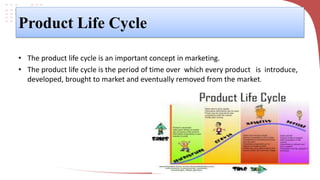
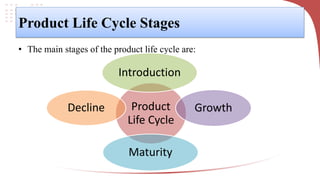
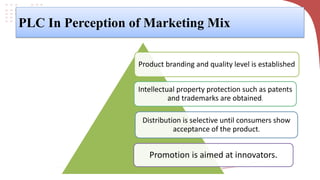
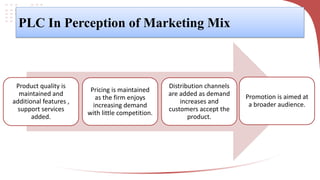
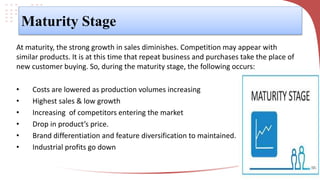
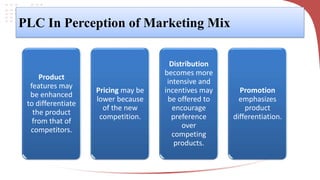
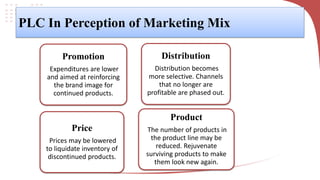
The product life cycle describes the typical stages a product goes through from introduction to decline. It includes introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. During introduction, sales are low and costs are high to create awareness. Growth sees increasing sales and profits as the product gains acceptance. Maturity is the most profitable as sales peak, though competition rises. Finally, decline occurs as sales decrease due to saturation or competition. Businesses can extend the cycle through advertising, price reductions, innovation, exploring new markets, or packaging changes. The model helps marketers strategize but products don't always follow predictable cycles.