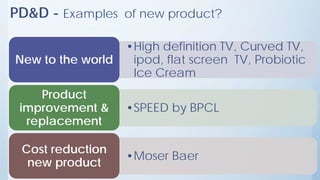
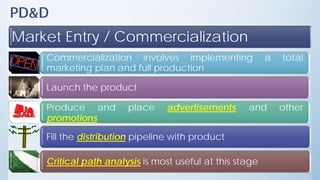
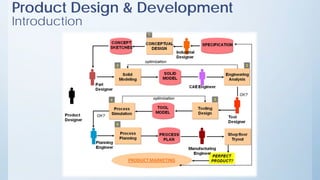
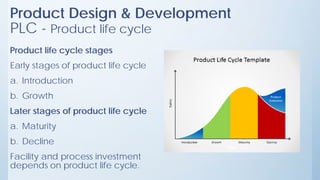
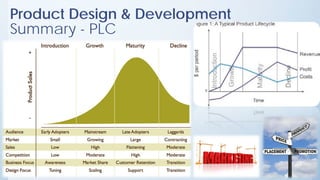
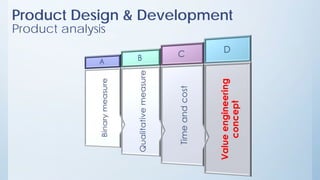
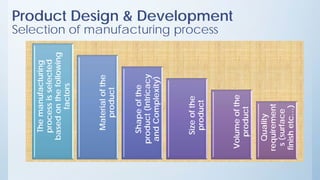
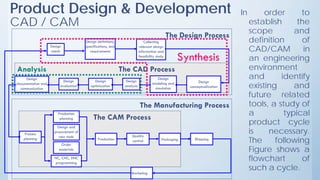
This document discusses product design and development. It covers factors that inspire product design such as identifying gaps in demand, underutilized resources, and new product ideas. It also discusses marketing factors to consider like market potential and competition. Additionally, it outlines the stages of new product development including idea generation, concept development, market strategy development, feasibility studies, product design, testing, and commercialization. Finally, it discusses the product life cycle and how investment depends on what stage the product is in such as introduction, growth, maturity, or decline.