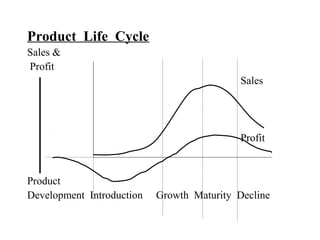
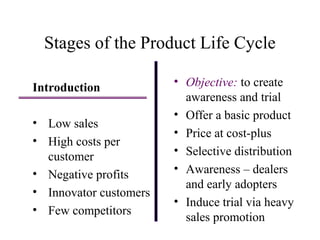
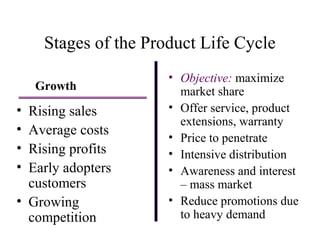
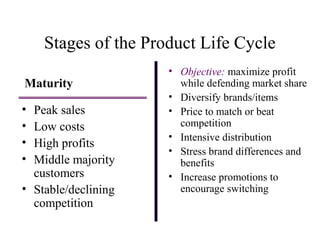
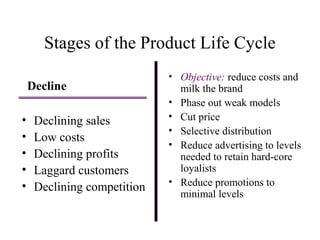
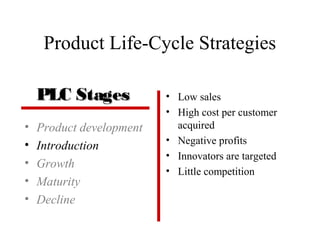
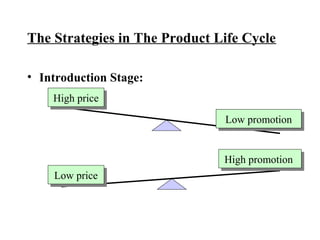
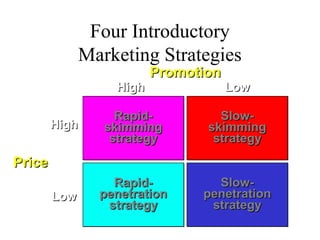
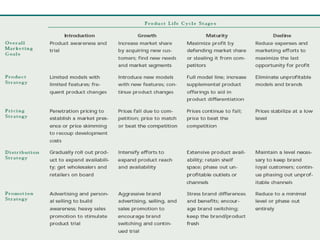
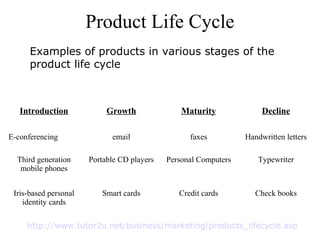
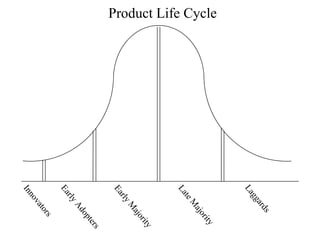
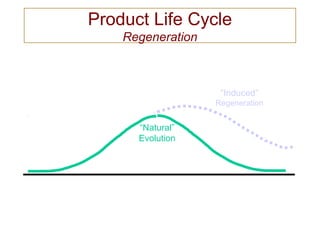
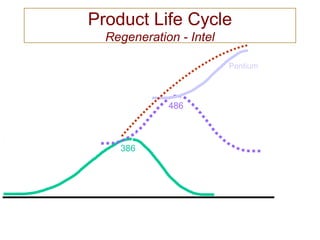
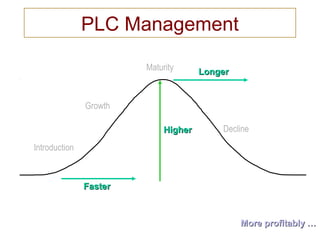
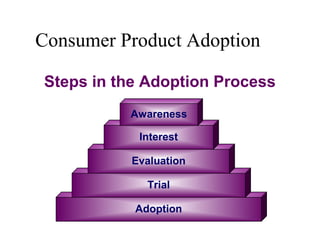
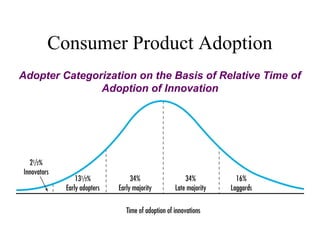
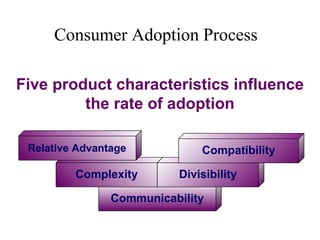
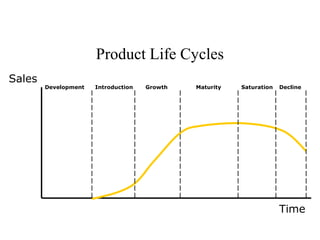
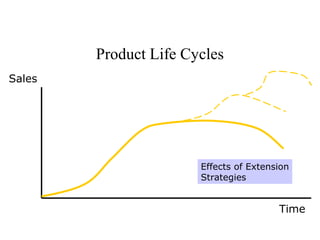
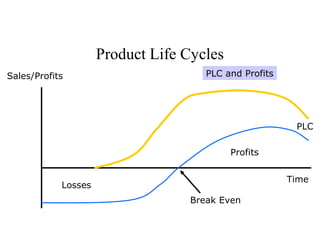
The document discusses product life cycles and how they can be used for strategic marketing planning. It describes the typical stages a product goes through - development, introduction, growth, maturity, decline, and withdrawal. During each stage, different marketing strategies are most effective, such as high promotion during introduction, market share growth during maturity, and cost reduction during decline. Understanding a product's life cycle helps companies plan when to support, redesign, or withdraw a product.