Finite fields are important in cryptography. They involve arithmetic operations on a finite set of elements called a Galois field. Two important examples are GF(p), the integers modulo a prime p, and GF(2n), polynomials modulo an irreducible polynomial of degree n with coefficients in GF(2). Polynomial arithmetic in GF(2n) can be performed using bitwise XOR and shift operations, with modulo reduction using the irreducible polynomial. This allows efficient computation in finite fields important for cryptography.

![INTRODUCTION
o Finite fields have its increasing importance in cryptography: –AES, Elliptic
Curve, IDEA, Public Key.
o Concern operations on “numbers”:–what constitutes a “number” and –the type
of operations and the properties.
o start with concepts of groups, rings, fields from abstract algebra
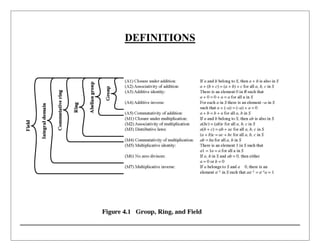
o FIELD: A field is a set of elements on which two arithmetic operations (addition
and multiplication) have been defined and which has the properties of ordinary
arithmetic, such as closure, associativity, commutativity, distributivity, and
having both additive and multiplicative inverses.
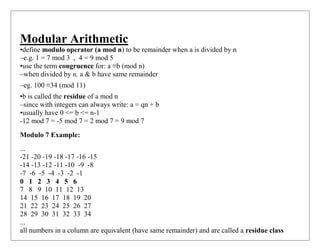
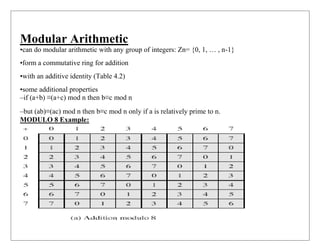
o Modular arithmetic: Modular arithmetic is a kind of integer arithmetic that
reduces all numbers to one of a fixed set [0...n 1] for some number n. Any integer
outside this range is reduced to one in this range by taking the remainder after
division by n.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finitefields-211025040834/85/Finite-fields-2-320.jpg)
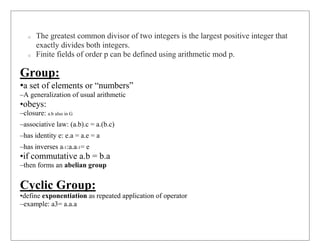
![•and let identity be: e=a0
•a group is cyclic if every element is a power of some fixed element
–i.e. b =ak for some a and every bin group
•a is said to be a generator of the group
•Example: positive numbers with addition
Ring:
•a set of “numbers” with two operations (addition and multiplication) which are:
•an abelian group with addition operation
•multiplication:
–has closure
–is associative
–distributive over addition: a(b+c) = ab + ac
•Ring is a set in which we can do addition, subtraction [a –b = a + (–b)], and multiplication
without leaving the set.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finitefields-211025040834/85/Finite-fields-4-320.jpg)







![–EUCLID[a(x), b(x)]
1.A(x) = a(x); B(x) = b(x)
2.2. if B(x) = 0 return A(x) = gcd[a(x), b(x)]
3. R(x) = A(x) mod B(x)
4. A(x) ¨B(x)
5. B(x) ¨R(x)
6. goto 2
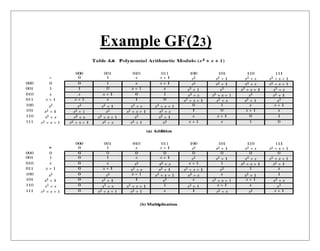
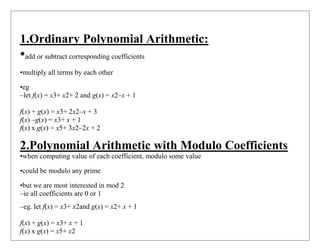
Modular Polynomial Arithmetic:
•can compute in field GF(2n)
–polynomials with coefficients modulo 2
–whose degree is less than n
–Coefficients always modulo 2 in an operation
–hence must modulo an irreducible polynomial of degree n (for multiplication only)
•form a finite field
•can always find an inverse
–can extend Euclid’s Inverse algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finitefields-211025040834/85/Finite-fields-17-320.jpg)