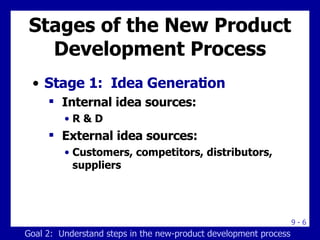
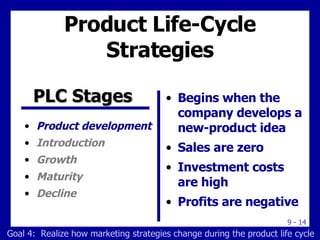
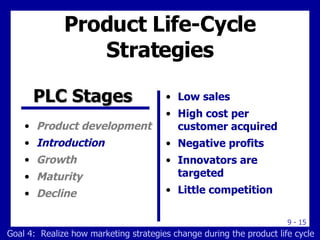
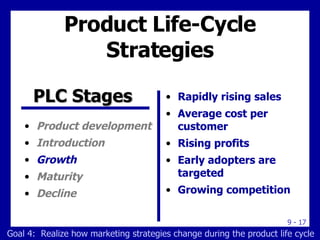
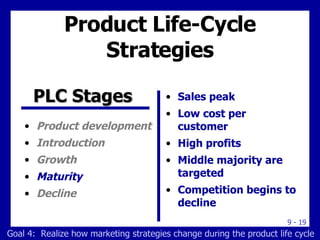
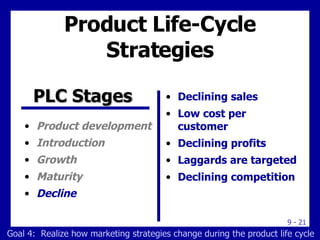
The document discusses new product development and the product life cycle. It describes the 8 stages of new product development as idea generation, screening, concept development, marketing strategy development, business analysis, product development, test marketing, and commercialization. It also outlines the 5 stages of the product life cycle as development, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Finally, it explains how marketing strategies must change during each stage of the product life cycle.