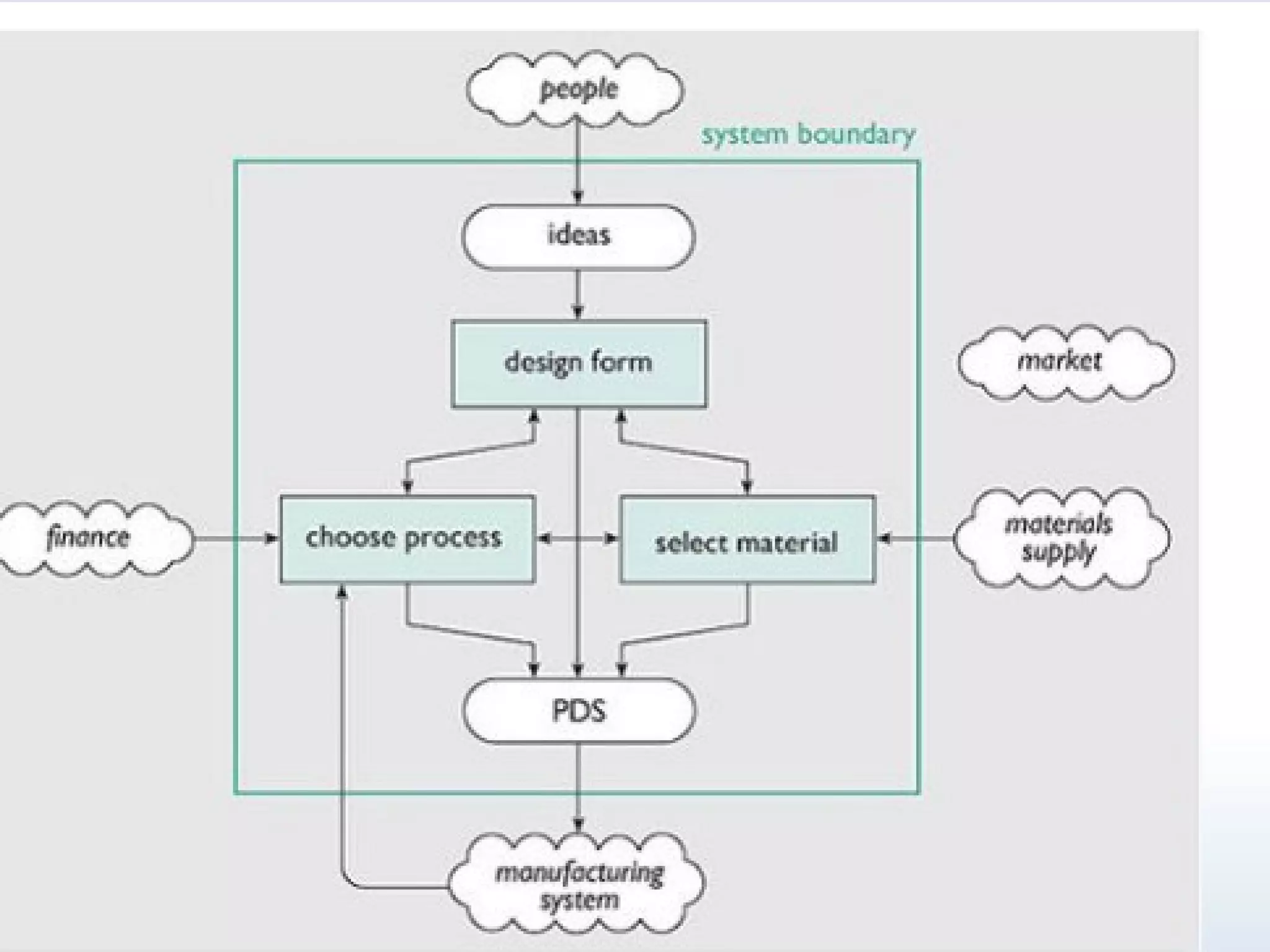
The document discusses product design specifications (PDS). A PDS defines the critical parameters, specifications, and requirements for a product being designed based on customer needs. It is created early in the design process and states what the product should be and do, not what it will end up as. A PDS considers product design/performance issues, market issues, and a company's capabilities. It provides guidelines for factors like quality, size, aesthetics, performance, and environmental impact. The document includes a sample PDS for a kiosk project that outlines design constraints like size limits, material restrictions, and counter height/display requirements.