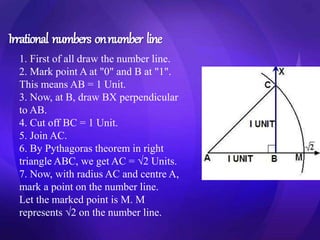
This document discusses different types of number systems. It begins by introducing natural numbers, which are counting numbers formed by repeated addition of 1. Whole numbers include all natural numbers and 0. Integers extend whole numbers infinitely in both the positive and negative directions. Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as fractions p/q where p and q are integers. Irrational numbers have non-repeating decimal expansions and cannot be written as fractions. Real numbers include all rational and irrational numbers and are represented on the number line. Methods for finding rational numbers between two given numbers and representing different types of numbers on the number line are also described.