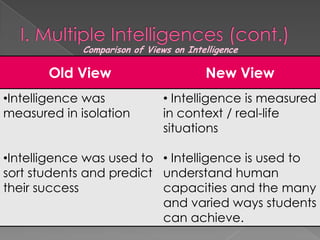
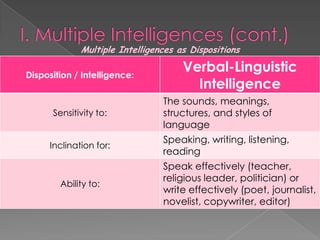
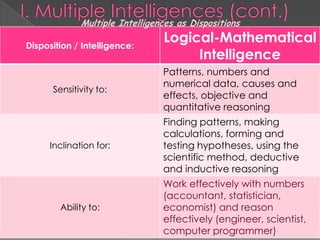
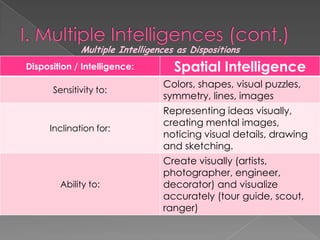
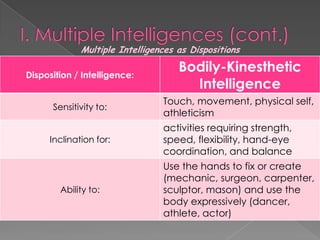
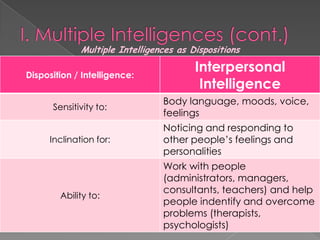
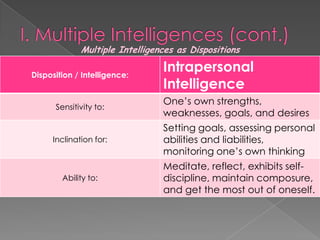
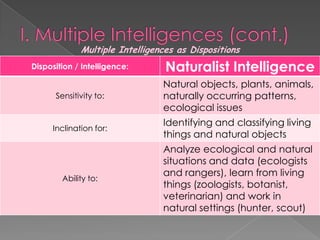
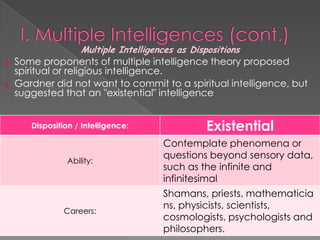
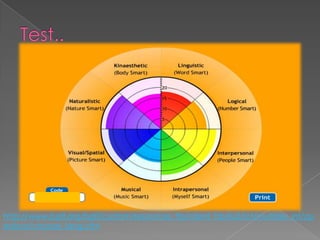
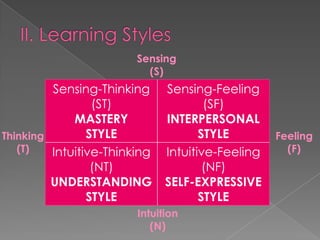
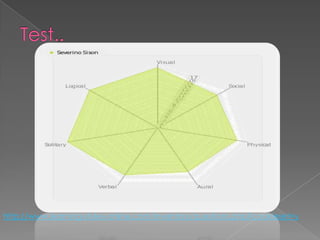
The document discusses Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences which proposes that intelligence is made up of several different abilities rather than a single general ability. It outlines various intelligences including verbal-linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical, interpersonal, intrapersonal, naturalist, and suggests existential intelligence. The document also compares old and new views of intelligence and describes different learning styles associated with combinations of sensing, intuition, thinking, and feeling preferences.