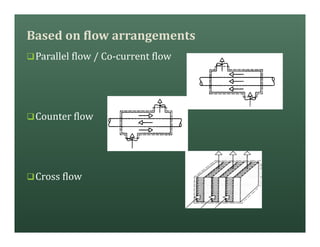
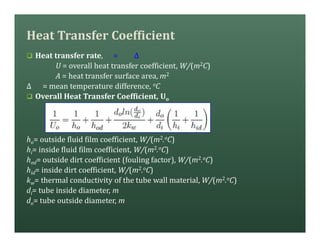
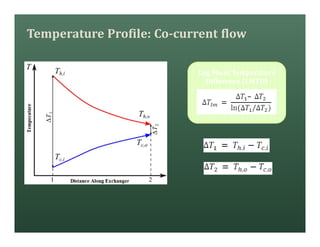
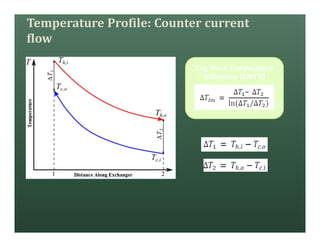
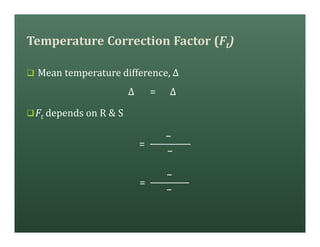
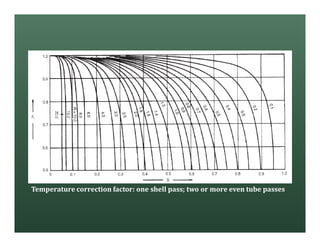
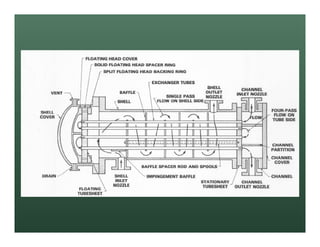
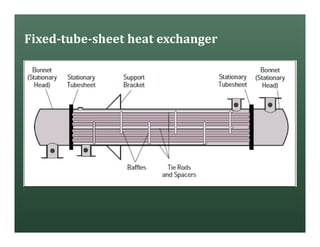
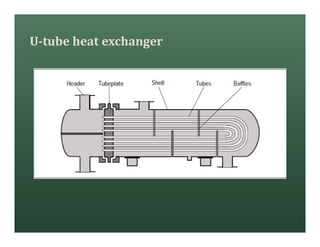
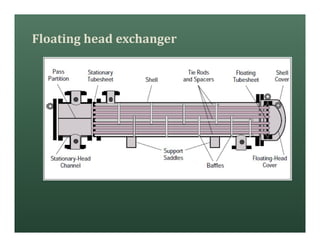
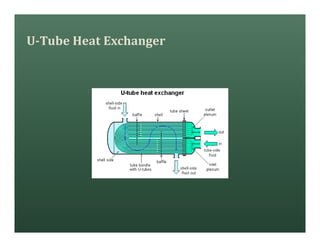
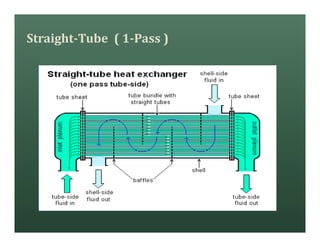
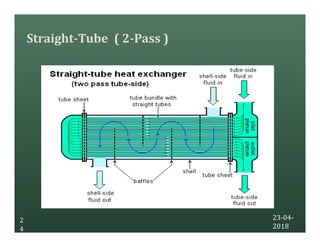
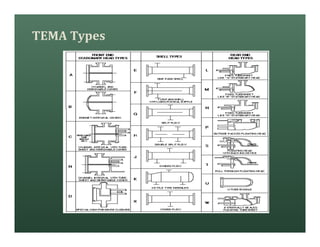
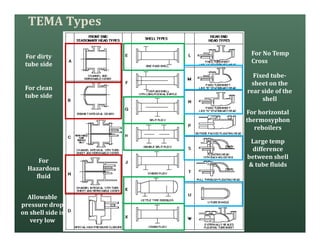
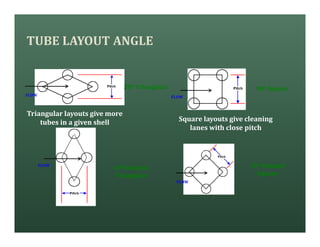
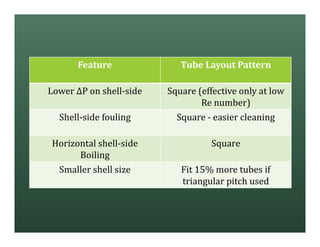
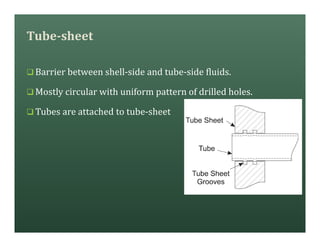
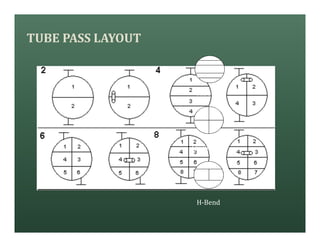
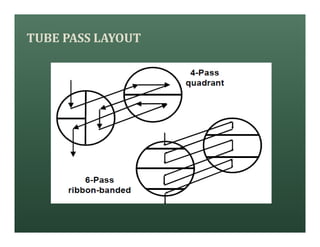
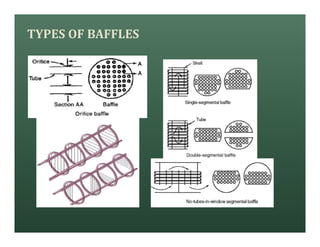
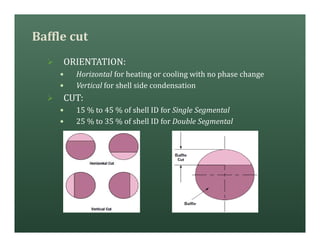
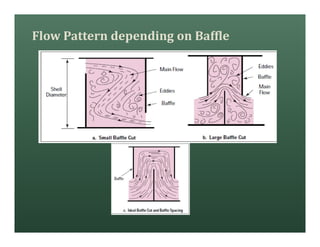
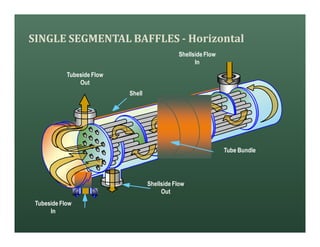
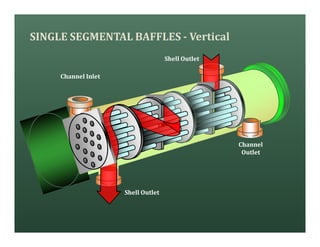
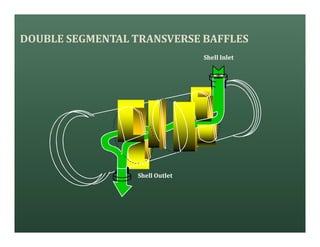
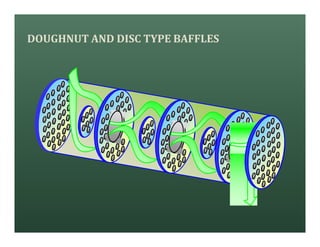
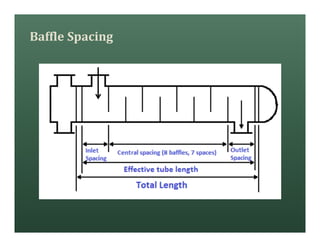
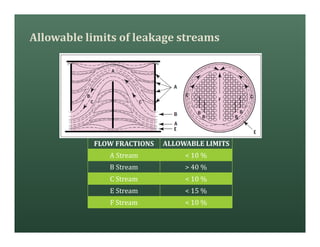
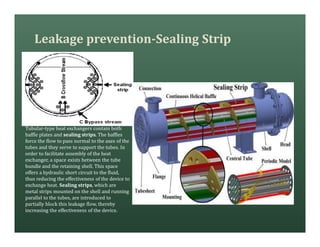
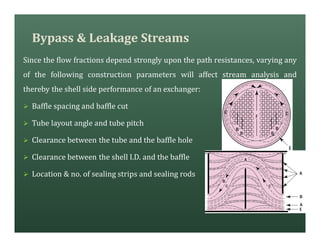
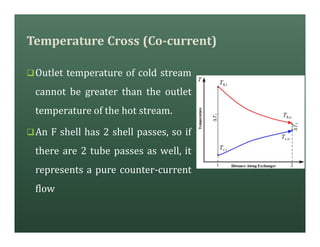
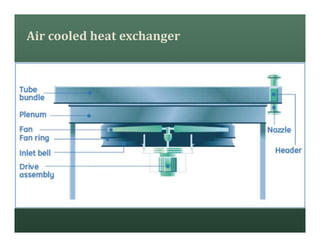
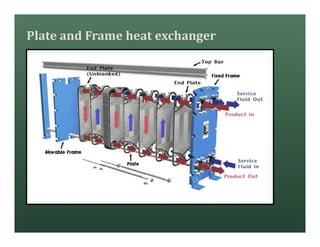
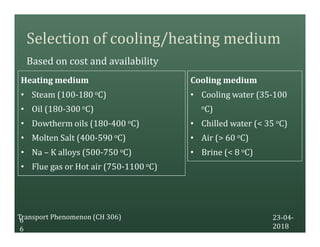
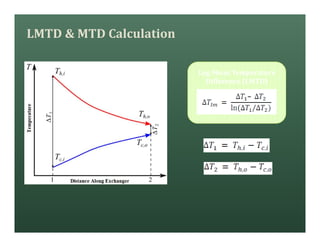
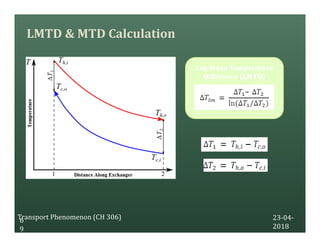
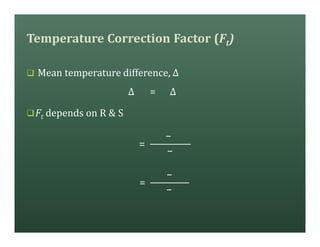
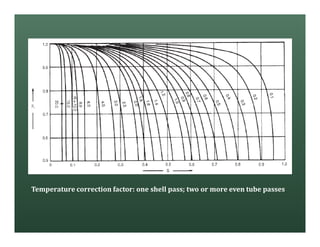
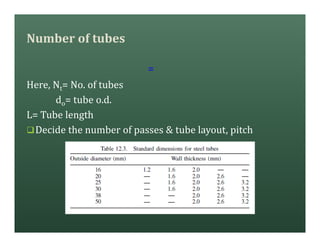
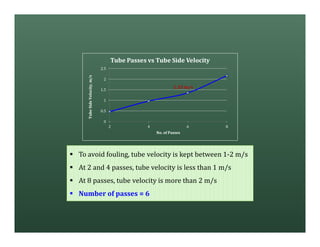
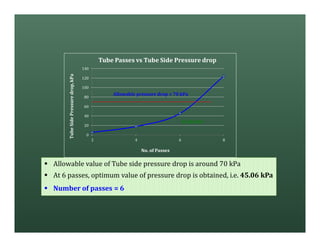
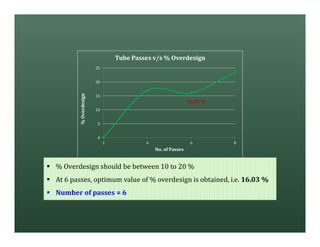
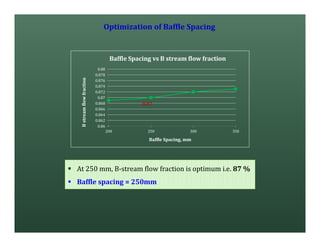
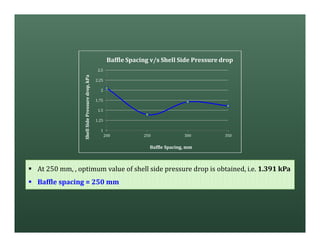
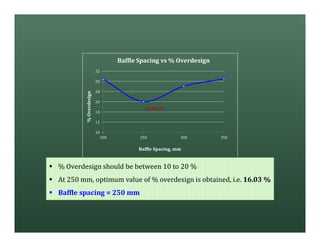
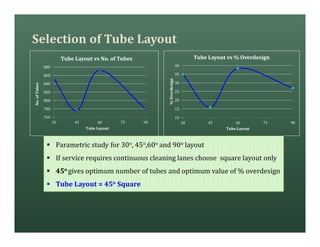
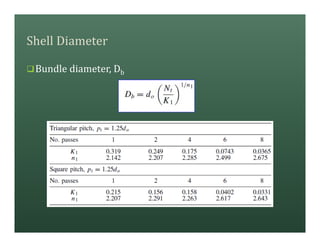
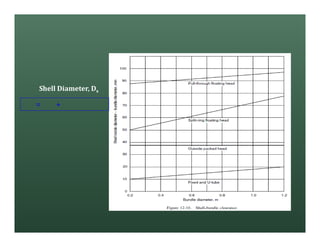
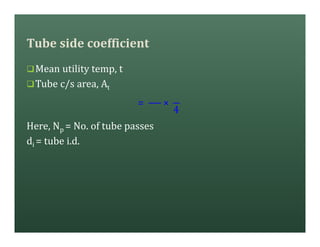
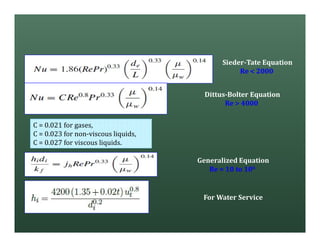
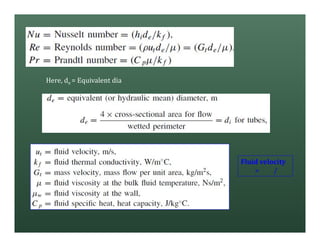
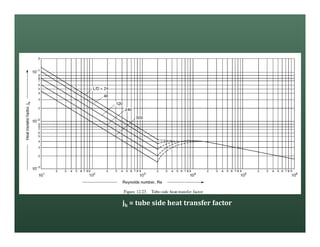
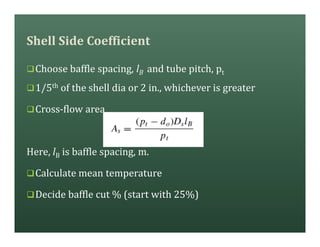
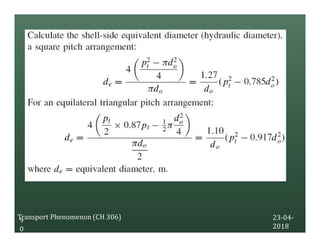
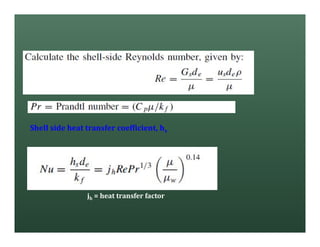
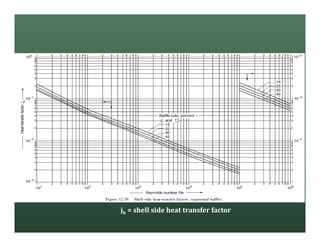
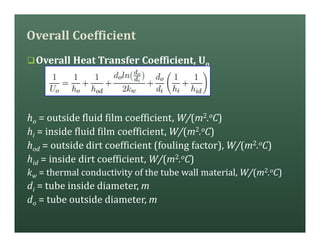
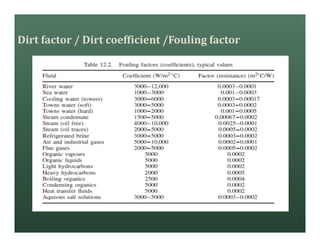
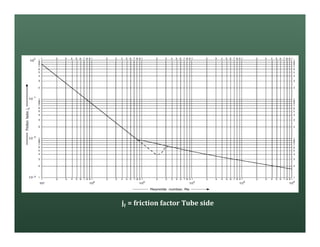
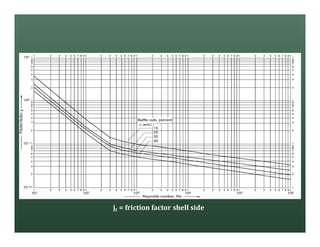
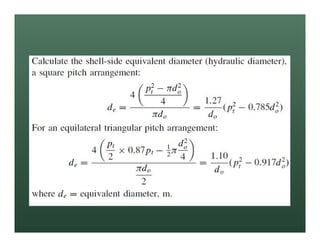
A heat exchanger transfers heat between two fluids. There are various types including shell and tube, plate and frame, and air cooled. A shell and tube heat exchanger consists of tubes, a shell, baffles, and nozzle inlets and outlets. Proper design of the baffle cut, spacing, and orientation is important for efficient heat transfer and to prevent bypass and leakage streams from reducing effectiveness. Sealing strips are also used to block leakage paths and improve performance.