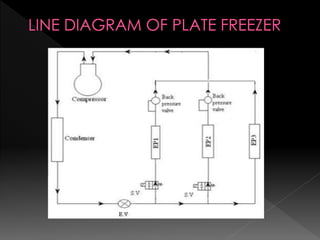
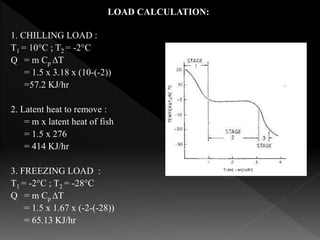
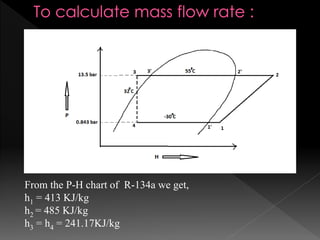
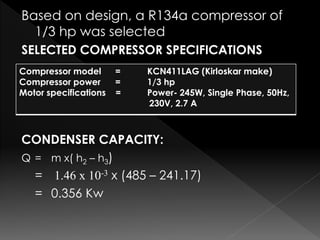
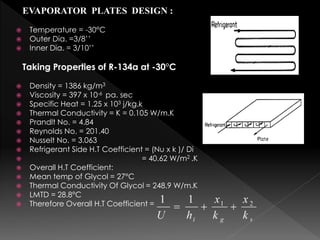
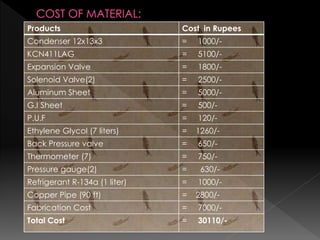
This document summarizes the design of a plate freezer for low-temperature fish freezing applications. It includes calculations of refrigeration load based on fish specifications, selection of refrigerant R-134a and compressor capacity of 0.08 TR. Dimensions and specifications are provided for major components like condenser, expansion valve, evaporator plates and solenoid valves. Total materials cost for the designed plate freezer is estimated to be Rs. 30110.