The document outlines several key linguistic principles for teaching a foreign language:
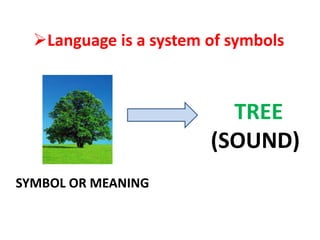
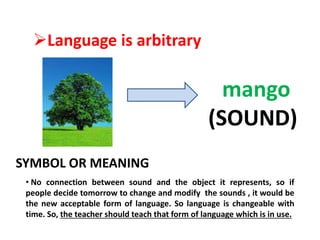
1) Language is a system of symbols that are arbitrary and primarily vocal, so the teacher should use oral-aural methods and teach speaking before reading and writing.
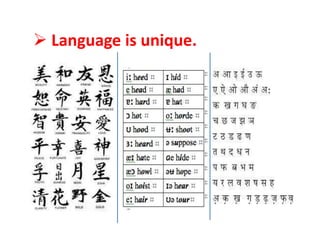
2) Each language has a unique structure and cannot be learned through another language alone, but the learner's native language can help facilitate learning.
3) Language is for communication, so oral usage should be encouraged, and it grows out of and changes with culture over time.
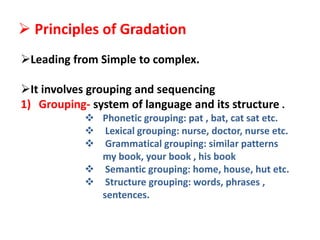
It then provides general principles for teaching a foreign language, including following a natural order of skills, using imitation and forming habits, selecting controlled vocabulary, and using gradation, coordination, and multiple methods while