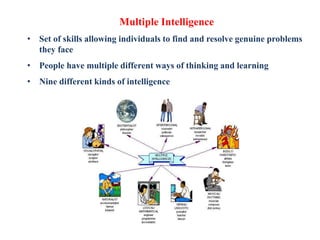
This document provides an overview of Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences. It discusses the nine types of intelligence identified by Gardner: verbal-linguistic, logical-mathematical, visual-spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical-rhythmic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, naturalistic, and existential. For each type of intelligence, the document provides a definition and examples of related careers or fields of study. It concludes that Gardner's theory is popular in education because it validates students' varied thinking and provides a framework to organize curriculum, assessment, and teaching practices.