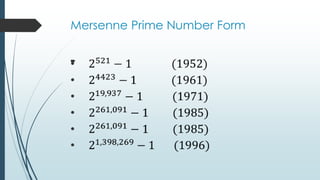
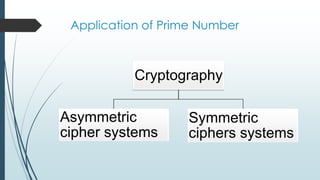
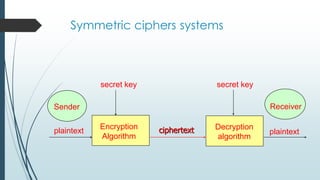
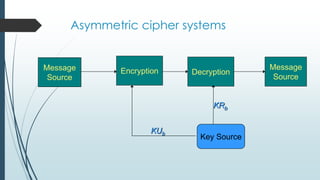
The document discusses prime numbers, defining them as integers greater than one with only 1 and itself as factors, and exploring their applications in nature and cryptography. It highlights the significance of prime numbers in the cicada lifecycle and details their role in encryption methods like RSA. The document concludes with the concept of Mersenne primes and the importance of prime numbers in mathematics and security.










![Example: Confidentiality
• Imran wants to secretly send Mhd the message "HELLO"
• H E L L O
• 08 05 12 12 15
• 0817 mod 77 = 57
• 0517 mod 77 = 03
• 1217 mod 77 = 45
• 1217 mod 77 = 45
• 1517 mod 77 = 71
• Imran sends ciphertext [57 3 45 45 71]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primenumberslideshar-140429182737-phpapp01/85/Prime-numbers-15-320.jpg)