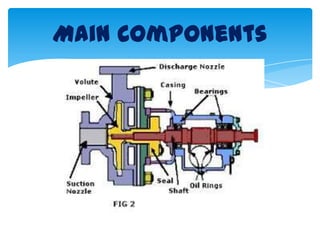
The document discusses the importance of creating a specification in the design process, particularly in relation to pump equipment for transferring liquids. It outlines the main components of a centrifugal pump, how it operates by converting rotational kinetic energy into fluid pressure, and potential issues that may arise, such as cavitation and wear of the impeller. Overall, it emphasizes the significance of meticulous specification to ensure effective design and functioning of pump systems.