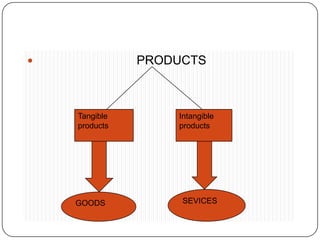
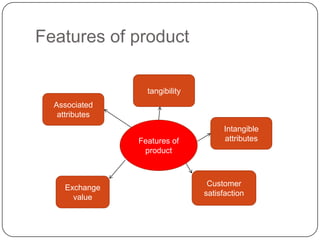
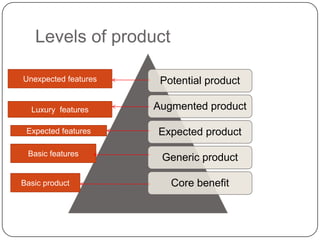
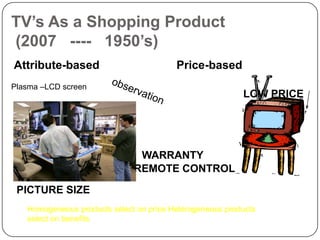
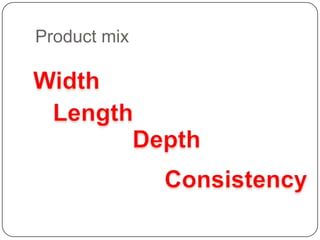
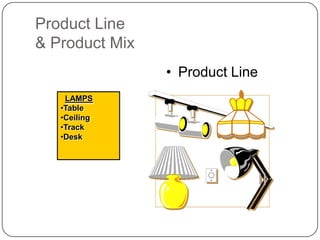
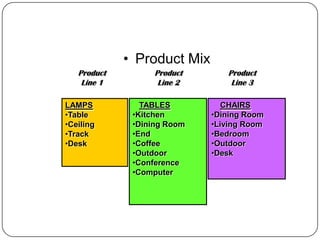
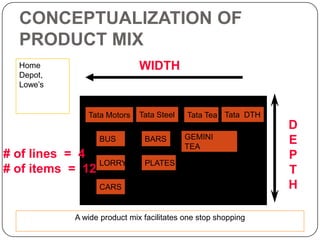
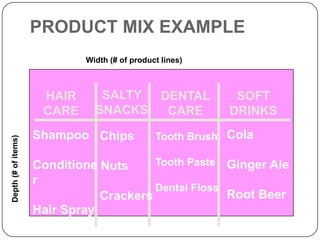
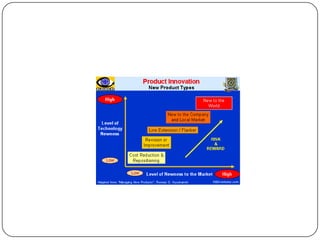
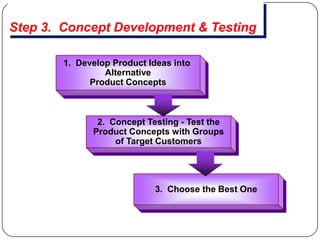
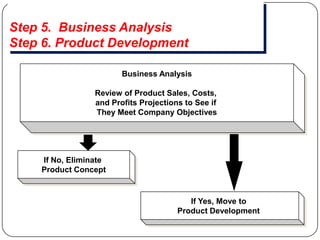
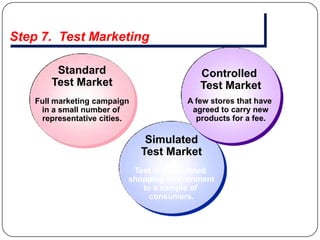
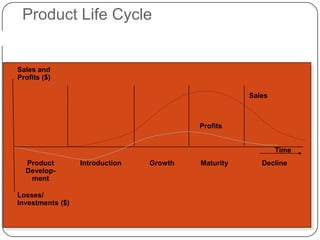
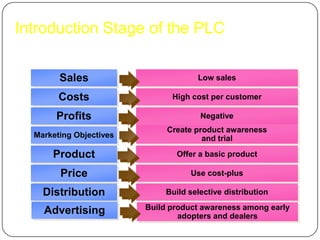
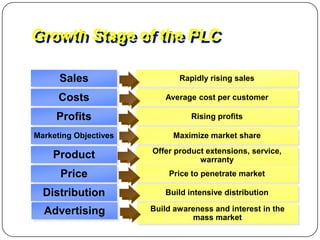
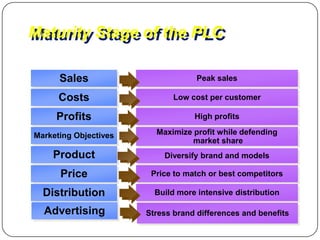
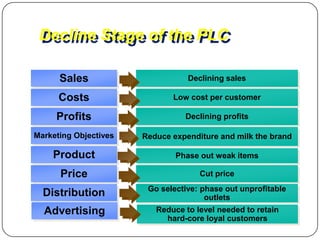
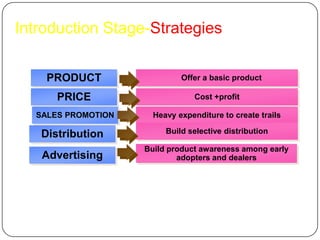
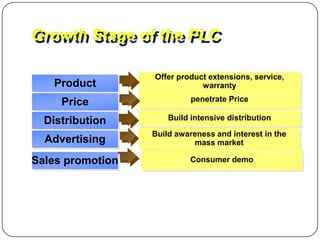
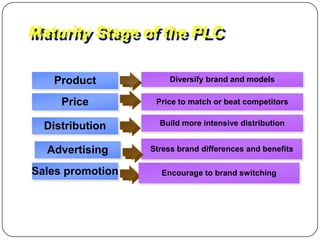
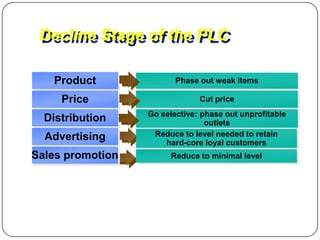
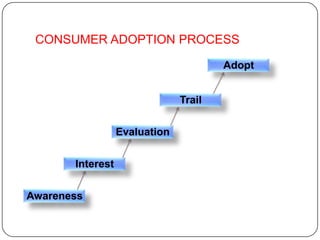
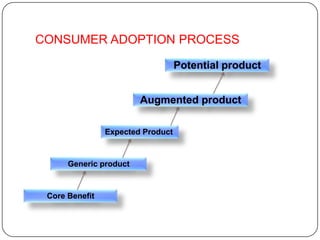
The document provides an overview of products, including definitions, types, features, and classifications such as durable, non-durable, and consumer goods. It discusses product mix strategies, the new product development process, and the product life cycle stages, emphasizing the importance of market analysis and consumer needs. Additionally, it outlines common causes of new product failures and the consumer adoption process.