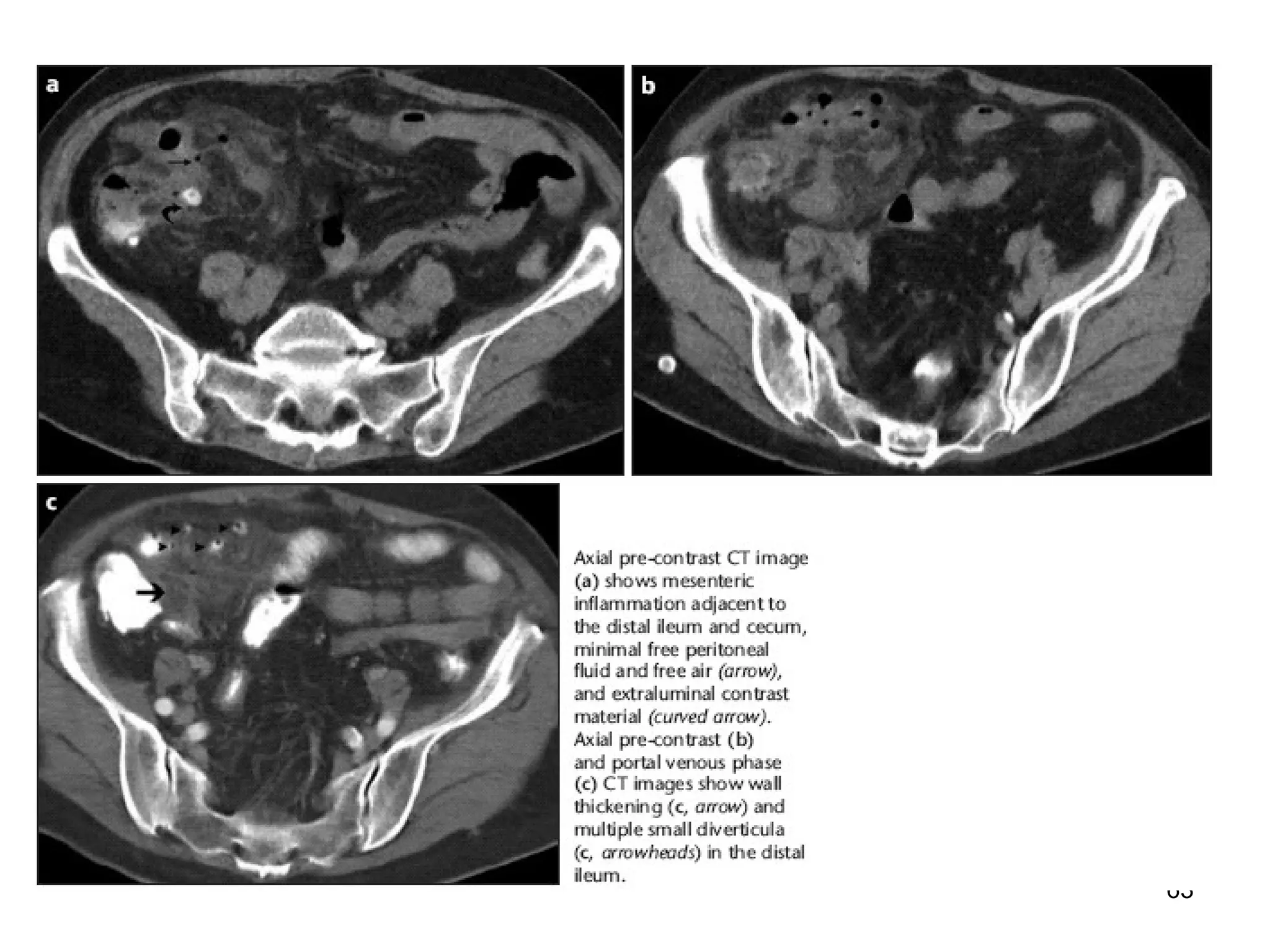
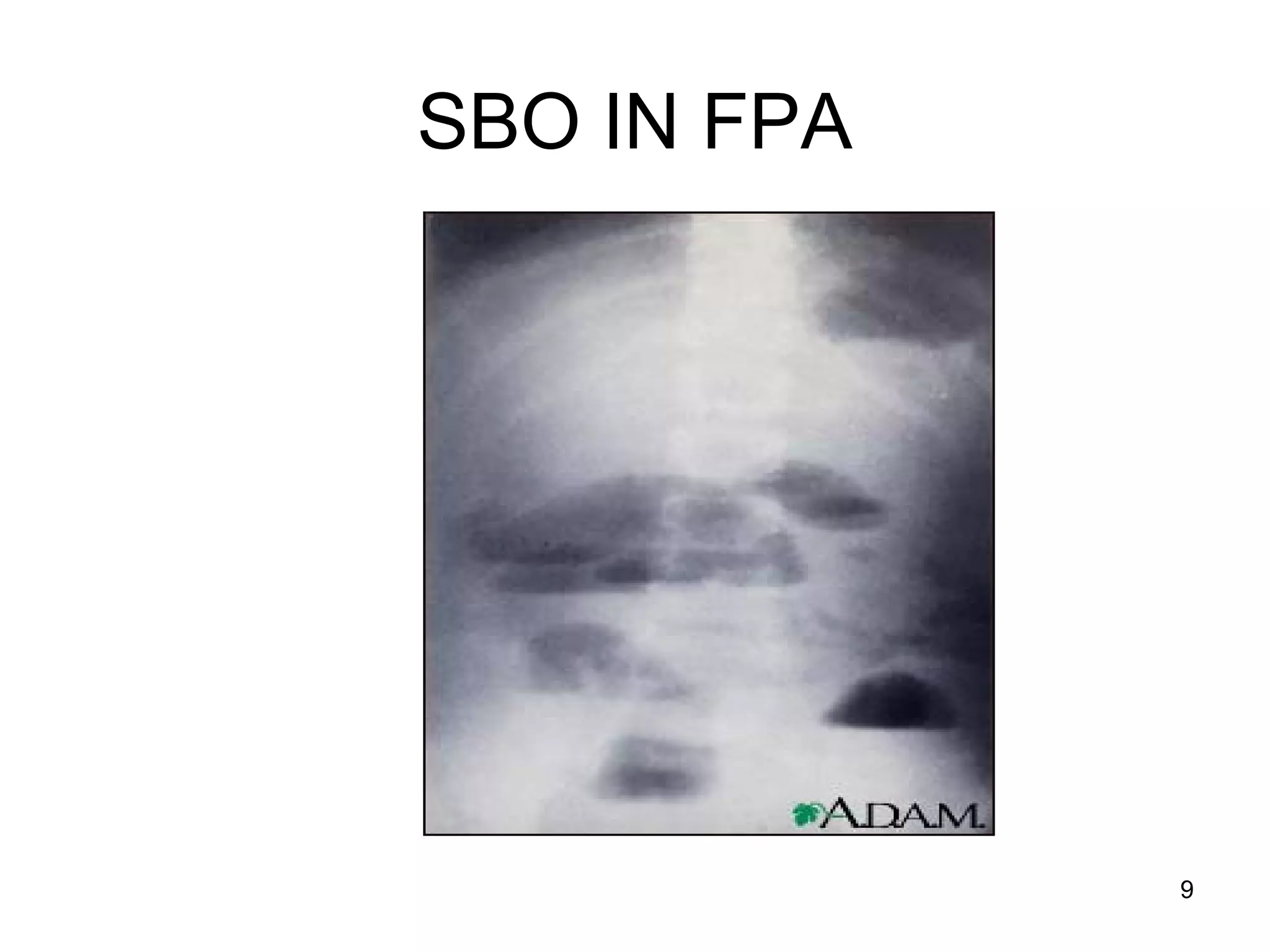
This document discusses various imaging techniques for the small intestine, including their indications, advantages, and disadvantages. Conventional radiography has limited ability to distinguish abnormalities due to overlying bowel loops. Barium studies like follow through and enteroclysis provide better distension but have low yield. Ultrasound is useful for detecting terminal ileitis but relies on operator skill. CT enteroclysis and CT enterography provide extraluminal detail but involve radiation. MR enteroclysis is preferable to CT in children due to lack of radiation, but images can be degraded by peristalsis. No single technique is considered the gold standard.




![6
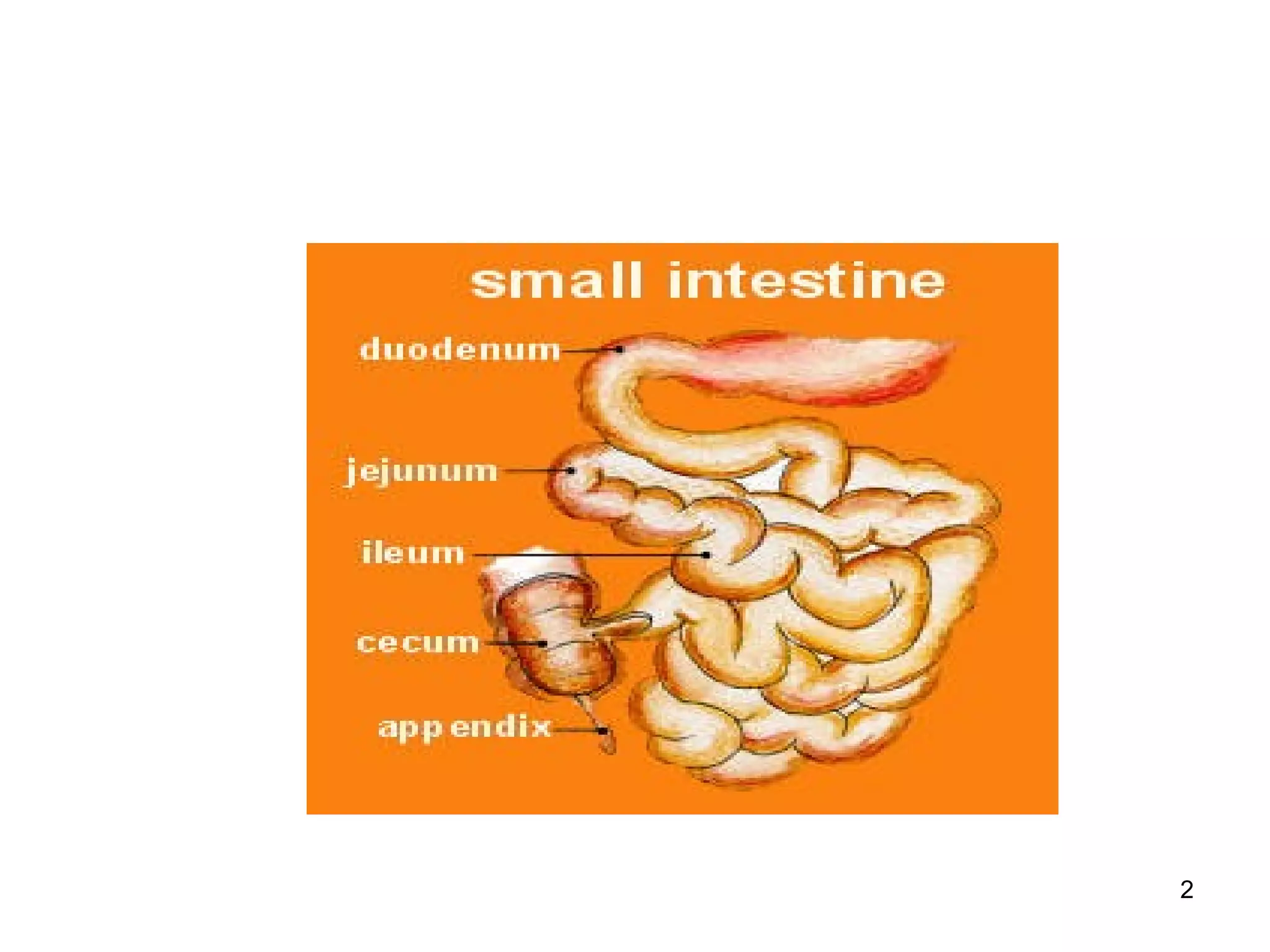
Techniques
• Conventional radiography
• Bariummeal follow through& enteroclysis
• Sonography
• CT-CT enteroclysis,CTenterography
• MRI-MRenteroclysis
• Capsule endoscopy
• Enteroscopy –push enteroscopy,push-pull
enteroscopy[also called double-balloon] and
intraoperative enteroscopy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12smallintestineimaging-150815204443-lva1-app6891/75/small-intestine-imaging-6-2048.jpg)



















![38
Advantages
• Shorter examination time
• Better distension
• Greater positive and negative for a wide
range of S B pathology,including
strictures,adhesions and intrinsic SB
disease[eg sprue]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12smallintestineimaging-150815204443-lva1-app6891/75/small-intestine-imaging-38-2048.jpg)



![42
• Disadvantage
• 1.operator dependent modality
• 2.lack of standardisation
• 3.less useful in obese[images are better in
children] or in the presence of large
volumes of bowel gases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12smallintestineimaging-150815204443-lva1-app6891/75/small-intestine-imaging-42-2048.jpg)