1. The document discusses strategies for building strong account relationships with customers, including reducing supplier counts, performing value analysis to lower total costs, and establishing different stages of relationships from awareness to commitment.
2. It also provides tips for pricing flexibility depending on market conditions, questions to consider for business expansion, benefits of just-in-time philosophies, and warning signs for the dissolution stage of a relationship.
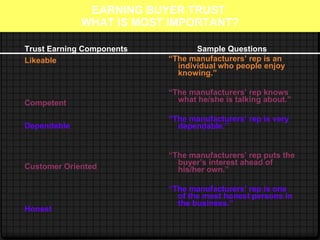
3. Building trust is emphasized as an important relationship enhancer through demonstrating competence, dependability, customer focus, and honesty.