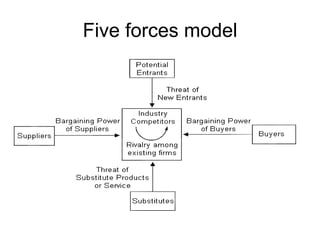
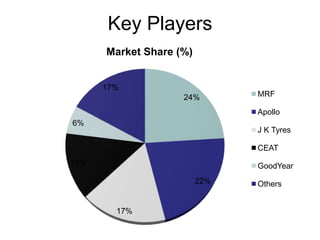
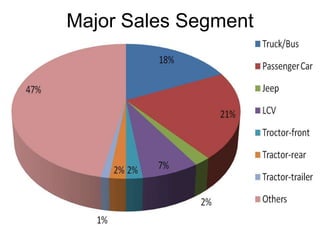
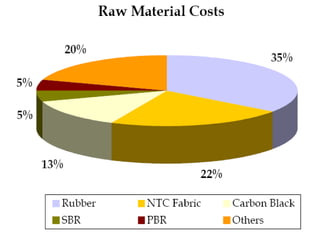
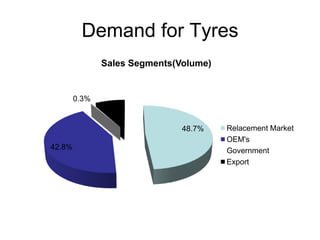
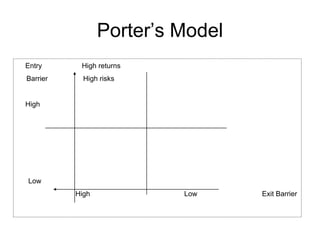
The tyre manufacturing industry in India faces significant competition and pressure on costs and prices from the growing automotive industry. While vehicle volumes have increased, profitability has decreased for tyre manufacturers due to rising raw material costs. The industry has high barriers to entry due to being capital intensive and requiring large investments. There is also high intensity of rivalry among the top five major players that control over 80% of the market.