Embed presentation

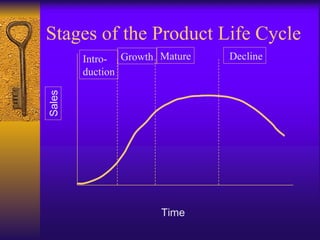


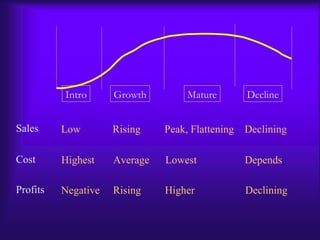
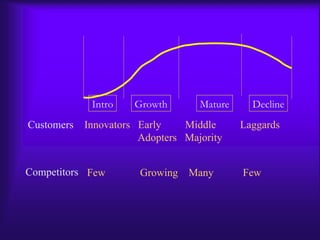






The document discusses the product life cycle model which outlines typical stages of introduction, growth, maturity, and decline that products go through over time. It notes benefits of the model for resource allocation and strategy choice but also criticisms that patterns can vary and changes may be unexpected. Key aspects of each stage are identified such as types of customers, competitors, issues faced, and common strategies used.












