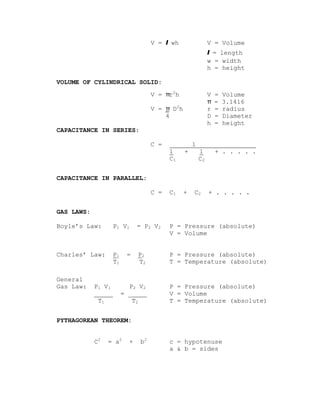
The document provides formulas and definitions for various HVAC concepts. Some key formulas include: the ton of refrigeration which is equal to 288,000 BTU/24 hr or 12,000 BTU/hr; one horsepower equals 33,000 ft-lb of work in one minute or 746 Watts; converting between BTUs, KWs and Watts for heating and cooling equipment. Common gas laws and formulas for area, perimeter, volume and capacitance are also listed.