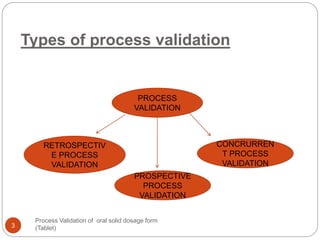
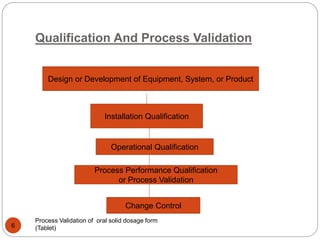
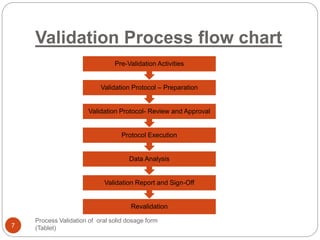
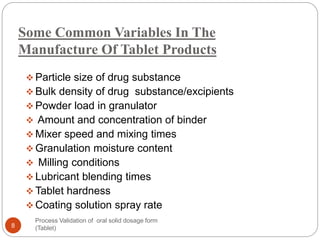
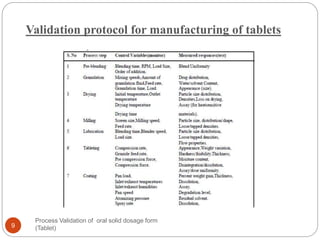
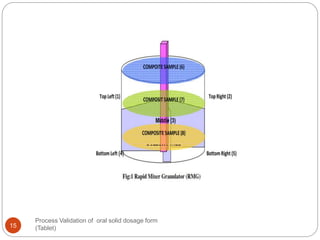
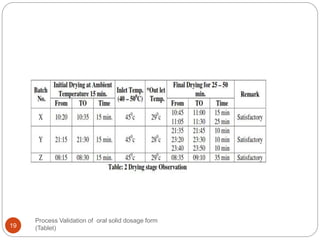
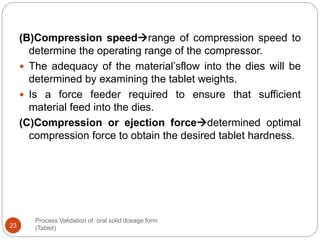
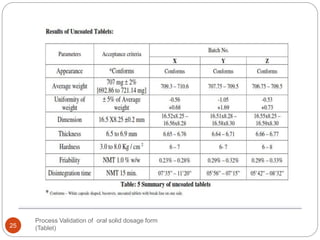
The document outlines the process validation of oral solid dosage forms, specifically tablets, emphasizing the importance of documented evidence to ensure consistent product quality. It details various types of validation, including prospective, retrospective, and concurrent validation, and provides an overview of critical parameters and methodologies involved in the manufacturing process, such as mixing, granulation, drying, and compression. The conclusion highlights the necessity of a comprehensive validation program that addresses product and process characteristics to meet quality and regulatory requirements.