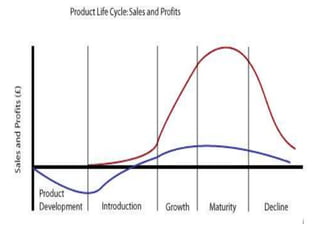
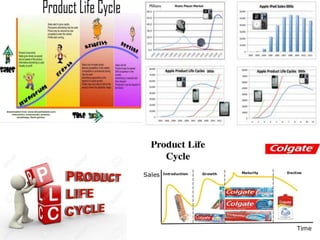
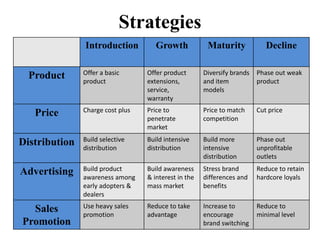
The document summarizes the stages of a product's life cycle: introduction, growth, maturity, saturation, and decline. It notes that during the introduction stage, sales are slow but marketing costs are high, leading to little or no profit. In the growth stage, sales and profits increase as the company tries to maximize market share. During maturity and saturation, sales peak and then decline while profits also start declining. Finally, in the decline stage both sales and profits decrease. The document also lists strategies companies use at each stage, such as pricing and advertising approaches, as well as factors that can affect a product's life cycle.