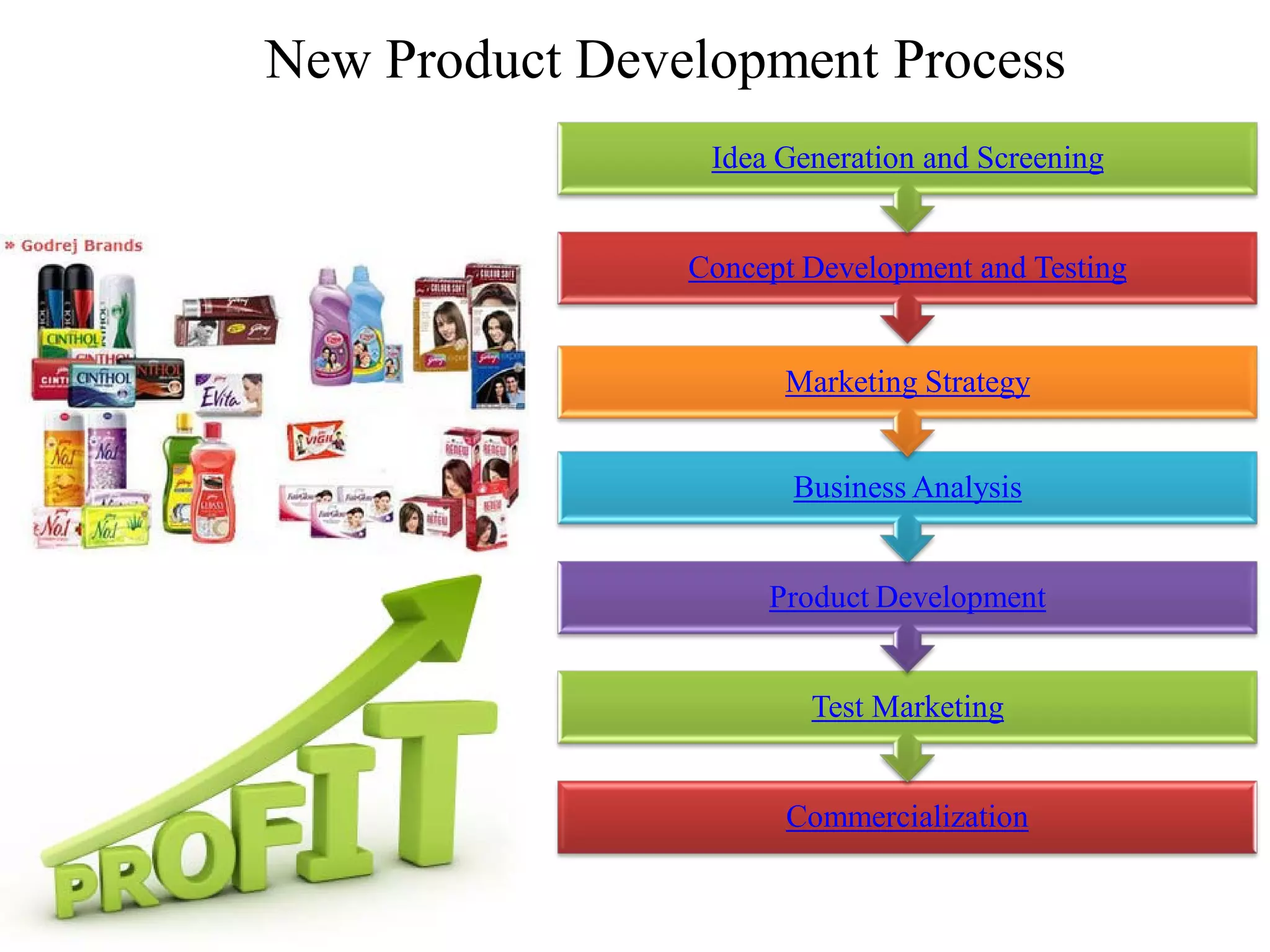
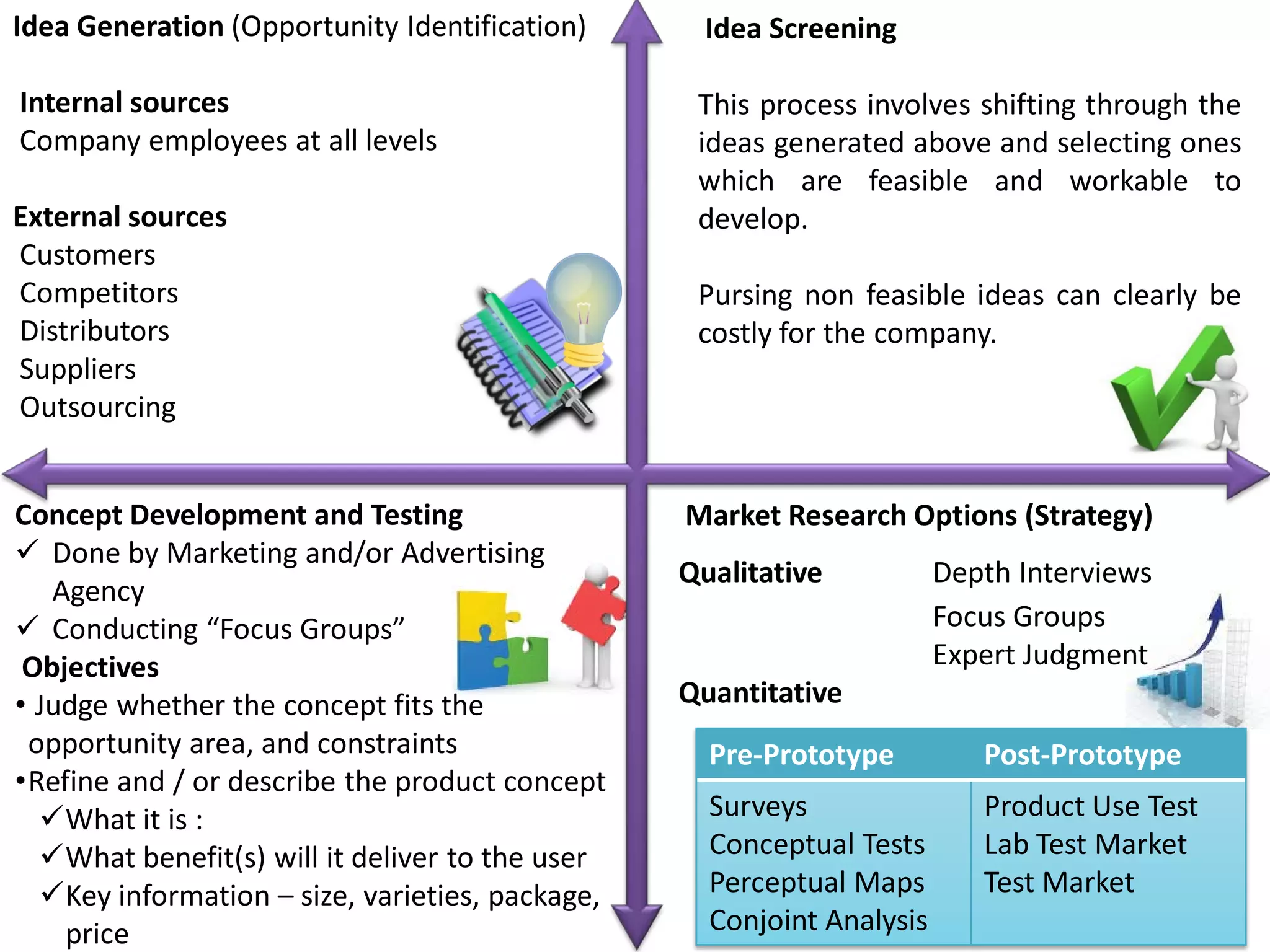
The document discusses key aspects of product development and management. It defines what a product is, explains why products fail, and outlines the new product development process. This includes idea generation, concept development and testing, determining marketing strategy, business analysis, product development, test marketing, and commercialization. Developing and updating product lines is important for organizational success, while failure to change could lead to declining sales amid competition. The new product development process aims to bring superior products to market through rigorous planning and testing.