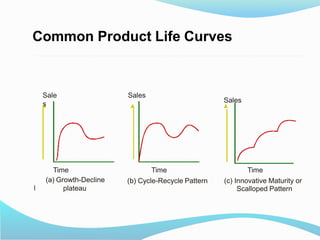
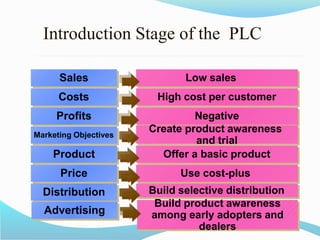
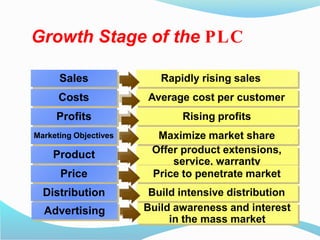
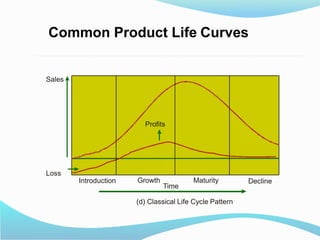
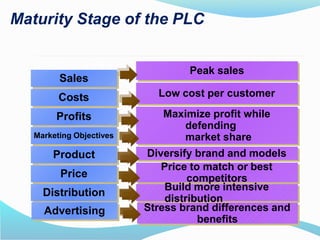
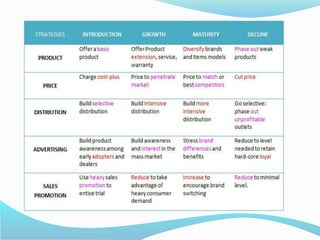
The document discusses the product life cycle (PLC) which consists of four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Each stage presents unique challenges and requires different strategies for marketing, sales, and distribution, exemplified by products like 3D televisions in the introduction phase and laptops in the maturity phase. As customer preferences evolve, products may decline, necessitating a responsive approach to sustain market relevance and profitability.