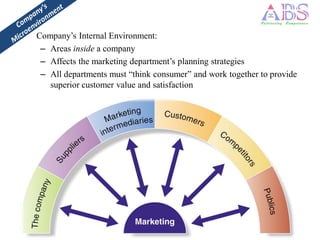
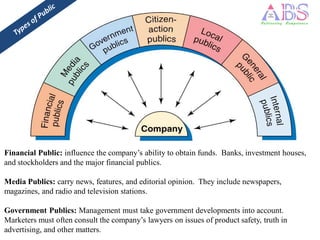
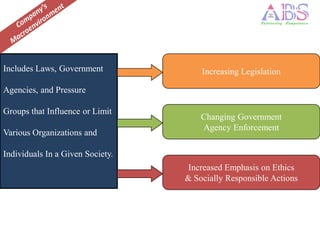
The marketing environment consists of internal and external factors that affect marketing management's ability to build relationships with customers. The microenvironment includes actors close to the company like suppliers and intermediaries. The macroenvironment comprises larger societal forces like demographic, economic, natural, technological, political, and cultural forces beyond the company's control. Companies must monitor the changing marketing environment and respond to opportunities and threats.