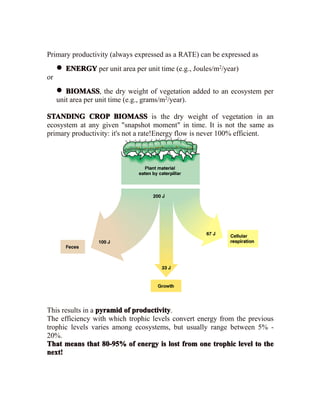
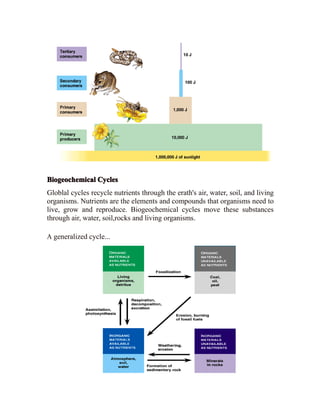
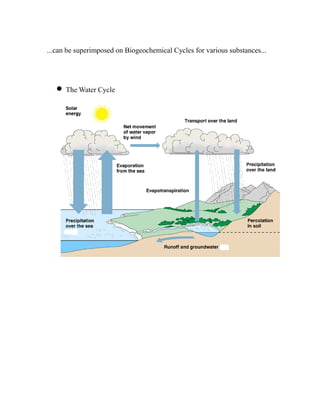
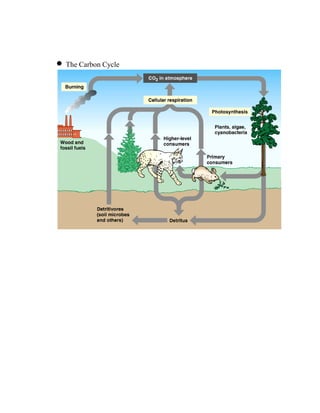
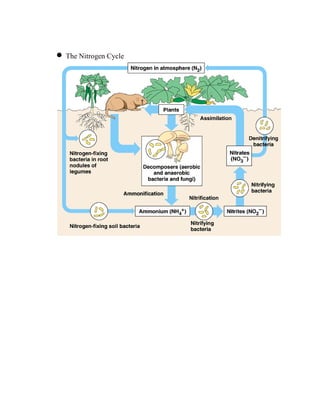
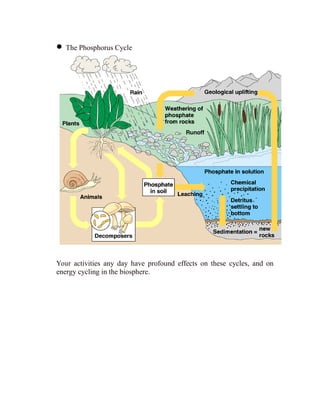
Primary productivity refers to the conversion of light energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis by autotrophs. There are three main types of primary productivity: gross primary productivity, respiration, and net primary productivity. Primary productivity can be expressed as either the energy captured per unit area per time, or the biomass produced per unit area per time. Standing crop biomass refers to the dry weight of vegetation at a moment in time, not a rate like primary productivity. Energy flow through ecosystems is inefficient, forming a pyramid of productivity where the majority of energy is lost at each trophic level. Biogeochemical cycles recycle nutrients through different components of the Earth system, moving substances through air, water, soil, rocks and organisms.