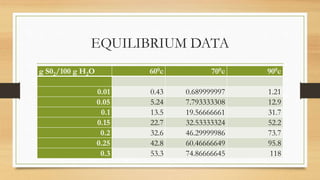
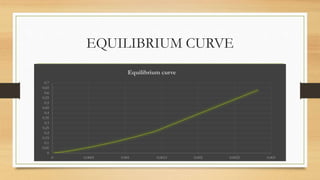
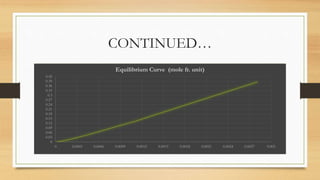
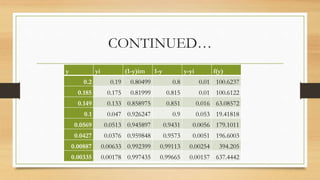
The document summarizes the design of an absorption column to remove SO2 from an air stream using water. It involves selecting water as the solvent, 1.5 inch Raschig rings as the packing material, calculating the minimum water flow rate of 116,641 kg/h, determining the flooding velocity, diameter of 1.106 m, and height of 3.88 m for the packed column. The column will treat 40,000 ft3/h of air containing 20% SO2 and recover 96% of the SO2 using 30% excess water than the minimum flow rate.