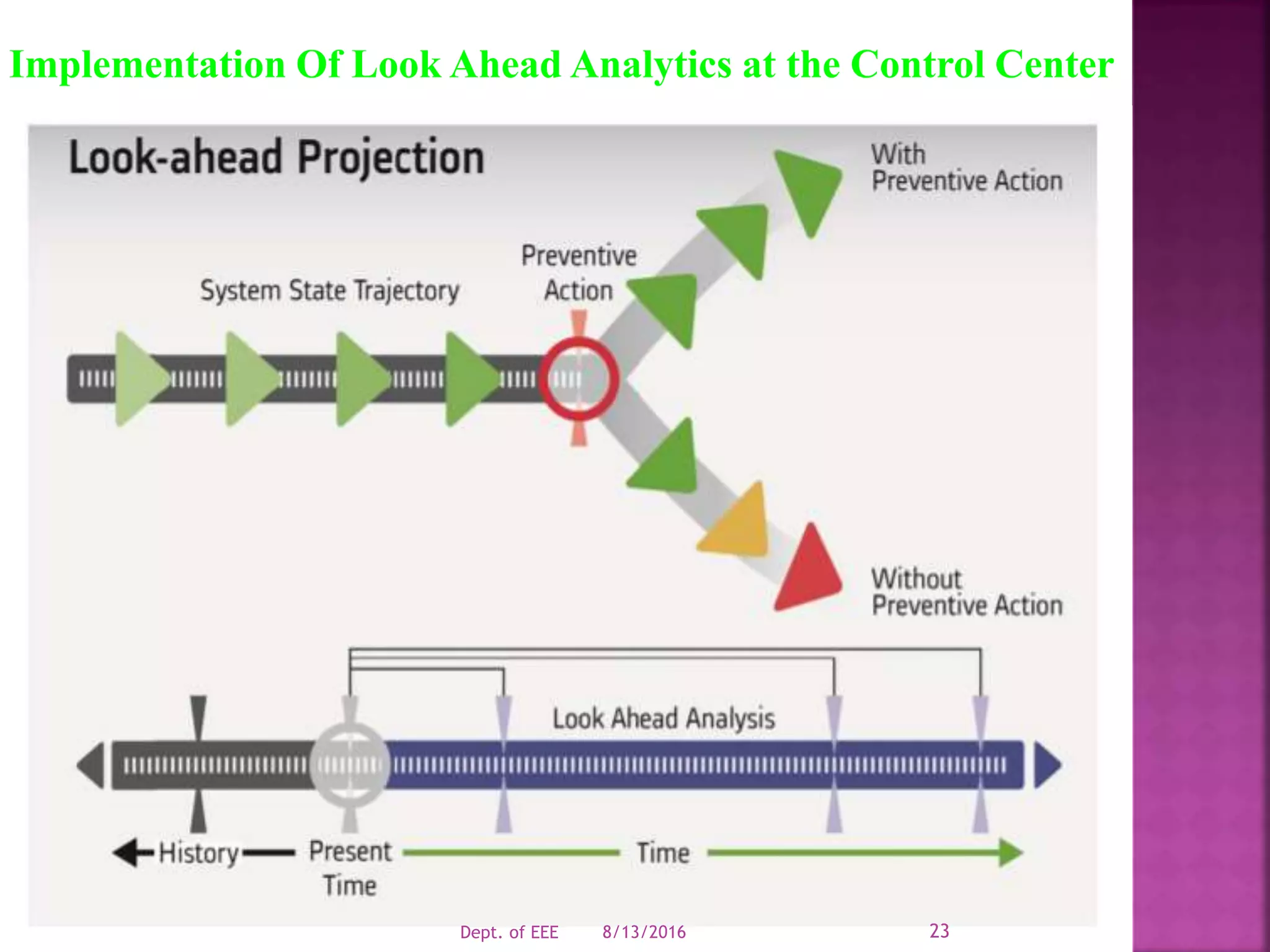
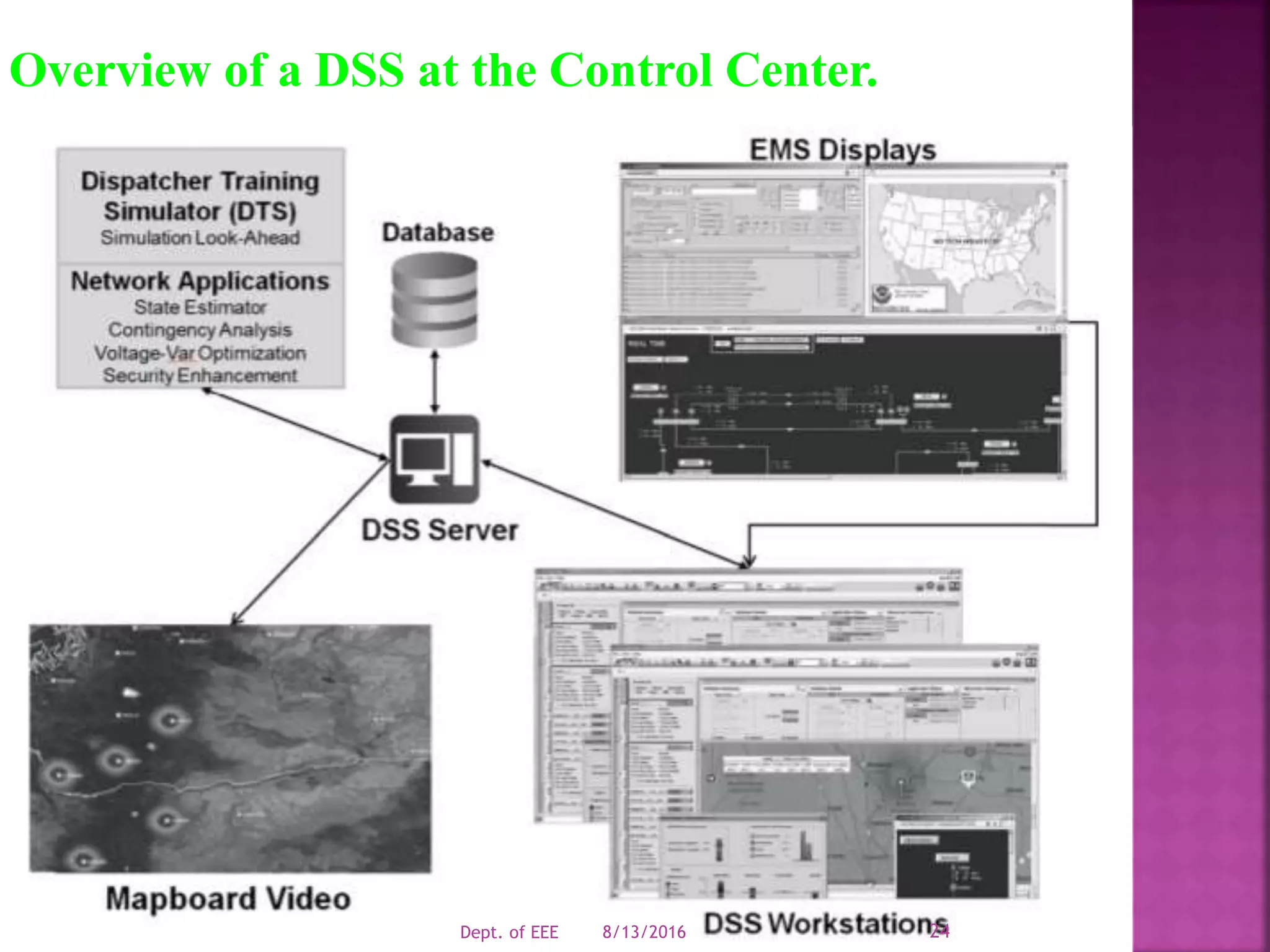
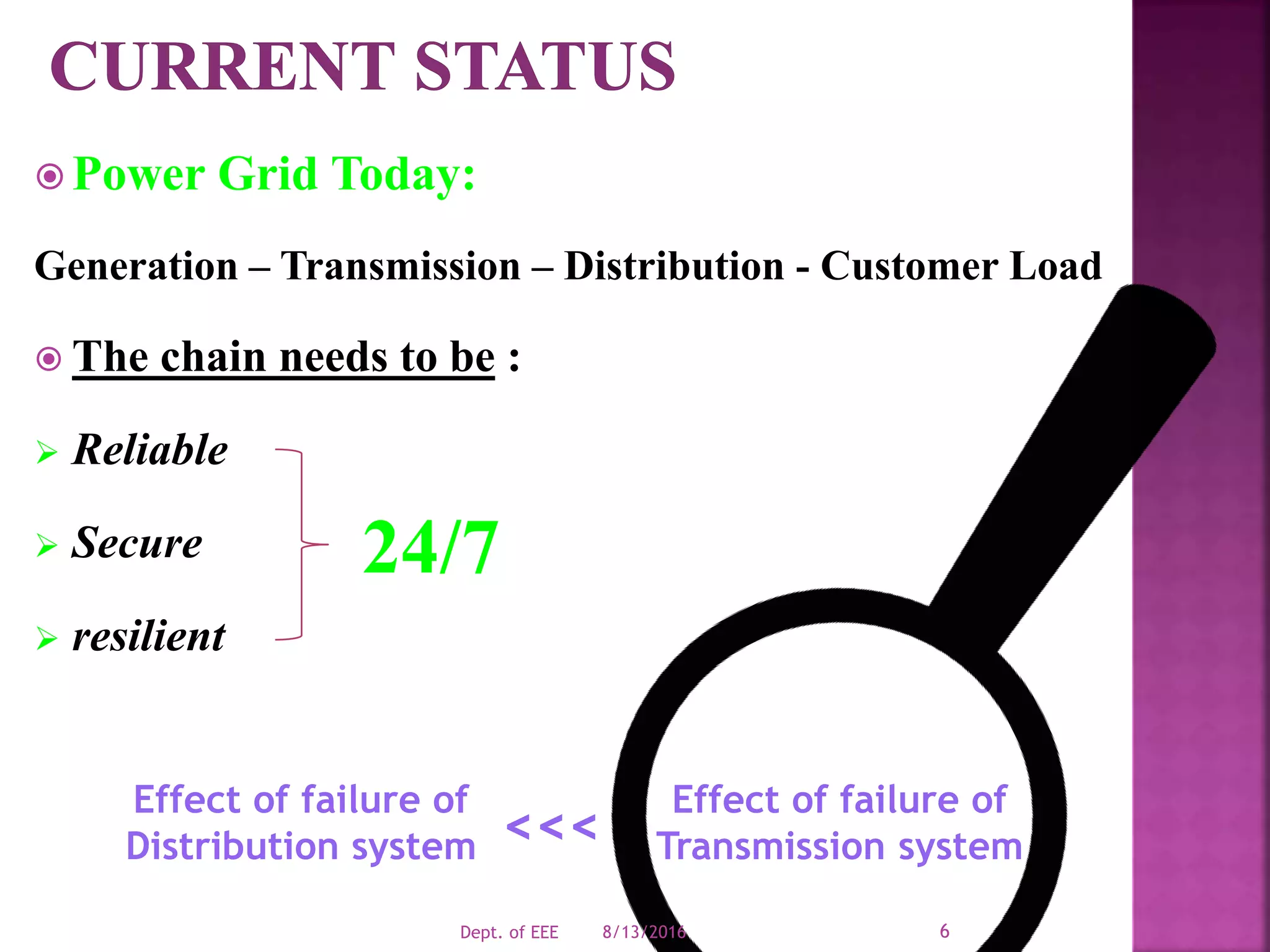
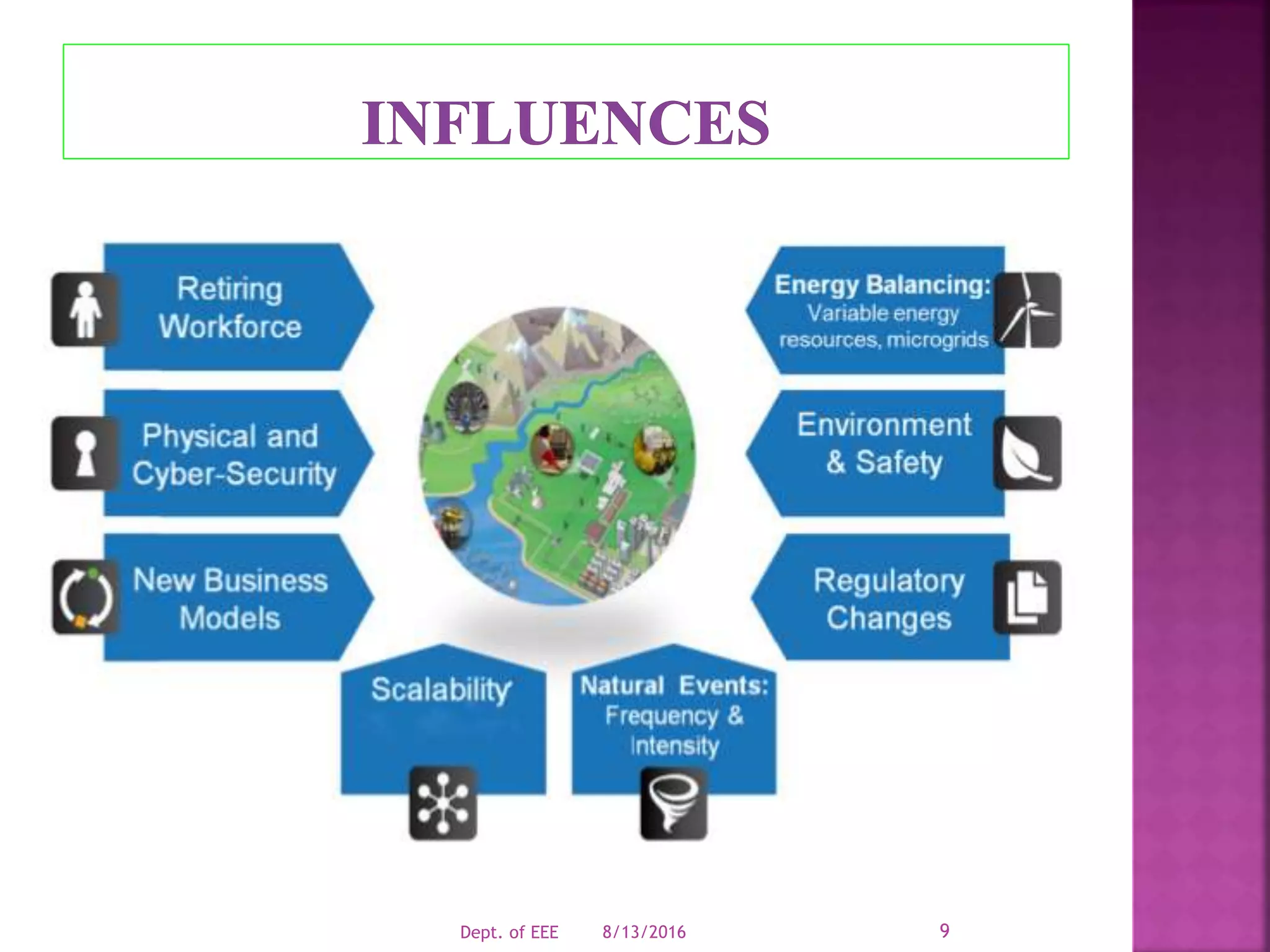
The document discusses challenges facing modern power grids and emerging solutions. It notes that grids must be reliable, secure and resilient to handle changing conditions. New technologies like synchrophasor measurement, advanced computing, smart meters and energy storage can help operators better monitor grids and maintain integrity. Decision support systems use analytics to forecast future grid conditions and help operators mitigate risks.








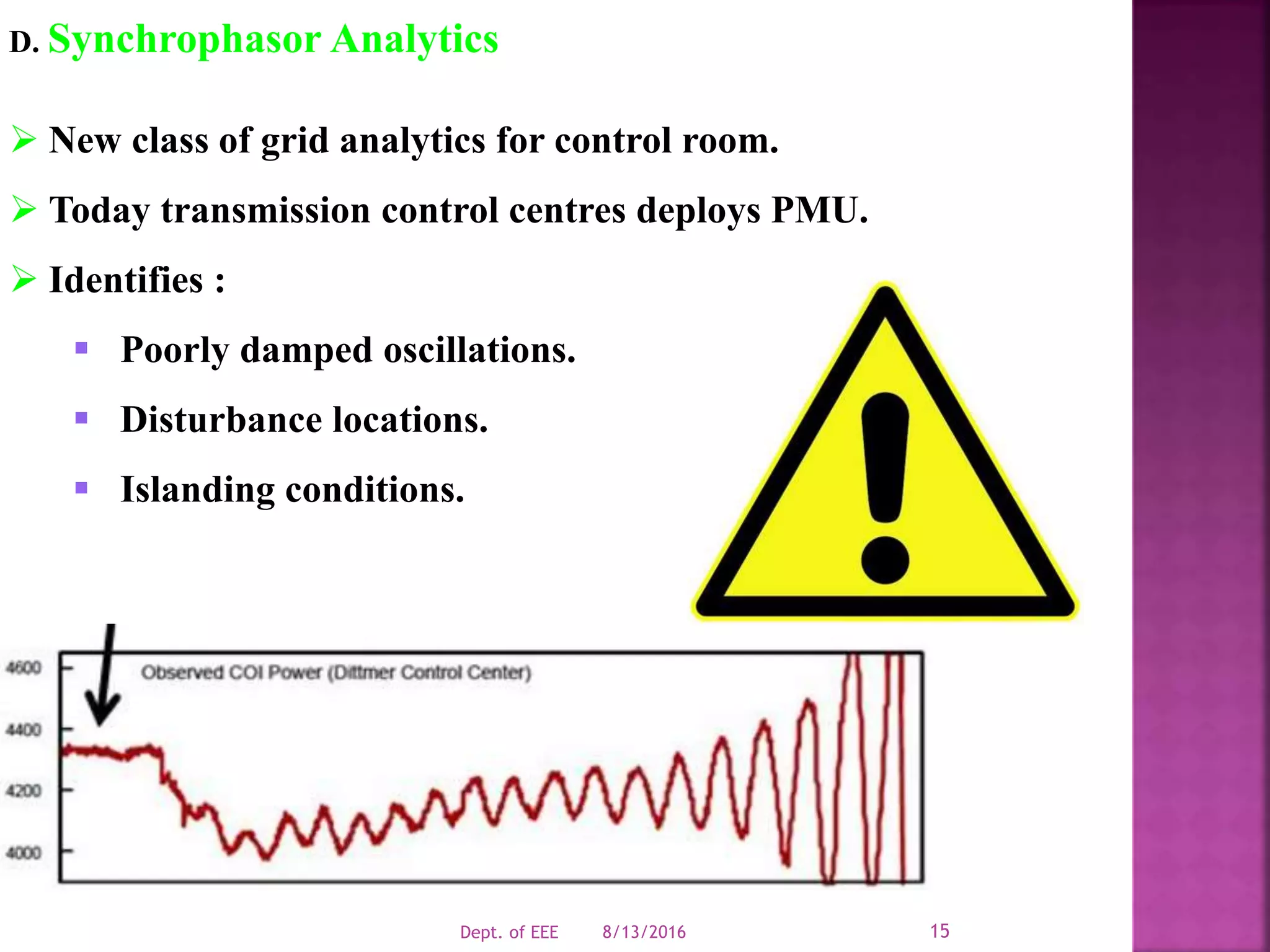
![C. Synchrophasor Measurement
“Synchronized phasors (synchrophasors) provide a real-time
measurement of electrical quantities from across the power
system.”
Increasingly deployed worldwide.
Captures upto 60 values at each second with precise time
tag.
Replaces traditional way of measuring values every 2-4s.
[SCADA: Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition]
Similar to High Definition Microscopic picture.
8/13/2016Dept. of EEE 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mithunseminar-160813131956/75/Proactive-Management-of-Future-Grid-mithun_p_c-14-2048.jpg)