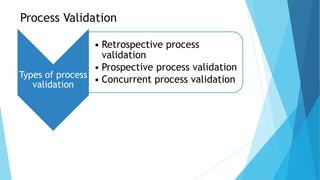
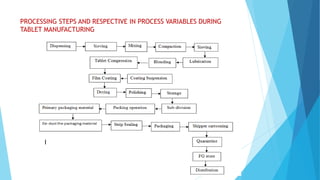
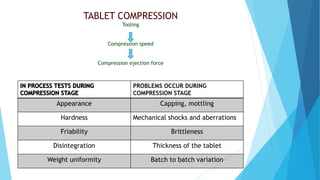
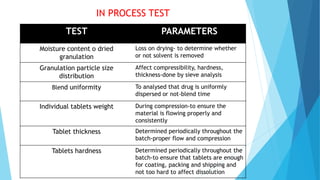
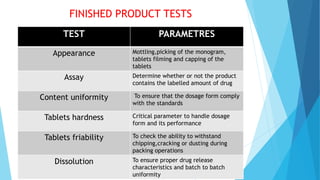
The document outlines the validation process for tablet manufacturing, emphasizing the importance of establishing documented evidence to ensure consistency in product quality. It details the types of process validation, stages involved, and critical parameters affecting each phase, including mixing, granulation, compression, and coating. Additionally, it discusses the advantages of validation, such as reduced costs and improved efficiency in manufacturing.