Presentation1, radiological imaging of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
49 likes•12,979 views
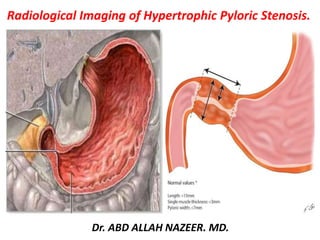
Ultrasonography is the preferred imaging method for diagnosing hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Key findings on ultrasound include thickening of the pyloric muscle greater than 3mm and elongation of the pyloric channel greater than 17mm. Doppler ultrasound can also detect increased blood flow to the hypertrophied pyloric muscle and mucosa. While upper gastrointestinal studies with barium can identify signs like double tracking, ultrasonography has greater sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Ultrasound of groin & anterior abdominal wall hernias

ultrasound of different groin and anterior abdominal wall hernias with ultrasound features of differential diagnosis
Pancreas ultrasound

The pancreas normally has a head, body, tail, and uncinate process. It develops from two anlagen that fuse during embryological development. The pancreatic duct typically drains the entire pancreas. Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed based on abdominal pain, elevated pancreatic enzymes, and imaging findings of pancreatic swelling, decreased echogenicity, and heterogeneity. Sonography can detect pancreatic enlargement, duct dilation, peripancreatic fluid collections, and decreased echogenicity in acute pancreatitis.
Ultrasound of the abdominal wall hernias

This document discusses the ultrasound evaluation of anterior abdominal wall hernias. It describes the different types of hernias including epigastric, periumbilical, umbilical, inguinal, femoral and incisional hernias. For each type of hernia, it provides ultrasound images demonstrating the normal abdominal wall anatomy and signs of the hernia. It also discusses some pitfalls in hernia evaluation that can be mistaken for hernias, such as atrophied muscles, lymph nodes, hematomas and subcutaneous masses. In summary, the document provides a comprehensive overview of abdominal wall hernia ultrasound evaluation through descriptions and images of normal findings and various hernia types.
Imaging of Bowel Obstruction

This document discusses imaging techniques for evaluating bowel obstruction, including radiography and CT. It covers the clinical presentation, imaging features, and causes of gastric, small bowel, and large bowel obstruction. Key points include using CT to identify the location and cause of obstruction, assess for complications like strangulation or closed loop obstruction that may require emergent surgery. The most common causes of small bowel obstruction are adhesions, hernias, and malignancies, while large bowel obstruction is usually due to malignancy, volvulus, or diverticulitis in older patients.
Diagnositc Imaging of the Esophagus

The document discusses the gastro-intestinal tract and esophagus. It provides details on various conditions that can affect the esophagus including diverticula, ulcers, tumors, and motility disorders. Pharyngeal/esophageal pouches and diverticula are discussed for the upper, middle, and lower third of the esophagus. Esophageal ulceration can be inflammatory from sources like reflux or viral, or neoplastic. Benign esophageal tumors are discussed along with specifics on leiomyoma features on barium swallow and CT imaging.
IMAGING IN ABDOMINAL TUBERCULOSIS

ABDOMINAL TUBERCULOSIS : ETIOLOGY, SPREAD AND IMAGING FEATURES....ON CONVENTIONAL AND CROSS SECTIONAL IMAGING
Presentation2, radiological imaging of diaphagmatic hernia.

This document discusses radiological imaging of diaphragmatic hernias. It describes various types of diaphragmatic hernias including congenital diaphragmatic herniation (CDH), which accounts for a small proportion but is one of the most common non-cardiac fetal anomalies. CDH occurs in around 1 in 2000-4000 live births and can be detected on antenatal ultrasound or after birth. Imaging techniques discussed for evaluating CDH include ultrasound, MRI, CT and plain radiography. Ultrasound findings suggestive of CDH include absent bowel loops in the abdomen and intra-thoracic herniation of organs. MRI and CT may further assess hernia contents and complications like pulmonary hypoplas
Presentation1.pptx, radiological imaging of large bowel diseases

This document discusses congenital anomalies and diseases of the large bowel. It begins by describing congenital abnormalities that can cause obstruction in neonates and the importance of radiological imaging to diagnose the location and cause. It then discusses different types of intestinal obstructions and how radiography and contrast enema exams are used to further evaluate obstructions and make a specific diagnosis. Examples of different congenital anomalies and diseases seen on imaging are also presented, including colonic atresia, meconium ileus, Hirschsprung disease, and colon cancer.
Recommended
Ultrasound of groin & anterior abdominal wall hernias

ultrasound of different groin and anterior abdominal wall hernias with ultrasound features of differential diagnosis
Pancreas ultrasound

The pancreas normally has a head, body, tail, and uncinate process. It develops from two anlagen that fuse during embryological development. The pancreatic duct typically drains the entire pancreas. Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed based on abdominal pain, elevated pancreatic enzymes, and imaging findings of pancreatic swelling, decreased echogenicity, and heterogeneity. Sonography can detect pancreatic enlargement, duct dilation, peripancreatic fluid collections, and decreased echogenicity in acute pancreatitis.
Ultrasound of the abdominal wall hernias

This document discusses the ultrasound evaluation of anterior abdominal wall hernias. It describes the different types of hernias including epigastric, periumbilical, umbilical, inguinal, femoral and incisional hernias. For each type of hernia, it provides ultrasound images demonstrating the normal abdominal wall anatomy and signs of the hernia. It also discusses some pitfalls in hernia evaluation that can be mistaken for hernias, such as atrophied muscles, lymph nodes, hematomas and subcutaneous masses. In summary, the document provides a comprehensive overview of abdominal wall hernia ultrasound evaluation through descriptions and images of normal findings and various hernia types.
Imaging of Bowel Obstruction

This document discusses imaging techniques for evaluating bowel obstruction, including radiography and CT. It covers the clinical presentation, imaging features, and causes of gastric, small bowel, and large bowel obstruction. Key points include using CT to identify the location and cause of obstruction, assess for complications like strangulation or closed loop obstruction that may require emergent surgery. The most common causes of small bowel obstruction are adhesions, hernias, and malignancies, while large bowel obstruction is usually due to malignancy, volvulus, or diverticulitis in older patients.
Diagnositc Imaging of the Esophagus

The document discusses the gastro-intestinal tract and esophagus. It provides details on various conditions that can affect the esophagus including diverticula, ulcers, tumors, and motility disorders. Pharyngeal/esophageal pouches and diverticula are discussed for the upper, middle, and lower third of the esophagus. Esophageal ulceration can be inflammatory from sources like reflux or viral, or neoplastic. Benign esophageal tumors are discussed along with specifics on leiomyoma features on barium swallow and CT imaging.
IMAGING IN ABDOMINAL TUBERCULOSIS

ABDOMINAL TUBERCULOSIS : ETIOLOGY, SPREAD AND IMAGING FEATURES....ON CONVENTIONAL AND CROSS SECTIONAL IMAGING
Presentation2, radiological imaging of diaphagmatic hernia.

This document discusses radiological imaging of diaphragmatic hernias. It describes various types of diaphragmatic hernias including congenital diaphragmatic herniation (CDH), which accounts for a small proportion but is one of the most common non-cardiac fetal anomalies. CDH occurs in around 1 in 2000-4000 live births and can be detected on antenatal ultrasound or after birth. Imaging techniques discussed for evaluating CDH include ultrasound, MRI, CT and plain radiography. Ultrasound findings suggestive of CDH include absent bowel loops in the abdomen and intra-thoracic herniation of organs. MRI and CT may further assess hernia contents and complications like pulmonary hypoplas
Presentation1.pptx, radiological imaging of large bowel diseases

This document discusses congenital anomalies and diseases of the large bowel. It begins by describing congenital abnormalities that can cause obstruction in neonates and the importance of radiological imaging to diagnose the location and cause. It then discusses different types of intestinal obstructions and how radiography and contrast enema exams are used to further evaluate obstructions and make a specific diagnosis. Examples of different congenital anomalies and diseases seen on imaging are also presented, including colonic atresia, meconium ileus, Hirschsprung disease, and colon cancer.
Acute appendicitis - Ultrasound first

1. The document discusses ultrasound techniques for diagnosing acute appendicitis, including visualizing the normal appendix and primary and secondary signs of inflammation.
2. Primary ultrasound signs of acute appendicitis include an appendix diameter over 6mm, a target sign of hypoechoic center with hyper- and hypoechoic rings, tenderness over the appendix, lack of compressibility, and increased vascularity of the wall.
3. Secondary ultrasound signs include free fluid around the appendix, abscess formation, thickening of surrounding tissues, and signs of small bowel obstruction.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of barium studies.

The document discusses various radiographic procedures used to examine the esophagus and surrounding structures, including barium swallows, upper GI series, and barium enemas. It provides details on normal esophageal anatomy and appearances, as well as many pathological conditions that can affect the esophagus such as achalasia, Barrett's esophagus, esophageal cancer, and hiatal hernias. Images demonstrate examples of normal esophagus examinations along with abnormalities.
Radiological approach to gastric ulcer disease

This document discusses barium meal (contrast x-ray) studies and their uses in evaluating gastrointestinal conditions. It notes that barium meals are now largely replaced by endoscopy but are still used when endoscopy is incomplete, confusing, or to better visualize certain morphological changes. It then describes the normal radiographic appearance of the stomach and discusses findings for conditions like acute gastritis, peptic ulcers, ulcer complications, and bleeding sites identified on scintigraphy scans.
The Radiology of Malrotation

Thank you for the presentation. I learned a lot about the evaluation and imaging of intestinal malrotation.
Ultrasound imaging of Bowel pathology

1. The document discusses the use of ultrasound imaging techniques for diagnosing bowel pathology in cases of acute abdomen. It outlines normal ultrasound appearances of the bowel and key signs of various diseases.
2. Dynamic ultrasound techniques like assessing peristalsis, compressibility, and the valsalva maneuver can provide additional diagnostic information. Focused scanning with high-frequency probes can aid in evaluating superficial lesions.
3. Ultrasound has benefits as a first-line imaging method due to its availability, low cost, and lack of radiation or contrast agents. With experience in ultrasound appearances of the bowel and careful technique, it can effectively evaluate abdominal complaints and guide management.
Ultrasoud hernia

This document provides an overview of ultrasound for evaluating hernias. It describes the anatomy of the inguinal region and sites of common hernias. Inguinal hernias can be indirect or direct. Spigelian hernias occur along the spigelian fascia. Femoral hernias are located in the femoral canal. Linea alba hernias occur through the abdominal wall. Umbilical and incisional hernias also are reviewed. Ultrasound is useful for diagnosing hernia contents and complications like incarceration, obstruction, and strangulation. Findings suggestive of strangulation include hyperechoic fat, thickened sac walls, fluid within the sac, and
Radiology ----Classical Signs in GIT Dr. Muhammad Bin Zulfiqar

Radiology ----Classical Signs in GIT Dr. Muhammad Bin Zulfiqar.
It is very difficult to learn much in the sea of radiology.
This presentation is the way to memorize classical signs in radiology.
small intestine imaging

This document discusses various imaging techniques for the small intestine, including their indications, advantages, and disadvantages. Conventional radiography has limited ability to distinguish abnormalities due to overlying bowel loops. Barium studies like follow through and enteroclysis provide better distension but have low yield. Ultrasound is useful for detecting terminal ileitis but relies on operator skill. CT enteroclysis and CT enterography provide extraluminal detail but involve radiation. MR enteroclysis is preferable to CT in children due to lack of radiation, but images can be degraded by peristalsis. No single technique is considered the gold standard.
Acute Abdomen-Radiology

1) The document discusses various imaging modalities used to diagnose conditions that present with acute abdomen such as abdominal pain, including plain radiography, ultrasound, CT, and MRI.
2) Common causes of acute abdomen discussed include appendicitis, diverticulitis, cholecystitis, small bowel obstruction, mesenteric lymphadenitis, epiploic appendagitis, urolithiasis, ruptured aneurysm, and acute pancreatitis.
3) Imaging findings for diagnosing these conditions are provided, with ultrasound and CT noted as important first-line tests to identify the cause of acute abdomen and exclude serious complications.
Paediatric chest imaging

1. The initial assessment of a pediatric chest x-ray should include evaluation of technique, tubes/lines, mediastinum, airways, lungs, and pulmonary vasculature. Inspiration level and thymic tissue should not be mistaken for pathology.
2. Causes of neonatal respiratory distress are categorized as medical or surgical. Common medical causes include transient tachypnea of the newborn, pneumonia, respiratory distress syndrome, and meconium aspiration syndrome. Surgical causes include diaphragmatic hernia and congenital lung malformations.
3. Complications of respiratory distress treatment include barotrauma manifestations like pneumothorax and pulmonary interstitial emphysema. Other
Signs in pneumoperitoneum

Pneuperitoneum is best discovered on Abdominal Radiograph.
These signs help in easy detection of the condition
Presentation1, interpretation of x ray of the abdomen.

This document provides information about interpreting abdominal x-rays. It discusses indications for abdominal x-rays such as suspected bowel obstruction or perforation. It then describes how to systematically review the x-ray by assessing bowel gas patterns, soft tissues, bones, and abnormal calcifications. The document outlines normal stomach, small bowel, and large bowel appearances. It also describes various pathologies that can be seen, such as pneumoperitoneum, bowel obstructions, volvulus, and intra-abdominal calcifications. Signs of bowel inflammation and different types of calcifications are also discussed.
Ultrasound of acute & chronic cholecystitis

This document discusses ultrasound findings related to cholecystitis. It describes the ultrasound appearance of acute cholecystitis, including signs like gallbladder wall thickening, pericholecystic fluid, and hyperemia on Doppler. Complications of acute cholecystitis are also reviewed, such as emphysematous cholecystitis where gas is visible in the gallbladder wall. Chronic cholecystitis is also summarized, noting findings like gallstones, wall thickening, and occasionally calcification or nodules indicative of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of undescended testis.

This document discusses radiological imaging techniques for undescended testes (cryptorchidism). Ultrasound has moderate sensitivity and specificity for locating undescended testes, but MRI is the best imaging method, with sensitivity around 90% and specificity of 100%. MRI can identify locations of undescended testes that may be intra-abdominal, inguinal, or ectopic. The document presents several case examples demonstrating appearances of undescended testes on different imaging techniques.
Doppler ultrasound of acute scrotum

testicular torsion, testicular trauma, testicular tumor, acute epididymitis, Fournier gangrene, varicocele.
Radiological imaging of mediastinal masses

1. CT is the most important tool for evaluating mediastinal masses and characterizing their nature and extent.
2. Thymomas are the most common primary mediastinal neoplasm, typically occurring in patients over 40 and appearing on CT as well-defined solid masses in the anterior mediastinum that can demonstrate calcification.
3. CT is useful for staging thymomas and identifying features like invasion of surrounding tissues or distant metastases that indicate more advanced disease.
Invertogram ANORECTAL MALFORMATION ( ARM ) PRANAYA

A 3-day-old female child presented with abdominal distension and inability to pass meconium. Examination revealed a normal anal opening but resistance to passage of a feeding tube beyond 2 cm. An invertogram showed rectal atresia. Endoscopy visualized a distal rectal membrane, which was incised. A fistulogram then revealed a fistula between the upper anal canal and the labia. Key points discussed include techniques for evaluating anorectal malformations like invertograms and classifications of ARM like the Wingspread and PENA systems. Relationship between sacral development and pelvic floor muscle function is also summarized.
Imaging of the Pancreas

This document discusses imaging of the pancreas. Ultrasound and CT scan are the primary modalities used. Ultrasound is useful as a screening tool due to its availability, low cost and lack of radiation. CT scan is the gold standard modality as it can accurately detect pancreatic abnormalities and complications. MRCP and MRI provide additional information and are used as problem-solving tools. The document reviews imaging features of various pancreatic pathologies such as acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis, tumors and trauma.
Presentation1.pptx, radiological imaging of esophageal lesions.

This document discusses the radiological imaging features of various esophageal lesions and conditions. It provides over 40 images showing examples of esophageal rings, achalasia, diverticula, varices, hernias, infections, strictures, tumors, vascular anomalies and other esophageal pathologies. For each condition, it describes the typical radiographic findings and appearances seen on imaging studies like barium swallows.
Imaging of Acute Appendicitis 

Describes the clinical and radiological diagnostic signs of acute appendicitis ,complications and differential diagnosis .
Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis

Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is a condition characterized by thickening of the pyloric muscle which causes projectile vomiting in infants usually starting around 3 weeks of age. It occurs more commonly in males and the risk is increased if the father also had IHPS. Diagnosis is suggested by symptoms and confirmed by ultrasound showing thickening of the pyloric wall over 4mm. Treatment involves rehydration followed by pyloromyotomy surgery to cut the thickened pyloric muscle and relieve the obstruction.
Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis

Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (CHPS) is a condition where the circular muscle of the pylorus becomes thickened, causing a narrowing of the pyloric channel. It most commonly affects firstborn male infants around one month of age, presenting with projectile vomiting, feeding intolerance, and signs of dehydration. Ultrasound is the gold standard for diagnosis, showing pyloric wall thickening over 3.5mm and elongation over 15mm. Surgical pyloromyotomy is required to correct the narrowing, after which feeds can resume within 6 hours with no long term complications.
More Related Content
What's hot
Acute appendicitis - Ultrasound first

1. The document discusses ultrasound techniques for diagnosing acute appendicitis, including visualizing the normal appendix and primary and secondary signs of inflammation.
2. Primary ultrasound signs of acute appendicitis include an appendix diameter over 6mm, a target sign of hypoechoic center with hyper- and hypoechoic rings, tenderness over the appendix, lack of compressibility, and increased vascularity of the wall.
3. Secondary ultrasound signs include free fluid around the appendix, abscess formation, thickening of surrounding tissues, and signs of small bowel obstruction.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of barium studies.

The document discusses various radiographic procedures used to examine the esophagus and surrounding structures, including barium swallows, upper GI series, and barium enemas. It provides details on normal esophageal anatomy and appearances, as well as many pathological conditions that can affect the esophagus such as achalasia, Barrett's esophagus, esophageal cancer, and hiatal hernias. Images demonstrate examples of normal esophagus examinations along with abnormalities.
Radiological approach to gastric ulcer disease

This document discusses barium meal (contrast x-ray) studies and their uses in evaluating gastrointestinal conditions. It notes that barium meals are now largely replaced by endoscopy but are still used when endoscopy is incomplete, confusing, or to better visualize certain morphological changes. It then describes the normal radiographic appearance of the stomach and discusses findings for conditions like acute gastritis, peptic ulcers, ulcer complications, and bleeding sites identified on scintigraphy scans.
The Radiology of Malrotation

Thank you for the presentation. I learned a lot about the evaluation and imaging of intestinal malrotation.
Ultrasound imaging of Bowel pathology

1. The document discusses the use of ultrasound imaging techniques for diagnosing bowel pathology in cases of acute abdomen. It outlines normal ultrasound appearances of the bowel and key signs of various diseases.
2. Dynamic ultrasound techniques like assessing peristalsis, compressibility, and the valsalva maneuver can provide additional diagnostic information. Focused scanning with high-frequency probes can aid in evaluating superficial lesions.
3. Ultrasound has benefits as a first-line imaging method due to its availability, low cost, and lack of radiation or contrast agents. With experience in ultrasound appearances of the bowel and careful technique, it can effectively evaluate abdominal complaints and guide management.
Ultrasoud hernia

This document provides an overview of ultrasound for evaluating hernias. It describes the anatomy of the inguinal region and sites of common hernias. Inguinal hernias can be indirect or direct. Spigelian hernias occur along the spigelian fascia. Femoral hernias are located in the femoral canal. Linea alba hernias occur through the abdominal wall. Umbilical and incisional hernias also are reviewed. Ultrasound is useful for diagnosing hernia contents and complications like incarceration, obstruction, and strangulation. Findings suggestive of strangulation include hyperechoic fat, thickened sac walls, fluid within the sac, and
Radiology ----Classical Signs in GIT Dr. Muhammad Bin Zulfiqar

Radiology ----Classical Signs in GIT Dr. Muhammad Bin Zulfiqar.
It is very difficult to learn much in the sea of radiology.
This presentation is the way to memorize classical signs in radiology.
small intestine imaging

This document discusses various imaging techniques for the small intestine, including their indications, advantages, and disadvantages. Conventional radiography has limited ability to distinguish abnormalities due to overlying bowel loops. Barium studies like follow through and enteroclysis provide better distension but have low yield. Ultrasound is useful for detecting terminal ileitis but relies on operator skill. CT enteroclysis and CT enterography provide extraluminal detail but involve radiation. MR enteroclysis is preferable to CT in children due to lack of radiation, but images can be degraded by peristalsis. No single technique is considered the gold standard.
Acute Abdomen-Radiology

1) The document discusses various imaging modalities used to diagnose conditions that present with acute abdomen such as abdominal pain, including plain radiography, ultrasound, CT, and MRI.
2) Common causes of acute abdomen discussed include appendicitis, diverticulitis, cholecystitis, small bowel obstruction, mesenteric lymphadenitis, epiploic appendagitis, urolithiasis, ruptured aneurysm, and acute pancreatitis.
3) Imaging findings for diagnosing these conditions are provided, with ultrasound and CT noted as important first-line tests to identify the cause of acute abdomen and exclude serious complications.
Paediatric chest imaging

1. The initial assessment of a pediatric chest x-ray should include evaluation of technique, tubes/lines, mediastinum, airways, lungs, and pulmonary vasculature. Inspiration level and thymic tissue should not be mistaken for pathology.
2. Causes of neonatal respiratory distress are categorized as medical or surgical. Common medical causes include transient tachypnea of the newborn, pneumonia, respiratory distress syndrome, and meconium aspiration syndrome. Surgical causes include diaphragmatic hernia and congenital lung malformations.
3. Complications of respiratory distress treatment include barotrauma manifestations like pneumothorax and pulmonary interstitial emphysema. Other
Signs in pneumoperitoneum

Pneuperitoneum is best discovered on Abdominal Radiograph.
These signs help in easy detection of the condition
Presentation1, interpretation of x ray of the abdomen.

This document provides information about interpreting abdominal x-rays. It discusses indications for abdominal x-rays such as suspected bowel obstruction or perforation. It then describes how to systematically review the x-ray by assessing bowel gas patterns, soft tissues, bones, and abnormal calcifications. The document outlines normal stomach, small bowel, and large bowel appearances. It also describes various pathologies that can be seen, such as pneumoperitoneum, bowel obstructions, volvulus, and intra-abdominal calcifications. Signs of bowel inflammation and different types of calcifications are also discussed.
Ultrasound of acute & chronic cholecystitis

This document discusses ultrasound findings related to cholecystitis. It describes the ultrasound appearance of acute cholecystitis, including signs like gallbladder wall thickening, pericholecystic fluid, and hyperemia on Doppler. Complications of acute cholecystitis are also reviewed, such as emphysematous cholecystitis where gas is visible in the gallbladder wall. Chronic cholecystitis is also summarized, noting findings like gallstones, wall thickening, and occasionally calcification or nodules indicative of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of undescended testis.

This document discusses radiological imaging techniques for undescended testes (cryptorchidism). Ultrasound has moderate sensitivity and specificity for locating undescended testes, but MRI is the best imaging method, with sensitivity around 90% and specificity of 100%. MRI can identify locations of undescended testes that may be intra-abdominal, inguinal, or ectopic. The document presents several case examples demonstrating appearances of undescended testes on different imaging techniques.
Doppler ultrasound of acute scrotum

testicular torsion, testicular trauma, testicular tumor, acute epididymitis, Fournier gangrene, varicocele.
Radiological imaging of mediastinal masses

1. CT is the most important tool for evaluating mediastinal masses and characterizing their nature and extent.
2. Thymomas are the most common primary mediastinal neoplasm, typically occurring in patients over 40 and appearing on CT as well-defined solid masses in the anterior mediastinum that can demonstrate calcification.
3. CT is useful for staging thymomas and identifying features like invasion of surrounding tissues or distant metastases that indicate more advanced disease.
Invertogram ANORECTAL MALFORMATION ( ARM ) PRANAYA

A 3-day-old female child presented with abdominal distension and inability to pass meconium. Examination revealed a normal anal opening but resistance to passage of a feeding tube beyond 2 cm. An invertogram showed rectal atresia. Endoscopy visualized a distal rectal membrane, which was incised. A fistulogram then revealed a fistula between the upper anal canal and the labia. Key points discussed include techniques for evaluating anorectal malformations like invertograms and classifications of ARM like the Wingspread and PENA systems. Relationship between sacral development and pelvic floor muscle function is also summarized.
Imaging of the Pancreas

This document discusses imaging of the pancreas. Ultrasound and CT scan are the primary modalities used. Ultrasound is useful as a screening tool due to its availability, low cost and lack of radiation. CT scan is the gold standard modality as it can accurately detect pancreatic abnormalities and complications. MRCP and MRI provide additional information and are used as problem-solving tools. The document reviews imaging features of various pancreatic pathologies such as acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis, tumors and trauma.
Presentation1.pptx, radiological imaging of esophageal lesions.

This document discusses the radiological imaging features of various esophageal lesions and conditions. It provides over 40 images showing examples of esophageal rings, achalasia, diverticula, varices, hernias, infections, strictures, tumors, vascular anomalies and other esophageal pathologies. For each condition, it describes the typical radiographic findings and appearances seen on imaging studies like barium swallows.
Imaging of Acute Appendicitis 

Describes the clinical and radiological diagnostic signs of acute appendicitis ,complications and differential diagnosis .
What's hot (20)
Presentation1, radiological imaging of barium studies.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of barium studies.
Radiology ----Classical Signs in GIT Dr. Muhammad Bin Zulfiqar

Radiology ----Classical Signs in GIT Dr. Muhammad Bin Zulfiqar
Presentation1, interpretation of x ray of the abdomen.

Presentation1, interpretation of x ray of the abdomen.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of undescended testis.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of undescended testis.
Invertogram ANORECTAL MALFORMATION ( ARM ) PRANAYA

Invertogram ANORECTAL MALFORMATION ( ARM ) PRANAYA
Presentation1.pptx, radiological imaging of esophageal lesions.

Presentation1.pptx, radiological imaging of esophageal lesions.
Viewers also liked
Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis

Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is a condition characterized by thickening of the pyloric muscle which causes projectile vomiting in infants usually starting around 3 weeks of age. It occurs more commonly in males and the risk is increased if the father also had IHPS. Diagnosis is suggested by symptoms and confirmed by ultrasound showing thickening of the pyloric wall over 4mm. Treatment involves rehydration followed by pyloromyotomy surgery to cut the thickened pyloric muscle and relieve the obstruction.
Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis

Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (CHPS) is a condition where the circular muscle of the pylorus becomes thickened, causing a narrowing of the pyloric channel. It most commonly affects firstborn male infants around one month of age, presenting with projectile vomiting, feeding intolerance, and signs of dehydration. Ultrasound is the gold standard for diagnosis, showing pyloric wall thickening over 3.5mm and elongation over 15mm. Surgical pyloromyotomy is required to correct the narrowing, after which feeds can resume within 6 hours with no long term complications.
Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis

Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis (IHPS) is a condition where the pyloric muscle thickens, preventing food from passing normally through the stomach. It typically affects young infants, especially boys. Ramstedt's surgery, developed in 1912, remains the standard treatment where the thickened pyloric muscle is cut to widen the opening. The exact cause is unknown but theories involve hormones, muscle spasms, and nitric oxide deficiencies in the pyloric muscle. Clinical features include projectile vomiting and signs on imaging like delayed gastric emptying. Ramstedt's operation provides effective relief of symptoms with minimal complications when performed by an experienced surgeon.
Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis- An Overview

IHPS is the commonest cause for non-bilious vomiting in infants. Treatment is Ramsted's pyloromyotomy either open or laparoscopic.
Hypertrophic pyloric-stenosis-in-infants

Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is caused by hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the pyloric muscle in infants 2-8 weeks old, resulting in narrowing of the pyloric canal. Genetic studies have identified susceptibility loci and molecular studies show improper innervation of smooth muscle cells. It occurs in 1 in 500 live births but can be as high as 1 in 200 in some regions, affecting males more than females. Presentation includes projectile vomiting 30-60 minutes after feeding with hunger, weight loss, and dehydration. Ultrasound confirms diagnosis while pyloromyotomy via open or laparoscopic surgery effectively treats the condition with excellent prognosis.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of hirshsprung disease.

Hirschsprung disease is a congenital disorder causing colonic obstruction. It results from the absence of ganglion cells in portions of the colon and rectum. This document discusses the epidemiology, clinical presentation, pathology, diagnosis and radiological findings of Hirschsprung disease. Key points include that it typically presents in newborn infants as failure to pass meconium. Diagnosis involves rectal biopsy and contrast enema to identify the transition zone between normal and aganglionic segments. Radiography may show dilated bowel and a narrow rectum. Barium enema can further define the transition zone location.
Presentation1.pptx, pediatric radiology.

This document discusses radiological imaging techniques for pediatric diseases. It focuses on imaging of the chest and urinary system to diagnose conditions like bilateral or left fronto-temporo-parietal recent infarction in children. The document is written by Dr. ABD ALLAH NAZEER and thanks the reader at the end.
Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis

This document discusses congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (CHPS), a condition where the pyloric muscle thickens, obstructing food passage from stomach to small intestine. It affects young infants, more commonly males. Presentation includes projectile vomiting after feeding. Diagnosis involves abdominal ultrasound and upper GI study. Treatment is pyloromyotomy surgery to cut the thickened pyloric muscle. The document covers epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment including surgical procedure and postoperative care of CHPS.
Pyloric Stenosis

Congenital pyloric stenosis is a condition where the pylorus becomes enlarged, blocking food from exiting the stomach. It most commonly affects male infants and presents with non-bilious vomiting. Diagnosis is typically made by palpating an olive-shaped mass in the stomach or via ultrasound showing thickening of the pyloric muscle. Treatment involves pyloromyotomy surgery to divide the thickened muscle and allow food to pass through the pylorus.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of ear microcia.

Microtia refers to underdeveloped or absent external ears. The document discusses the anatomy of normal ears, classifications of microtia, associated abnormalities, and imaging findings. HRCT is useful for evaluating microtia and associated ear anomalies. Common findings include external ear canal atresia, middle ear abnormalities like ossicular anomalies, facial nerve anomalies, and occasionally inner ear or vascular anomalies. Imaging helps surgeons plan reconstruction by identifying important structures like the facial nerve course. Microtia is often associated with ear and other organ developmental anomalies.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of macleod syndrome.

Radiological imaging is useful for diagnosing and characterizing Macleod syndrome. CT scans show the affected lung is hyperlucent with diminished vascularity and bronchietasis may be present. MRI scans appear the pulmonary vessels of the affected lung are smaller. Angiography shows the pulmonary artery and its branches are small and hypoplastic on the involved side. Nuclear medicine scans show no ventilation or perfusion in the affected lung.
Presentation1 radiological imaging of tarsal tunnel syndrome.

- Tarsal tunnel syndrome refers to entrapment of the posterior tibial nerve as it passes through the tarsal tunnel in the ankle. Common symptoms include pain, numbness and tingling in the foot.
- Causes of tarsal tunnel syndrome include ganglion cysts, bone deformities, varicose veins, space-occupying lesions, and muscle or structural abnormalities that compress the nerve.
- Radiological imaging techniques like ultrasound and MRI can identify potential compressive elements, assess nerve damage, and help determine appropriate treatment which may be conservative therapy or surgery.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of leigh disease.

Radiological imaging plays an important role in diagnosing and monitoring Leigh disease.
Leigh disease is a rare, progressive neurodegenerative disorder that typically presents in infants and leads to death in childhood. MRI is commonly used and shows characteristic symmetrical lesions in areas like the brainstem, basal ganglia, and thalamus. Over time, the lesions enlarge and involve more areas of the brain. Spectroscopy may reveal elevated lactate levels. The patterns of involvement on imaging can help confirm a diagnosis of Leigh disease.
Fever in children for medical students

Fever is a common reason children see doctors and causes concern for parents. A fever is defined as a temperature over 37.2°C orally or 37.7°C rectally. Fever has many potential causes from minor self-limiting infections to life-threatening disorders. Treatment of fever focuses on identifying the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms through antipyretic medications like acetaminophen. Accurate temperature measurement is important to guide diagnosis and treatment.
Amebiasis in children

This document provides information on Entamoeba histolytica, a pathogenic protozoan parasite. It outlines the etiology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and complications of E. histolytica infection. Key points include:
- E. histolytica infects up to 10% of the world's population and is a major cause of parasitic death. It typically causes asymptomatic colonization but can lead to amebic colitis or liver abscess.
- Infection occurs through ingestion of cysts in contaminated food/water. Cysts excyst in the intestine and trophozoites may invade the colonic mucosa.
- Diagnosis involves antigen detection in stool
Presentation1, radiological imaging of placenta accreta.

1. The document discusses radiological imaging of placenta accreta, specifically focusing on ultrasound and MRI findings.
2. Key ultrasound findings that suggest placenta accreta include placental lacunae, disruption of normal color Doppler blood flow patterns in the myometrium, loss of the retroplacental clear space, and reduced myometrial thickness.
3. Important MRI findings include uterine bulging, heterogeneous placental signal intensity, and dark intraplacental bands on T2-weighted images. Visualization of direct placental invasion of the bladder is also suggestive of placenta percreta.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of intra cranial dermoid tumours.

This document provides an overview of radiological imaging features of intra-cranial dermoid tumors. It discusses that dermoid tumors are benign inclusion cysts composed of ectodermal elements that are typically located in the midline. On imaging, dermoid tumors often appear as well-defined lobulated masses with low attenuation on CT and high signal intensity on T1-weighted MRI, and they typically do not enhance with contrast. The document outlines characteristics, locations, epidemiology, clinical presentations, pathology, and radiographic features of dermoid tumors.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of hyperparathyroidism.

This document discusses radiological imaging features of hyperparathyroidism. It begins by explaining the pathology of the disease and its subtypes. Characteristic skeletal findings are described, including subperiosteal bone resorption of the phalanges and various sites of osteopenia, osteosclerosis, and brown tumors. Various imaging modalities are then discussed for localizing parathyroid adenomas and hyperplasia, including ultrasound, CT, nuclear medicine scans, and MRI. Characteristic appearances on imaging include subperiosteal bone changes, nephrocalcinosis, and enhancement patterns of parathyroid lesions.
Presentation1 radiological imaging of carpal tunnel syndrome.

- Carpal tunnel syndrome results from compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. It commonly occurs between ages 36-60 and is more frequent in women. Symptoms include pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand.
- Ultrasound and MRI are useful imaging modalities. Ultrasound can show bowing of the flexor retinaculum, flattening and swelling of the median nerve. MRI also demonstrates these findings and can detect additional causes like masses or arthritic changes.
- Various pathologies can cause carpal tunnel syndrome by decreasing the size of the tunnel or enlarging its contents, compressing the median nerve. Imaging allows visualization
Pediatric chest part 2

The document discusses various pediatric mediastinal masses including lymphoma, thymic hyperplasia, thymoma, germ cell tumors, and cysts. Hodgkin's lymphoma typically presents as a primary mediastinal lesion while non-Hodgkin's lymphoma usually manifests as generalised disease. Thymic hyperplasia appears as diffuse enlargement of the thymus on imaging. Thymoma is the most common primary tumor and appears as a well-defined anterior mediastinal mass. Teratomas often contain fat, soft tissue, and calcium. Cystic lesions include bronchogenic cysts which are usually located near the trachea or bronchi, and pericardial cysts which abut
Viewers also liked (20)
Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis- An Overview

Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis- An Overview
Presentation1, radiological imaging of hirshsprung disease.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of hirshsprung disease.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of ear microcia.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of ear microcia.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of macleod syndrome.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of macleod syndrome.
Presentation1 radiological imaging of tarsal tunnel syndrome.

Presentation1 radiological imaging of tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of leigh disease.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of leigh disease.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of placenta accreta.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of placenta accreta.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of intra cranial dermoid tumours.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of intra cranial dermoid tumours.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of hyperparathyroidism.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of hyperparathyroidism.
Presentation1 radiological imaging of carpal tunnel syndrome.

Presentation1 radiological imaging of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Similar to Presentation1, radiological imaging of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.
Presentation1, Ultrasound of the bowel loops and the lymph nodes..pptx

Ultrasonography is used to examine the bowel loops and abdominal lymph nodes. It can detect various pathologies of the bowel including hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, duodenal hematoma, midgut volvulus, incarcerated inguinal hernia, Henoch Schönlein purpura, Crohn's disease, intussusception, and acute appendicitis. The ultrasound technique and appearance of these conditions are described along with images showing normal bowel anatomy for comparison. Specific features that help differentiate these pathologies are discussed.
Presentation1, ultrasound of the bowel loops and the lymph nodes.

Ultrasonography is useful for evaluating bowel loops and abdominal lymph nodes. The normal bowel wall has 5 layers but only 2 are usually visible on ultrasound. Pathologies like hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, intramural duodenal hematoma, midgut volvulus, incarcerated hernia and various inflammatory conditions can be diagnosed using ultrasound. Acute appendicitis and its complications are also commonly evaluated. Ultrasound is helpful for assessing conditions like celiac disease, acute pancreatitis and focal acute bacterial nephritis.
Presentation1, ultrasound of the bowel loops and the lymph nodes.

Ultrasonography is used to examine the bowel loops and abdominal lymph nodes. It can detect various pathologies of the bowel including hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, duodenal hematoma, midgut volvulus, incarcerated hernias, and diseases like Crohn's, Henoch Schönlein purpura, and appendicitis. High frequency probes are used to assess bowel wall thickness and layers. Specific techniques are discussed for different pathologies and the ultrasound findings that help make the diagnosis in each case are described. Normal ultrasound anatomy and appearances of the bowel are also presented.
Oesophagus,,

The document discusses the anatomy and physiology of the esophagus. It describes the esophagus as a muscular tube that extends from the pharynx to the stomach. It has three portions - cervical, thoracic, and abdominal. The document outlines the relations of the esophagus in each portion and describes conditions like dysphagia, esophageal sphincters, gastroesophageal reflux disease, achalasia, Zenker's diverticulum and their clinical features and treatments.
Esophogeal and diaphramatic diseases

This document provides an overview of the esophagus, including its anatomy, physiology, common diseases, and diagnostic testing. Key points include:
- The esophagus connects the pharynx to the stomach and propels food through peristaltic contractions. It has three sections - cervical, thoracic, abdominal.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease is common, caused by backflow of gastric acid into the esophagus. Risk factors include obesity, smoking, diet.
- Esophageal tears can range from superficial mucosal tears to full perforations, which require urgent treatment due to risk of mediastinitis and sepsis.
- Diagnostic tests include barium swallow,
Hirschsprung's disease.pptx

This document discusses Hirschsprung's disease, a congenital disorder causing bowel obstruction. It begins with an introduction stating it affects 1 in 5,000-8,000 births and is caused by absence of ganglion cells in the colon. Embryology and clinical presentation are then described. The document further classifies Hirschsprung's disease and discusses various imaging modalities used in diagnosis such as radiography, ultrasound, CT scan, and biopsy. Differential diagnosis and treatment involving temporary colostomy followed by definitive surgery are also outlined.
Presentation1 (2).pptx

This document provides information about pyloric stenosis, including:
- The pylorus connects the stomach to the duodenum and contains glands and muscles that regulate food passage.
- Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the pylorus opening, usually due to muscle thickening. It most commonly affects infants and causes projectile vomiting after feeding.
- Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging, and endoscopy. Treatment is usually pyloromyotomy surgery to cut the thickened muscle and reopen the pylorus.
tracheo oesophagal fistula gihs

This document discusses tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF), including its definition, development, epidemiology, anatomical variations, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and nursing care. TEF is a congenital abnormality where the trachea and esophagus are connected. It develops due to incomplete separation of the trachea and esophagus during embryonic development. Clinical signs include drooling, choking, respiratory distress, inability to feed, and aspiration pneumonia. Treatment involves surgical repair to separate the trachea and esophagus.
Ped. surgery.ppt

This document discusses several pediatric surgical conditions including congenital diaphragmatic hernia, esophageal atresia, hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, intestinal atresia and stenosis, Hirschsprung's disease, and anorectal malformations. It covers the embryology, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of each condition. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal surgical repair are often important aspects of managing these acute or congenital pediatric conditions.
Pediatric High and Low intestinal Obstruction.pptx

This document summarizes various causes of pediatric high and low intestinal obstruction. For low intestinal obstruction, common causes presented include meconium ileus, ileal atresia, Hirschsprung's disease, functional immaturity of the colon, and rarely colonic atresia. Radiographic findings and treatments for each condition are described. For high intestinal obstruction, causes discussed are atresia or stenosis of the jejunum or proximal ileum, duodenal atresia/stenosis, inguinal hernia, necrotizing enterocolitis, and duplication cysts. Radiological features and management are outlined for each condition.
Emergent pediatric us what every radiologist should know

1) Longitudinal ultrasound shows an enlarged mesenteric lymph node acting as a lead point for an intussusception in a pediatric patient.
2) Transverse ultrasound shows thickening of the pyloric muscle and elongation of the pyloric channel consistent with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) in an infant.
3) Appendicitis, intussusception, and HPS are three common reasons for abdominal imaging in pediatric patients. Ultrasound is useful for diagnosing these conditions due to its lack of ionizing radiation, low cost, availability, and ability to assess bowel dynamics without sedation.
Stomach and duodenum_-_benign_lesions[2]![Stomach and duodenum_-_benign_lesions[2]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Stomach and duodenum_-_benign_lesions[2]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
This document summarizes various benign lesions of the stomach and duodenum. It describes the gross anatomy and embryology of the stomach and duodenum. It then discusses several specific benign conditions like idiopathic hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, duodenal atresia, gastric and duodenal diverticula, gastric and duodenal webs, gastric ulcers, and various inflammatory conditions of the stomach and duodenum including erosive gastritis, antral gastritis, helicobacter pylori gastritis, hypertrophic gastritis, and Menetrier's disease. It provides details on clinical features, investigative findings, treatment and prognosis for many of these conditions.
Causes of dysphagia

Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, can be caused by many factors. An accurate diagnosis requires a detailed history, examination, and special investigations. Special investigations may include barium swallows, endoscopies, pH monitoring, manometry, and others depending on suspected causes. Causes can include neurological issues, infections, inflammation, tumors, motility disorders, and more. Determining the underlying cause is important for guiding appropriate treatment of a patient's dysphagia.
Anorectal_malformations_(1).pptx

This document summarizes the case of a newborn baby born via elective C-section with anorectal malformations. Key details include:
- Baby was born at term with normal APGAR scores and weight of 2.83kg.
- During birth it was noted the baby had no patent anal opening and a single umbilical artery, so the baby was referred for further management.
- Investigations found the baby had an anorectal malformation, ASD, and L5 hemivertebrae, consistent with VACTERL association.
- A colostomy was performed on the baby. No growth was found on cultures and antibiotics were stopped. The baby was being managed for the
Hirschsprung Disease

Hirschsprung disease is a congenital disorder where the enteric nervous system fails to develop in parts of the colon, most commonly in the rectum. This leads to obstruction and complications like enterocolitis. The diagnosis is confirmed with biopsy showing lack of ganglion cells. Treatment involves surgical removal of the aganglionic segment and reconnection of the bowel, such as with a Swenson or Duhamel procedure. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications.
D034023026

International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention (IJPSI) is an international journal intended for professionals and researchers in all fields of Pahrmaceutical Science. IJPSI publishes research articles and reviews within the whole field Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Science, new teaching methods, assessment, validation and the impact of new technologies and it will continue to provide information on the latest trends and developments in this ever-expanding subject. The publications of papers are selected through double peer reviewed to ensure originality, relevance, and readability. The articles published in our journal can be accessed online.
Gastric volvulus and other types of volvulus

Bhori Singh, a 45-year-old male, presented with abdominal pain, distension and inability to pass flatus or stool for the past few days. Examination and investigations revealed acute intestinal obstruction likely due to gastric volvulus or perforation peritonitis. He underwent an exploratory laparotomy with gastropexy where gastric volvulus was found and repaired by suturing the stomach to the abdominal wall. Post-operatively, he recovered well and was discharged on the 8th day. Gastric volvulus is the twisting of the stomach and can be acute or chronic. Treatment involves endoscopic or surgical reduction and fixation of the stomach to prevent recurrence.
Fluoroscopic techniques and anatomy of pharynx and esophagus final

This document discusses fluoroscopic techniques and anatomy of the pharynx and esophagus. It outlines contrast media used, indications for fluoroscopic studies, patient positioning, and normal anatomy and function of the pharynx and esophagus. The pharynx and esophagus are evaluated using barium and iodinated contrast agents under fluoroscopy to assess for abnormalities in swallowing, motility, and anatomy.
Spontaneous Esophageal Rupture 修改后

This document summarizes the anatomy, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of spontaneous esophageal rupture (SER), also known as Boerhaave's syndrome. It describes the anatomy of the esophagus and explains that SER usually occurs due to vomiting against a closed upper esophageal sphincter, which increases intraesophageal pressure and can cause a tear. Diagnosis involves considering the patient's history, symptoms of chest and abdominal pain, and findings on imaging tests. Treatment involves antibiotics, nothing by mouth, gastric decompression, and possibly surgery if symptoms do not improve with initial non-operative management. Early diagnosis and treatment are important for prognosis.
Git anomalies

various congenital gastrointestinal diseases manifesting in childhood or even in adults, their radiographic findings on various imaging modalities such as radiograph, barium, ultrasound etc.
Similar to Presentation1, radiological imaging of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. (20)
Presentation1, Ultrasound of the bowel loops and the lymph nodes..pptx

Presentation1, Ultrasound of the bowel loops and the lymph nodes..pptx
Presentation1, ultrasound of the bowel loops and the lymph nodes.

Presentation1, ultrasound of the bowel loops and the lymph nodes.
Presentation1, ultrasound of the bowel loops and the lymph nodes.

Presentation1, ultrasound of the bowel loops and the lymph nodes.
Pediatric High and Low intestinal Obstruction.pptx

Pediatric High and Low intestinal Obstruction.pptx
Emergent pediatric us what every radiologist should know

Emergent pediatric us what every radiologist should know
Fluoroscopic techniques and anatomy of pharynx and esophagus final

Fluoroscopic techniques and anatomy of pharynx and esophagus final
More from Abdellah Nazeer
Muculoskeletal Pediatic Imaging..pptx

This document discusses various pediatric musculoskeletal disorders and conditions that can affect the knee joint, as seen on imaging such as MRI and radiography. It covers developmental disorders like congenital absence of cruciate ligaments and discoid meniscus. It also discusses infectious diseases like osteomyelitis, inflammatory diseases such as pigmented villonodular synovitis, neoplastic conditions including benign tumors like osteochondroma and malignant tumors like osteosarcoma. A variety of imaging findings are presented for each condition.
Presentation1 Short cases MD..pptx

This document contains 34 radiology case summaries. Case 1 describes a Salter-Harris type I ankle fracture with avulsion injury seen on X-ray. Case 2 describes bilateral triangle bone sclerosis of the iliac bones seen on pelvis X-ray and MRI in a patient with osteitis condensans ilii. Case 3 describes a Lisfranc fracture dislocation seen on foot X-ray.
Presentation1, MD MCQ Cases..pptx

This document contains multiple case studies and images related to soft tissue hemangiomas and neurofibromatosis. The cases demonstrate various imaging findings including: heterogeneous masses containing phleboliths characteristic of hemangiomas in muscle and soft tissue seen on X-ray and MRI; intramuscular hemangiomas appearing as well-circumscribed and hyperintense lesions on MRI; and neurofibromas appearing as plexiform masses showing atypical enhancement and causing skeletal abnormalities in neurofibromatosis type 1 and 2.
Presentation1, Short Cases Quiz..pptx

This document contains a list of over 80 medical conditions and diseases. It includes rare conditions like chondrodysplasia punctata, ranula, and lissencephaly as well as more common conditions like lipoma, adenomyosis, and osteosarcoma. The wide variety of medical topics covered suggests this list was intended as a study guide or reference for medical students or residents to test their knowledge of different pathologies.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of lateral hindfoot impingement.

This document discusses radiological imaging of lateral hindfoot impingement. It provides illustrations and images showing normal hindfoot anatomy as well as examples of talocalcaneal impingement, subfibular impingement, and combined impingement. MRI and CT images demonstrate bone marrow edema, cystic changes, sclerosis, and soft tissue swelling associated with impingement between the talus, calcaneus, and fibula. Measurements of hindfoot valgus angle are also shown on imaging to evaluate impingement and alignment. Case studies with patients presenting lateral ankle pain further demonstrate imaging findings of extra-articular hindfoot impingement.
Presentation2, radiological anatomy of the liver and spleen.

This document discusses the normal anatomy of the liver and spleen as seen on radiological CT scans. It describes the classic portal vein anatomy where the main portal vein bifurcates into right and left branches. It also shows images of variations in the arterial supply to segment IV of the liver, which can arise from either the left or right hepatic artery. Finally, it mentions examining the anatomy of the spleen but does not provide any details.
Presentation1, artifacts and pitfalls of the wrist and elbow joints.

1) The document discusses various normal anatomical structures and imaging artifacts that can be mistaken for abnormalities in MRI of the wrist and elbow joints.
2) Specific examples mentioned include "pseudoerosions" of wrist bones that are actually intraosseous blood vessels, as well as pseudodefects of the capitellum and trochlear bones of the elbow that appear as interruptions of the cortical bone.
3) The document emphasizes that these pseudodefects should not be confused with osteochondral lesions, as they do not exhibit marrow edema and occur in different locations. It provides images to illustrate examples of these normal variants.
Presentation1, artifact and pitfalls of the knee, hip and ankle joints.

The document summarizes common artifacts and pitfalls seen on MRI of the knee, hip, and ankle joints that can be mistaken for pathology but are actually normal anatomical variants or imaging findings. Some examples provided include meniscofemoral ligaments in the knee that can mimic meniscal tears, transverse ligaments that can appear to disrupt the meniscus, and popliteal tendon sheaths that can resemble lesions. For the hip, examples given are synovial pits, os acetabuli, the transverse acetabular ligament, perilabral recesses, and intraosseous contrast tracks in the acetabulum. Proper identification requires knowledge of anatomy and correlation across imaging planes.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of artifact and pitfalls in shoulder join...

This document discusses various normal anatomical variations and artifacts that can be mistaken for pathology on shoulder MRI images. It describes variations that can be seen in tendons like the biceps and rotator cuff, ligaments, labral structures, bone structures, and bone marrow. Specifically, it notes variations in tendon bifurcation and vascular structures, subtle differences between tendons in the rotator cuff, variants of ligaments and labral structures like the sublabral foramen, and normal anatomical grooves and depressions in bones that should not be confused with defects or lesions. Positioning artifacts are also discussed. The document aims to help radiologists avoid misdiagnosing these normal variants as pathological conditions.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of internal abdominal hernia.

This document summarizes different types of internal abdominal hernias as seen on radiological imaging. It describes the clinical presentation, anatomy, and characteristic radiographic features of various internal hernia types including paraduodenal, pericecal, transmesenteric, lesser sac, broad ligament, supravesical, and Petersen hernias. Key radiographic findings include clusters of small bowel loops in atypical locations and displacement or compression of surrounding organs. Vascular landmarks help identify the specific hernia type.
Presentation11, radiological imaging of ovarian torsion.

Ovarian torsion refers to the twisting of an ovary on its vascular pedicle, which can cut off its blood supply. It is a gynecological emergency that requires urgent surgery. Radiological imaging plays an important role in the diagnosis. Ultrasound is usually the initial imaging method, showing signs such as an enlarged ovary without blood flow. CT and MRI can further evaluate for complications like hemorrhage or infarction. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are needed to prevent ovarian necrosis from the loss of blood supply.
Presentation1, musculoskeletal anatomy.

This document provides an overview of musculoskeletal MRI anatomy of the knee, ankle, hip, elbow and shoulder joints. It describes the imaging planes used to study each joint and surrounding structures like ligaments, tendons, muscles and neurovascular elements. Key anatomic landmarks of the joints are identified on MRI in different planes. Normal appearances of tissues like cartilage, bone and synovial fluid are also outlined.
Presentation1, new mri techniques in the diagnosis and monitoring of multiple...

This document discusses new MRI techniques for diagnosing and monitoring multiple sclerosis (MS). It recommends protocols for baseline and follow-up brain and spinal cord MRIs, including mandatory and optional sequences. Advanced techniques like double inversion recovery, diffusion tensor imaging, and MR spectroscopy are highlighted for improving detection of gray matter lesions and diffuse white matter damage compared to conventional MRI. The document concludes that while conventional MRI is important for MS, advanced techniques provide higher sensitivity and specificity for both lesions and normal-appearing brain tissue, furthering understanding of MS pathophysiology.
Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted mri in neck mas...

This document summarizes the potential applications of diffusion-weighted MRI in evaluating neck masses. It discusses how DWI can help differentiate between benign and malignant neck masses based on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values. DWI is also useful for predicting and monitoring treatment response in head and neck tumors by detecting changes in ADC values before changes in tumor size. DWI can help distinguish tumor recurrence from post-treatment changes based on qualitative and quantitative ADC assessments. The document concludes that DWI shows promise for applications in head and neck oncology but larger multicenter studies are still needed.
Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted images in breas...

The document discusses the use of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values to characterize breast lesions. DWI was performed on 70 breast lesions which underwent biopsy. Malignant lesions showed lower ADC values than benign lesions. Using an ADC cutoff of 1.1×10^-3 mm2/s and normalized ADC ratio of 0.9 provided high sensitivity and specificity of 89.75% and 92.2% respectively in differentiating benign and malignant lesions. DWI is thus a potential adjunct to conventional breast MRI that can accurately characterize lesions.
Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted images in abdom...

The document discusses the use of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in abdominal and pelvic MRI. It finds that DWI improves lesion detection sensitivity, especially for metastases, and can help characterize lesions when gadolinium contrast is contraindicated. DWI provides quantitative tissue analysis without contrast and may help longitudinally assess tumor response to therapy. Given its merits and availability on most MRI systems, DWI should be considered a routine sequence in abdominal MRI protocols, particularly when contrast cannot be used.
Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted imges in neuror...

1) The document discusses the use of diffusion-weighted MRI in detecting areas of restricted diffusion in various neurological conditions and diseases. It provides examples of several conditions that appear bright on DWI imaging such as acute ischemic stroke, traumatic brain injuries, encephalitis, spinal cord ischemia, and arterial dissections.
2) Restricted diffusion occurs when there is a reduction in the normal random movement of water molecules within tissues, appearing as hyperintense signals on DWI images. This can be caused by cellular swelling, reduced extracellular space, or fragmentation of cellular components.
3) The timing of imaging after an event such as stroke or trauma influences the appearance of lesions on DWI and ADC maps, with restricted diffusion detectable
Presentation1, mr physics.

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was discovered in 1947 by two physicists and the first clinical images were obtained in 1977. MRI uses strong magnetic fields between 1-9 Tesla to align hydrogen atoms in the body and radio waves to elicit signals to form images. The document provides a brief history of MRI and discusses magnetic fields, relaxation processes, and pulse sequences used to generate MRI images.
Presentation1, ultrasound physics.

This document is a cover letter from Dr. ABD ALLAH NAZEER, an MD specializing in ultrasound physics. The letter introduces Dr. Nazeer and his area of expertise in a brief yet professional manner without providing unnecessary details. It closes with a simple thank you message.
More from Abdellah Nazeer (20)
Presentation1, radiological imaging of lateral hindfoot impingement.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of lateral hindfoot impingement.
Presentation2, radiological anatomy of the liver and spleen.

Presentation2, radiological anatomy of the liver and spleen.
Presentation1, artifacts and pitfalls of the wrist and elbow joints.

Presentation1, artifacts and pitfalls of the wrist and elbow joints.
Presentation1, artifact and pitfalls of the knee, hip and ankle joints.

Presentation1, artifact and pitfalls of the knee, hip and ankle joints.
Presentation1, radiological imaging of artifact and pitfalls in shoulder join...

Presentation1, radiological imaging of artifact and pitfalls in shoulder join...
Presentation1, radiological imaging of internal abdominal hernia.

Presentation1, radiological imaging of internal abdominal hernia.
Presentation11, radiological imaging of ovarian torsion.

Presentation11, radiological imaging of ovarian torsion.
Presentation1, new mri techniques in the diagnosis and monitoring of multiple...

Presentation1, new mri techniques in the diagnosis and monitoring of multiple...
Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted mri in neck mas...

Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted mri in neck mas...
Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted images in breas...

Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted images in breas...
Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted images in abdom...

Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted images in abdom...
Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted imges in neuror...

Presentation1, radiological application of diffusion weighted imges in neuror...
Recently uploaded
TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by...

TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by Stamler, Verified Chapters 1 - 33, Complete Newest Version Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by Stamler, Verified Chapters 1 - 33, Complete Newest Version Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by Stamler Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition TEST BANK by Stamler Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Chapters Download Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Download Stuvia Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Study Guide Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Ebook Download Stuvia Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Questions and Answers Quizlet Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Studocu Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Quizlet Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Chapters Download Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Download Course Hero Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Answers Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Ebook Download Course hero Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Questions and Answers Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Studocu Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Pdf Chapters Download Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Pdf Download Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Study Guide Questions and Answers Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Ebook Download Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Questions Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Studocu Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Stuvia
Efficacy of Avartana Sneha in Ayurveda

Avartana Sneha is a unique method of Preparation of Sneha Kalpana in Ayurveda, mainly it is indicated for the Vataja rogas.
8 Surprising Reasons To Meditate 40 Minutes A Day That Can Change Your Life.pptx

8 Surprising Reasons To Meditate 40 Minutes A Day That Can Change Your Life.pptxHolistified Wellness
We’re talking about Vedic Meditation, a form of meditation that has been around for at least 5,000 years. Back then, the people who lived in the Indus Valley, now known as India and Pakistan, practised meditation as a fundamental part of daily life. This knowledge that has given us yoga and Ayurveda, was known as Veda, hence the name Vedic. And though there are some written records, the practice has been passed down verbally from generation to generation.Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Swisschem Dermacare has mentioned the List of The Best Antifungal Soap In India 2022. All of these soaps are trusted by various Dermatology Experts.
Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central

Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa CentralClinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa CentralClinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa CentralClinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central
The Best Ayurvedic Antacid Tablets in India

Treat the symptoms of indigestion, heartburn and stomach reflux with the 10 Best Ayurvedic Antacid Tablets in India.
Cell Therapy Expansion and Challenges in Autoimmune Disease

There is increasing confidence that cell therapies will soon play a role in the treatment of autoimmune disorders, but the extent of this impact remains to be seen. Early readouts on autologous CAR-Ts in lupus are encouraging, but manufacturing and cost limitations are likely to restrict access to highly refractory patients. Allogeneic CAR-Ts have the potential to broaden access to earlier lines of treatment due to their inherent cost benefits, however they will need to demonstrate comparable or improved efficacy to established modalities.
In addition to infrastructure and capacity constraints, CAR-Ts face a very different risk-benefit dynamic in autoimmune compared to oncology, highlighting the need for tolerable therapies with low adverse event risk. CAR-NK and Treg-based therapies are also being developed in certain autoimmune disorders and may demonstrate favorable safety profiles. Several novel non-cell therapies such as bispecific antibodies, nanobodies, and RNAi drugs, may also offer future alternative competitive solutions with variable value propositions.
Widespread adoption of cell therapies will not only require strong efficacy and safety data, but also adapted pricing and access strategies. At oncology-based price points, CAR-Ts are unlikely to achieve broad market access in autoimmune disorders, with eligible patient populations that are potentially orders of magnitude greater than the number of currently addressable cancer patients. Developers have made strides towards reducing cell therapy COGS while improving manufacturing efficiency, but payors will inevitably restrict access until more sustainable pricing is achieved.
Despite these headwinds, industry leaders and investors remain confident that cell therapies are poised to address significant unmet need in patients suffering from autoimmune disorders. However, the extent of this impact on the treatment landscape remains to be seen, as the industry rapidly approaches an inflection point.
Post-Menstrual Smell- When to Suspect Vaginitis.pptx

Do you have abnormal smell after periods? It may be vaginitis. Do not worry, herbal medicine Fuyan Pill can help you get a cure.
Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad

- Video recording of this lecture in English language: https://youtu.be/kqbnxVAZs-0
- Video recording of this lecture in Arabic language: https://youtu.be/SINlygW1Mpc
- Link to download the book free: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/nephrotube-nephrology-books.html
- Link to NephroTube website: www.NephroTube.com
- Link to NephroTube social media accounts: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/join-nephrotube-on-social-media.html
Adhd Medication Shortage Uk - trinexpharmacy.com

The UK is currently facing a Adhd Medication Shortage Uk, which has left many patients and their families grappling with uncertainty and frustration. ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a chronic condition that requires consistent medication to manage effectively. This shortage has highlighted the critical role these medications play in the daily lives of those affected by ADHD. Contact : +1 (747) 209 – 3649 E-mail : sales@trinexpharmacy.com
Top-Vitamin-Supplement-Brands-in-India List

Swisschem Dermacare provides the Top 10 Vitamin Supplement Brands in India. To know more about us give us call at our official number
Role of Mukta Pishti in the Management of Hyperthyroidism

Muktapishti is a traditional Ayurvedic preparation made from Shoditha Mukta (Purified Pearl), is believed to help regulate thyroid function and reduce symptoms of hyperthyroidism due to its cooling and balancing properties. Clinical evidence on its efficacy remains limited, necessitating further research to validate its therapeutic benefits.
Histololgy of Female Reproductive System.pptx

Dive into an in-depth exploration of the histological structure of female reproductive system with this comprehensive lecture. Presented by Dr. Ayesha Irfan, Assistant Professor of Anatomy, this presentation covers the Gross anatomy and functional histology of the female reproductive organs. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in medical science, this lecture provides clear explanations, detailed diagrams, and valuable insights into female reproductive system. Enhance your knowledge and understanding of this essential aspect of human biology.
Recently uploaded (20)
TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by...

TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by...
8 Surprising Reasons To Meditate 40 Minutes A Day That Can Change Your Life.pptx

8 Surprising Reasons To Meditate 40 Minutes A Day That Can Change Your Life.pptx
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India
Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central

Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central
Cell Therapy Expansion and Challenges in Autoimmune Disease

Cell Therapy Expansion and Challenges in Autoimmune Disease
Post-Menstrual Smell- When to Suspect Vaginitis.pptx

Post-Menstrual Smell- When to Suspect Vaginitis.pptx
Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad

Hemodialysis: Chapter 4, Dialysate Circuit - Dr.Gawad
Role of Mukta Pishti in the Management of Hyperthyroidism

Role of Mukta Pishti in the Management of Hyperthyroidism
Presentation1, radiological imaging of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.
- 1. Radiological Imaging of Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis. Dr. ABD ALLAH NAZEER. MD.
- 2. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) refers to idiopathic thickening of gastric pyloric musculature which then results in progressive gastric outlet obstruction. Epidemiology Pyloric stenosis is relatively common and has a male predilection (M:F ~4:1), and is more commonly seen in Caucasians . It typically occurs between first week to 3 months of age. There may be a positive family history. Incidence of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is approximately 2-5 per 1,000 births per year in most white populations. HPS is less common in India and among black and other Asian populations. Clinical presentation Clinical presentation is typically with non-bilious projectile vomiting. The hypertrophied pylorus can be palpated as an olive sized mass in the right upper quadrant. A succession splash may be audible, and although common, is only relevant if heard hours after the last meal. Risk factors maternal history of pyloric stenosis
- 3. Pathology HPS is the result of both hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the pyloric circular muscles fibers. The pathogenesis of this is not understood. There are four main theories: immunohistochemical abnormalities genetic abnormalities infectious cause hyperacidity theory Associations Turner syndrome Tracheo-esophageal fistula esophageal atresia trisomy 18
- 4. Radiological imaging: Radiography Abdominal radiographs may show a fluid-filled or air-distended stomach, suggesting the presence of gastric outlet obstruction. A markedly dilated stomach with exaggerated incisura (caterpillar sign) may be seen, which represents increased gastric peristalsis in these patients (see the image below). This peristaltic wave may be seen on visual inspection of the abdomen. If the patient has recently vomited or has a nasogastric tube in place, the stomach is decompressed and the radiographic findings are normal An UGI study was once considered the test of choice for hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Findings on UGI studies include the following: Delayed gastric emptying (if severe, this may prevent barium from passing into the pylorus and severely limit the study) Cephalic orientation of the pylorus Shouldering (i.e., filling defect at the antrum created by prolapse of the hypertrophic muscle) Mushroom or umbrella sign (i.e., thickened muscle that indents the duodenal bulb; the name refers to the impression made by the hypertrophic pylorus on the duodenum) Double-track sign (i.e., redundant mucosa in the narrowed pyloric lumen, which results in separation of the barium column into 2 channels). Pyloric teat (i.e., outpouching created by distortion of the lesser curve by the hypertrophied muscle) Retained secretions and retrograde peristalsis Plain film radiography provides a low degree of confidence in making the diagnosis of or in ruling out hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. A UGI study has high sensitivity (>90%) and low specificity. High intestinal obstruction can be seen with midgut volvulus, duodenal obstruction (from stenosis, duodenal web, annular pancreas), gastric outlet obstruction caused by focal foveolar hyperplasia, and eosinophilic gastroenteritis, among others. False-negative radiographs can be seen in a child who has recently vomited.
- 5. Ultrasonography Ultrasonography is important in the diagnosis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis and has likely contributed to the changing face of the disease, because this modality results in earlier diagnosis and treatment owing to the accessibility and accuracy of ultrasonography.This modality is the method of choice for both the diagnosis and exclusion of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, because ultrasonography has a sensitivity and specificity of approximately 100%.Thus, ultrasonography is also recommended in patients whose disease is clinically suspected but in whom the pyloric olive cannot be felt. In a study by Leaphart et al, ultrasonography confirmed hypertrophic pyloric stenosis when the pyloric muscle thickness (MT) was greater than 4 mm and the pyloric channel length (CL) was greater than 15 mm. The investigators studied the diagnostic criteria for this disease in newborns younger than 21 days from 2000 to 2006 and found that ultrasonographic measurement of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis was significantly decreased in younger patients (MT, 3.7 +/- 0.65 mm; CL, 16.9 +/- 2.8 mm) versus older newborns (MT, 4.6 +/- 0.82 mm; CL, 18.2 +/- 3.4 mm). Of important note, the mean ultrasonographic measurement for young newborns with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis typically fell within the range currently defined as normal or borderline.A linear relationship existed between pyloric MT and CL and patient age, suggesting that 3.5 mm MT be considered the cutoff in younger patients.
- 6. Technique Ultrasonography is performed with a 7.5- to 13.5-MHz linear transducer in the supine child. Transverse images at the epigastrium identify the pylorus to the left of the gallbladder and anteromedial to the right kidney (see the image below). A distended stomach, however, displaces and distorts the pylorus and may require the placement of a nasogastric tube to withdraw the stomach's contents. A gastric aspirate of more than 5 mL in a baby who has been without oral intake (NPO) for several hours indicates gastric outlet obstruction. Right posterior oblique positioning and scanning from a posterior approach may help to improve visualization of the pylorus. Ultrasonographic signs of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, originally described in 1977and further defined, are as follows: A MT (serosa to mucosa) greater than 3 mm (a correlation between MT and the patient's age exists; the most reliable ultrasonographic sign is an MT greater than 3 mm. Because this measurement can be increased falsely with off-axis imaging, attention to technique is important.) Target sign on transverse images of the pylorus.
- 7. Pyloric channel length greater than 17 mm Pyloric thickness (serosa to serosa) of 15 mm or greater Failure of the channel to open during a minimum of 15 minutes of scanning Retrograde or hyper peristaltic contractions Antral nipple sign (i.e., a prolapse of redundant mucosa into the antrum, which creates a pseudomass Double-track sign on ultrasonography(i.e., redundant mucosa in the narrowed lumen, which creates 2 mucosal outlines) Other findings include reversible portal venous gas; nonuniform echogenicity of the pyloric muscle.
- 9. Supine radiograph in an infant with vomiting demonstrates the caterpillar sign of active gastric hyperperistalsis.
- 10. Lateral view from an upper gastrointestinal study demonstrates the double-track sign.
- 11. Upper gastrointestinal study from a child shows the string sign (see inset).
- 13. Stomach shows double tracking in region of pyloric canal, indentation on base of bulb and delayed gastric emptying.
- 14. Fluoroscopic image from UGI in a patient with IHPS. Contrast material courses through the mucosal interstices of the canal, forming the double-track sign (large arrowheads), with an additional central channel along the distal portion (small arrowhead). Mass impression on the gastric antrum (arrow), best seen during peristaltic activity, is termed the shoulder sign.
- 15. TYPICAL UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL SERIAL IN A 2 YEARS OLD BOY WITH HYPERTROPHIC PYLORIC STENOSIS. Narrowing of pyloric canal pushes hypertrophic pylorus upwards and posteriorly to the duodenal bulb impressing the lesser curvature of the stomach. All of that results as the "beak sign" and "tit sign" respectively.
- 16. HYPERTROPHIC PYLORIC STENOIS IN A 2 YEARS OLD BOY. Plain radiograph shows severe distension of the stomach with air-fluid level inside due to complete outlet stop. Lateral view on barium exam shows narrowing and elongation of pyloric canal as well as stretching of the duodenal bulb due to hypertrophied pylorus. Notice as ell, the existence of the “string sign” or the “double track sign”.
- 17. Double-track sign - Contrast studies showing redundant mucosa separates barium into two columns in pyloric channel.
- 18. Tit sign - contrast study showing an outpouching created on lesser curve by distorted muscle in hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.
- 19. INFANTILE HYPERTROPHIC PYLORIC STENOSIS.
- 20. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis demonstrates the target sign and heterogeneous echo texture of the muscular layer (the pylorus is deep to the anechoic gallbladder).
- 21. The distended stomach (*), posteriorly displacing the pylorus (arrow), which resembles the appearance of the uterine cervix, of congenital pyloric stenosis.
- 22. The hypertrophied muscular layer. Abnormal elongation of the pyloric canal (measure 1)
- 23. Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric stenosis.
- 24. Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric stenosis
- 25. Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric stenosis.
- 26. a. Sonograms in a patient with IHPS. (a) Longitudinal sonogram shows anterior thickened muscle (cursors). Double layer of crowded and redundant mucosa fills the channel and protrudes into fluid-filled antrum (arrow). D = fluid-filled duodenal cap. (b) Cross-sectional sonogram shows circumferential muscular thickening (cursors) surrounding the central channel and filled with mucosa (M).
- 27. Longitudinal sonograms obtained within a few minutes of each other show peristaltic activity and changes in pyloric anatomy in a patient with IHPS. Note the shorter canal in image on left and subsequent elongation coincident with peristaltic activity in image on right. There is failure of relaxation of the pyloric channel, and persistent obliteration of the lumen. Also note that on the left image, the gastric contents and pyloric mucosa have similar echogenicity, falsely suggestive of unimpeded passage of gastric contents through the canal. A = antrum, D = duodenal cap, arrows = outer muscular layer.
- 28. a The double layer of thickened mucosa (*), b protruding through the antrum
- 29. Peristaltic changes in antropyloric anatomy on normal sonographic study. Left: Antropyloric channel is closed during peristaltic activity. Right: Distal antrum (A) is fully relaxed. Arrows = pyloric ring, D = duodenal cap.
- 30. Sonographic measurement of pylorus canal length (Cervix sign in IHPS). Color Doppler Examination of the pylorus showing vascularity in the mucosa s& pyloric muscle.
- 31. 1a. Longitudinal plane showing the elongated pylorus with thickened pyloric muscle. 1b. Transverse plane showing ‘target sign’ with thickened pyloric muscle.
- 32. In longitudinal plane the pyloric canal length is 18mm, The pyloric muscle thickness measuring 4.6 mm and the pyloric diameter measuring 14 mm.
- 33. The ultrasound imaging showing the "donut" lesion. The ultrasound imaging showing the increase of the longitudinal length measure (16,9 mm) and an increase in the thickness of the pyloric muscular wall (11,9 mm).
- 34. Axial oblique ultrasound shows thickened, hypoechoic muscular wall (5.4 mm) and elongated pyloric canal (17.2 mm approximately).
- 35. The pyloric channel appears significantly elongated and the thickened, hypoechoic muscular layers are well appreciated. The pyloric lumen is reduced and the apposed echogenic mucosal layers of both sides are noted. The axial images demonstrate target sign.
- 37. Thickening of pyloric wall is seen. Single wall thickness is 4-5 mm (normal is up to 3 mm). Length of pyloric canal is 18-20 mm (normal is up to 16 mm).
- 38. Doppler US findings in patients with IHPS. (a) Longitudinal image shows markedly increased flow to hypertrophied pylorus in 4-week-old girl. Solid arrows point to muscle layer. Open arrow points to mucosal flow. (b) Transverse image obtained in 5-week-old girl. Note the collar of increased flow in the submucosal plexus, branching into the luminal mucosa and adjacent muscle layer (arrows). (c) Longitudinal image of hypertrophied pylorus in 3-week-old boy with typical IHPS. Note the increased flow to the mucosa within the canal, protruding into the adjacent fluid-filled antrum (A).Straight arrows outline the adjacent thickened muscle. Curved arrow points to base of duodenal bulb. (d) Longitudinal image of hypertrophied pylorus in 5-week-old boy with typical IHPS. Note the markedly increased flow to the mucosal layer, which is detailed in the spectral tracing at the bottom of the image. A = antrum. (e) Longitudinal image of hypertrophied pylorus in 2-week-old boy with IHPS. Note the markedly increased flow to the muscle layer, which is detailed in the spectral tracing at the bottom of the image. D = duodenal bulb. (f) Longitudinal image of atypical pylorus in 5-week-old boy with IHPS. Although there is detectable flow, it is less visible than that in most other patients with IHPS. Arrows point to muscle layer. (g) Transverse image of pylorus in same patient as in f, with similar findings. Arrows point to muscle layer.
- 39. Doppler US findings in patients without IHPS (control patients). A = antrum, D = duodenal bulb. Longitudinal images obtained in (a) a 2-month-old boy, (b) a 3-month-old boy, and (c) an 8-week-old girl show no detectable flow. Antropyloric canal is closed in a and open in b and c. (d) Longitudinal image obtained in 10-day-old girl shows atypical high flow in the open antropyloric canal. There is visible flow to the dorsal portion of the muscle layer.
- 40. Thank You.
