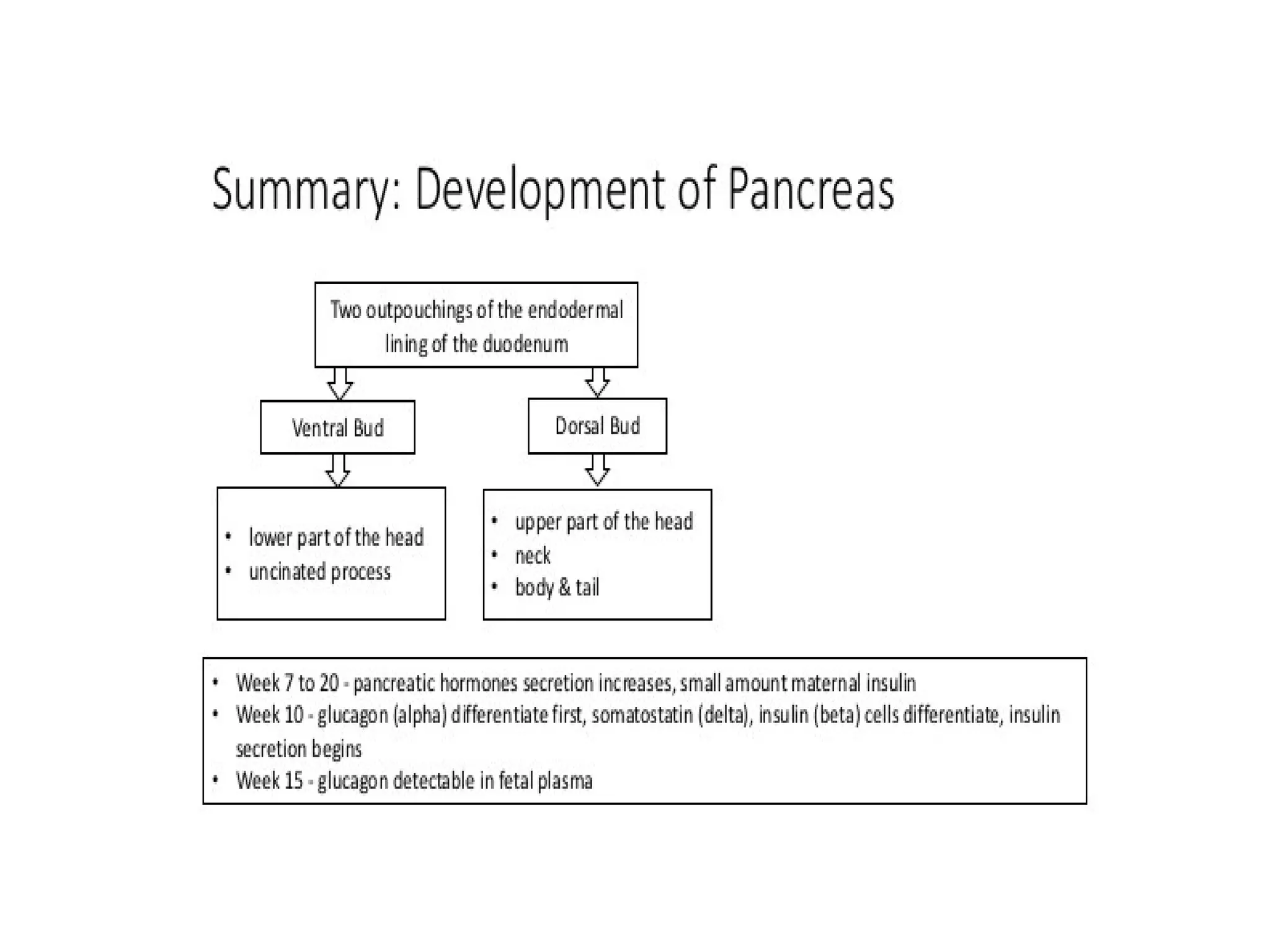
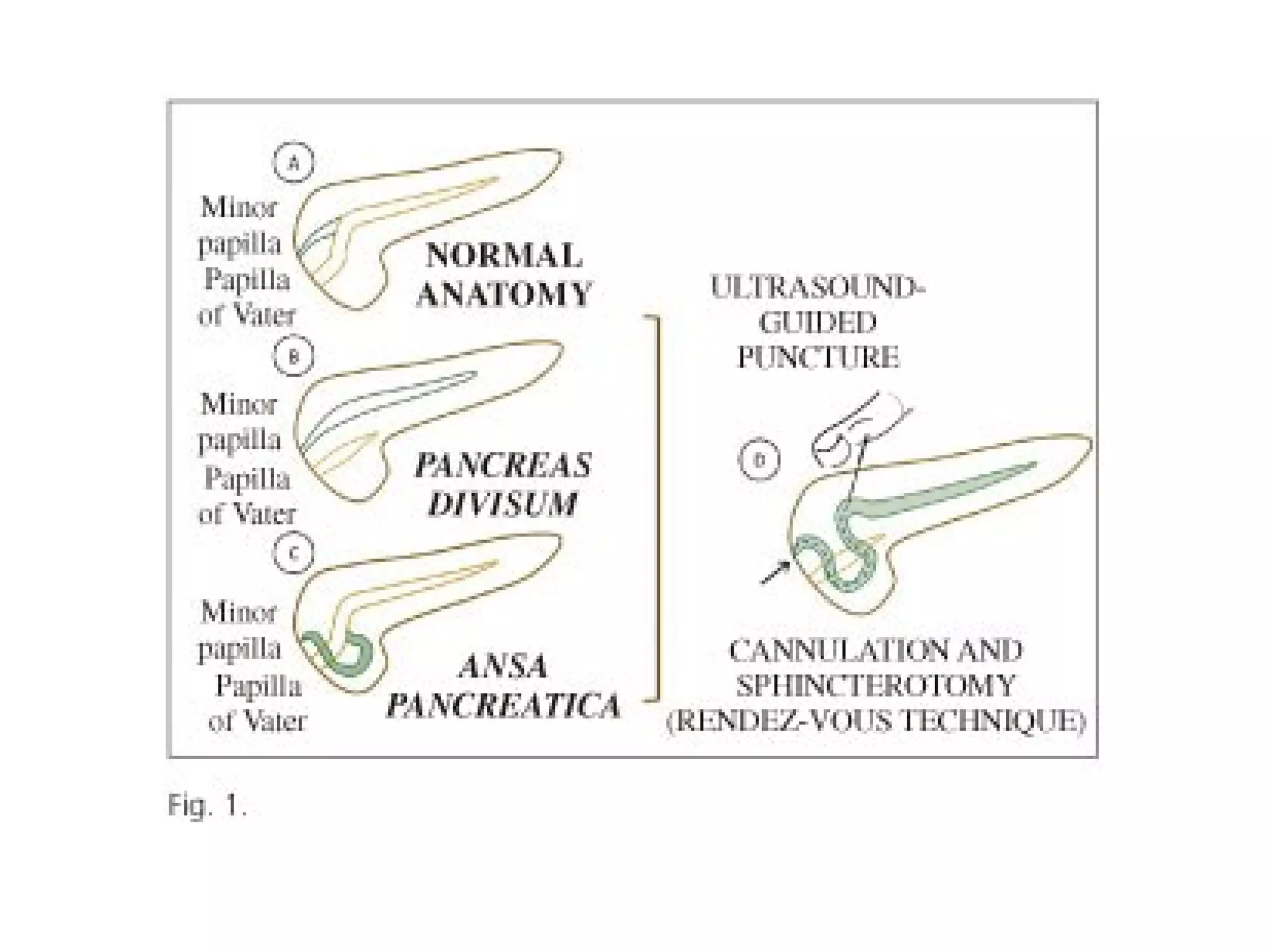
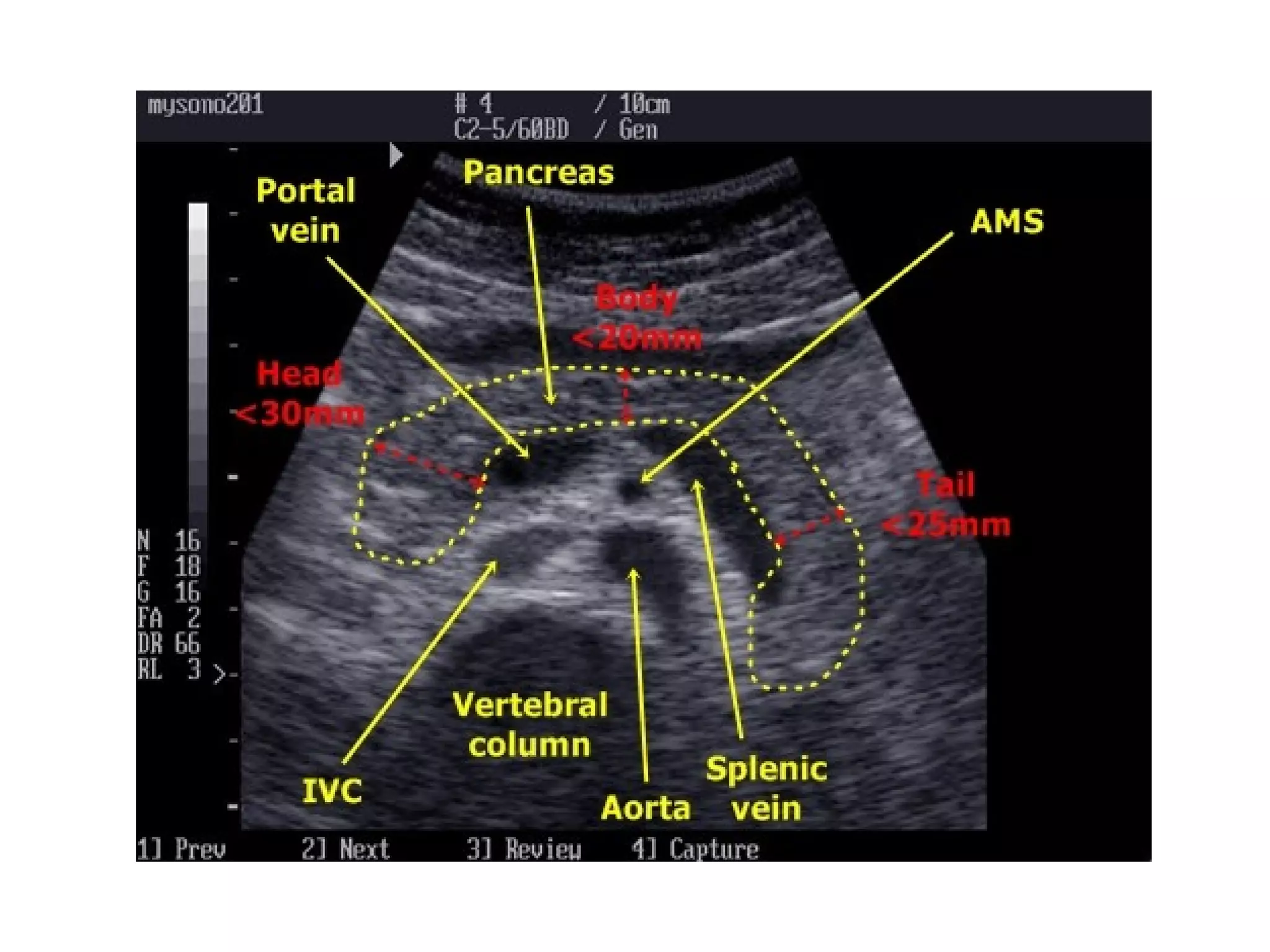
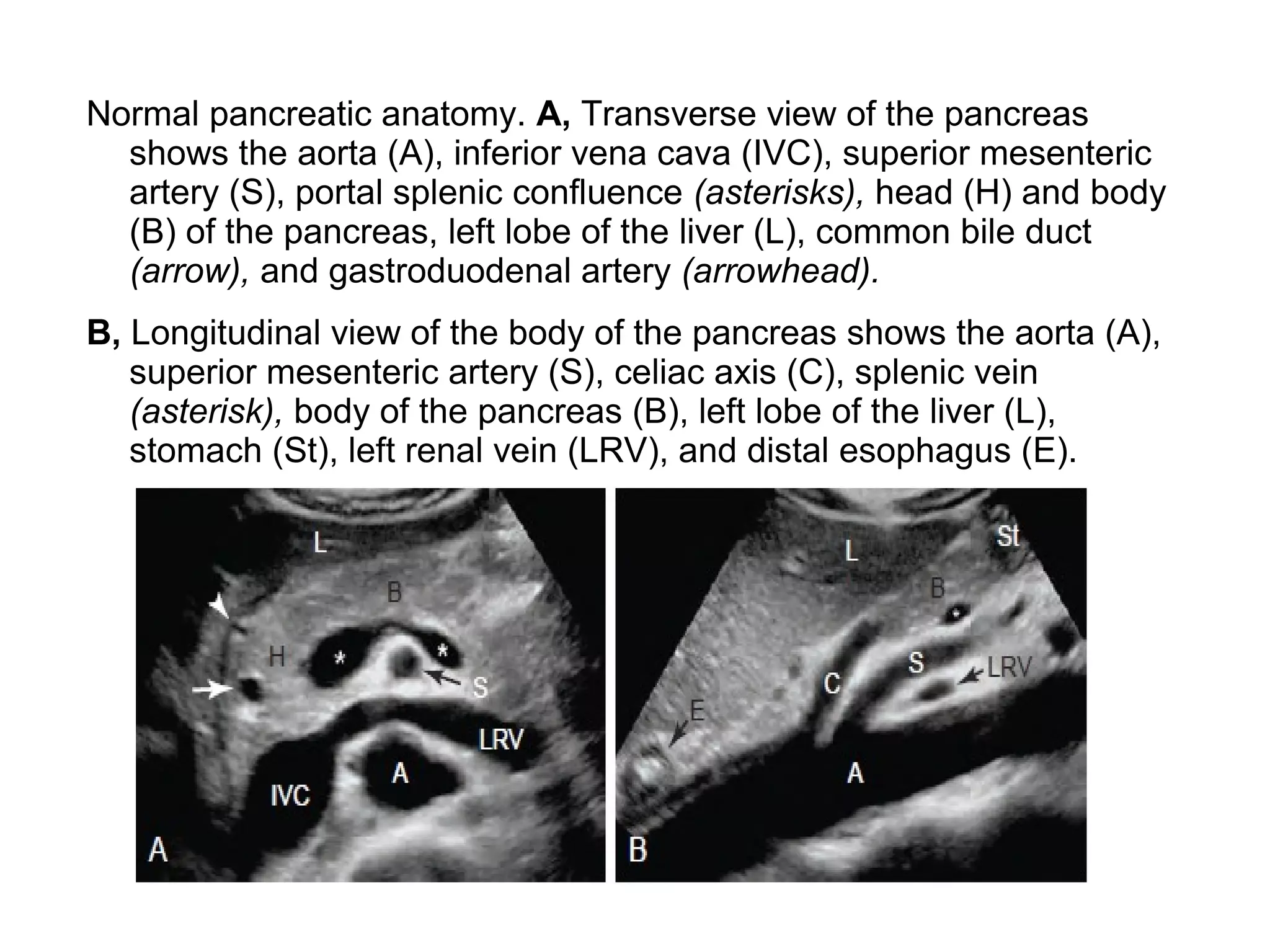
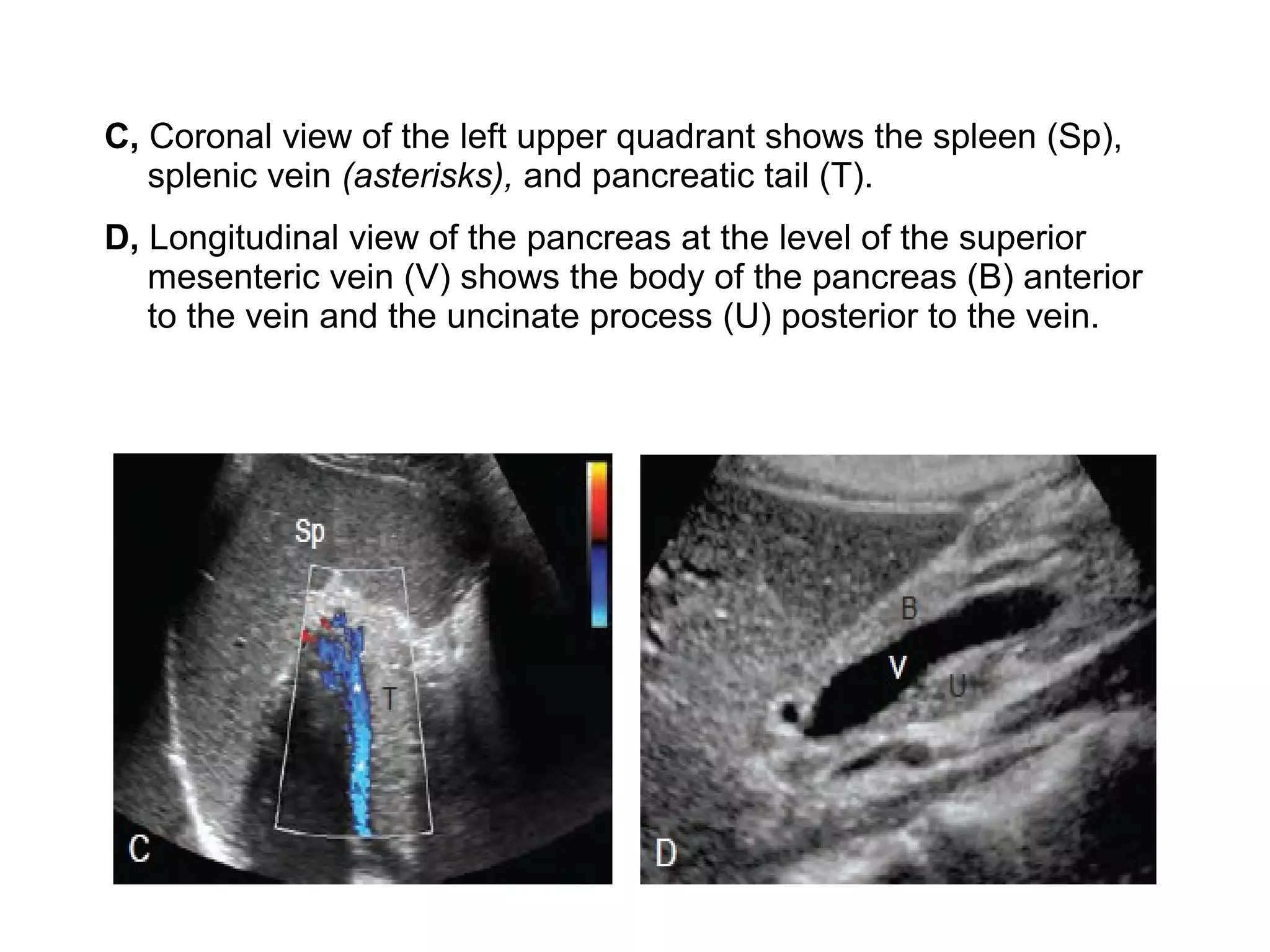
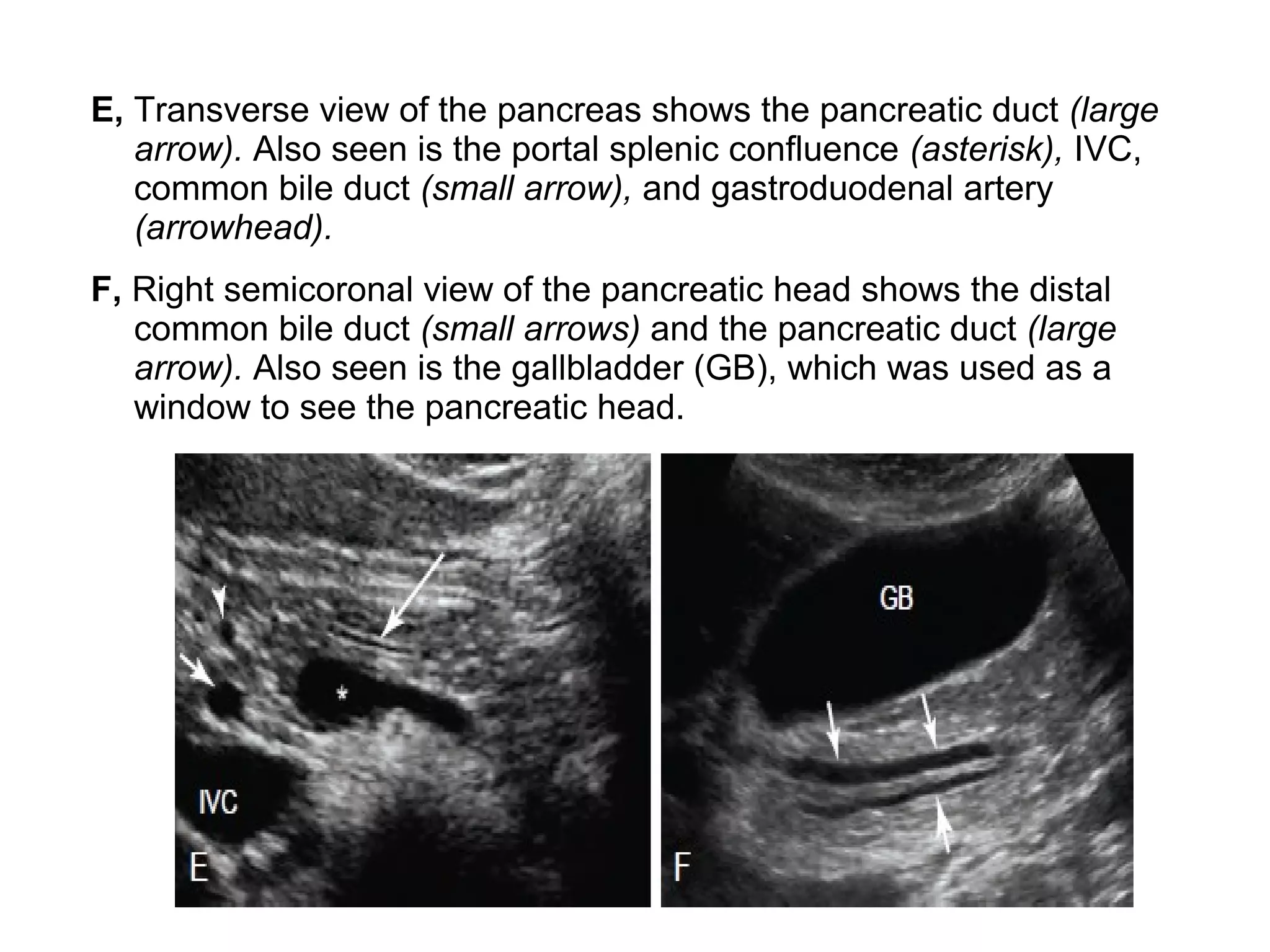
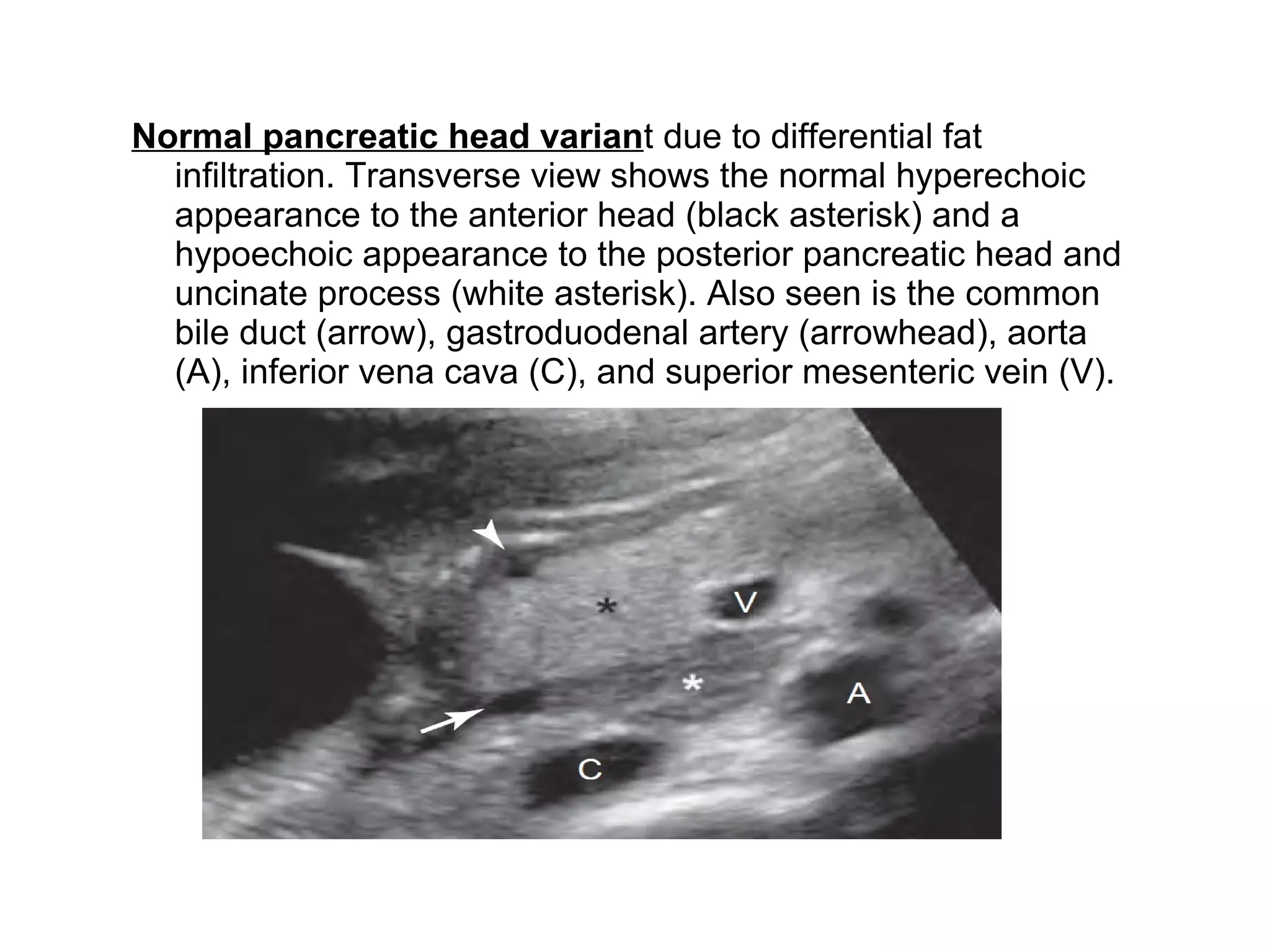
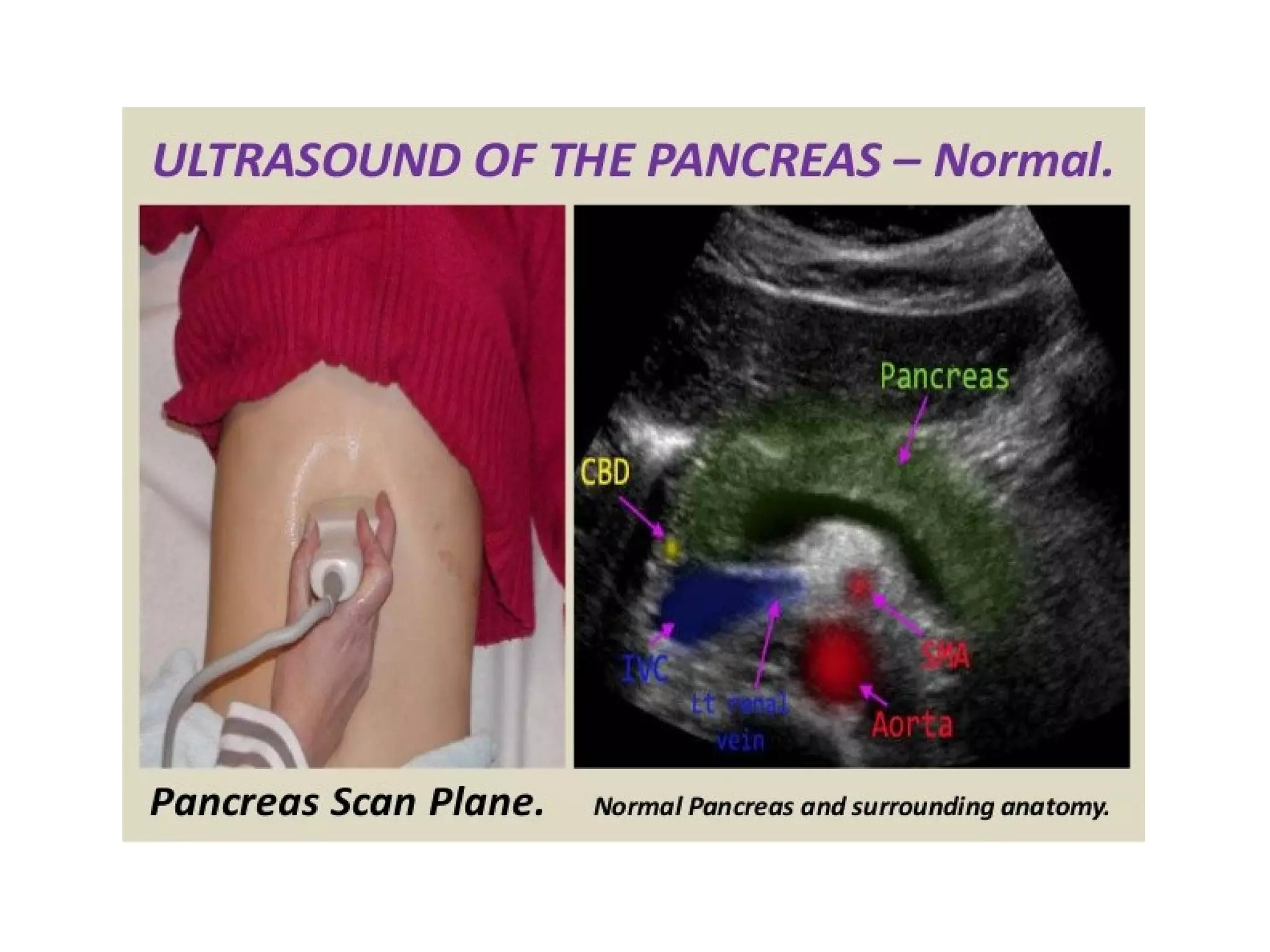
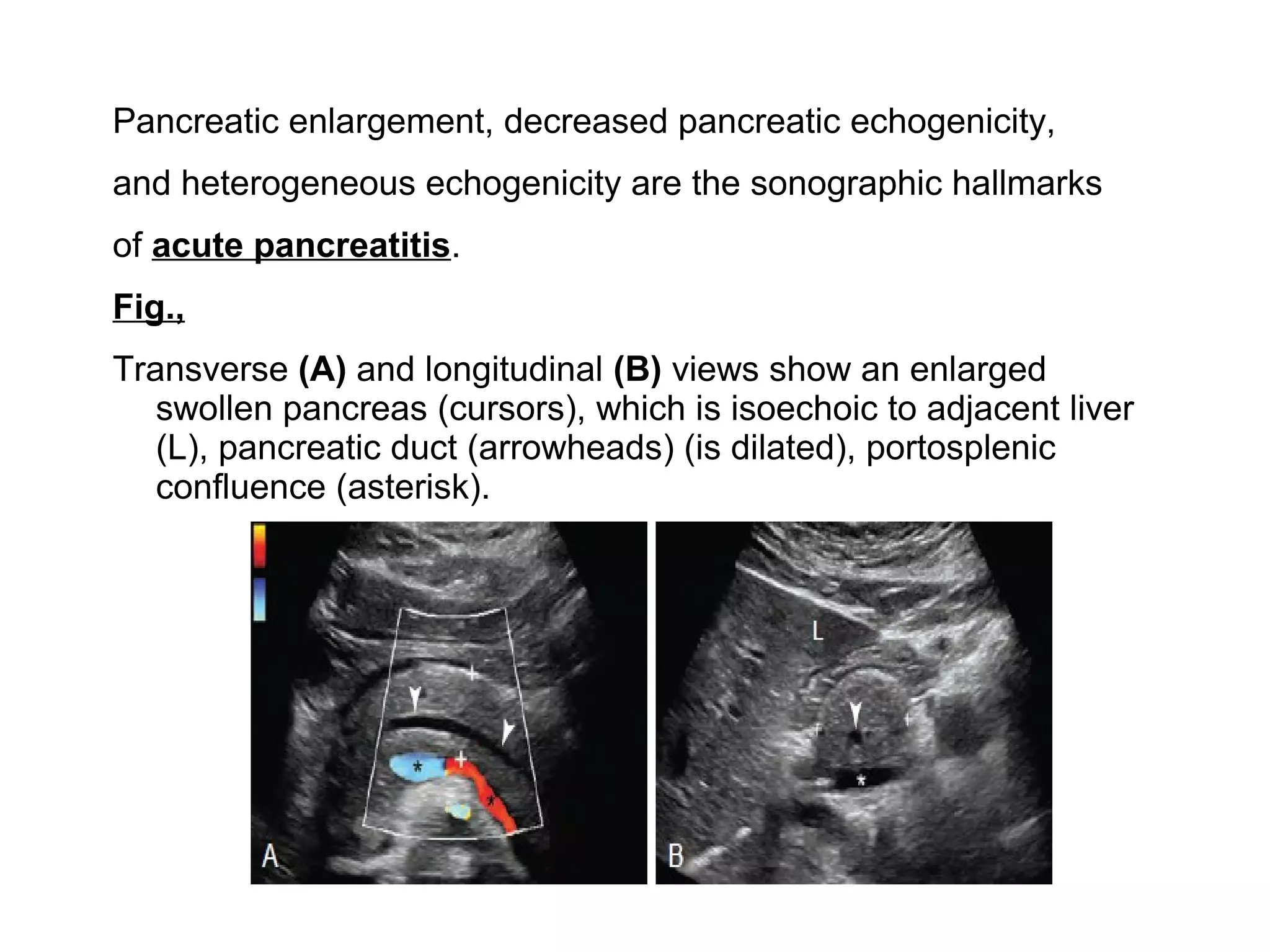
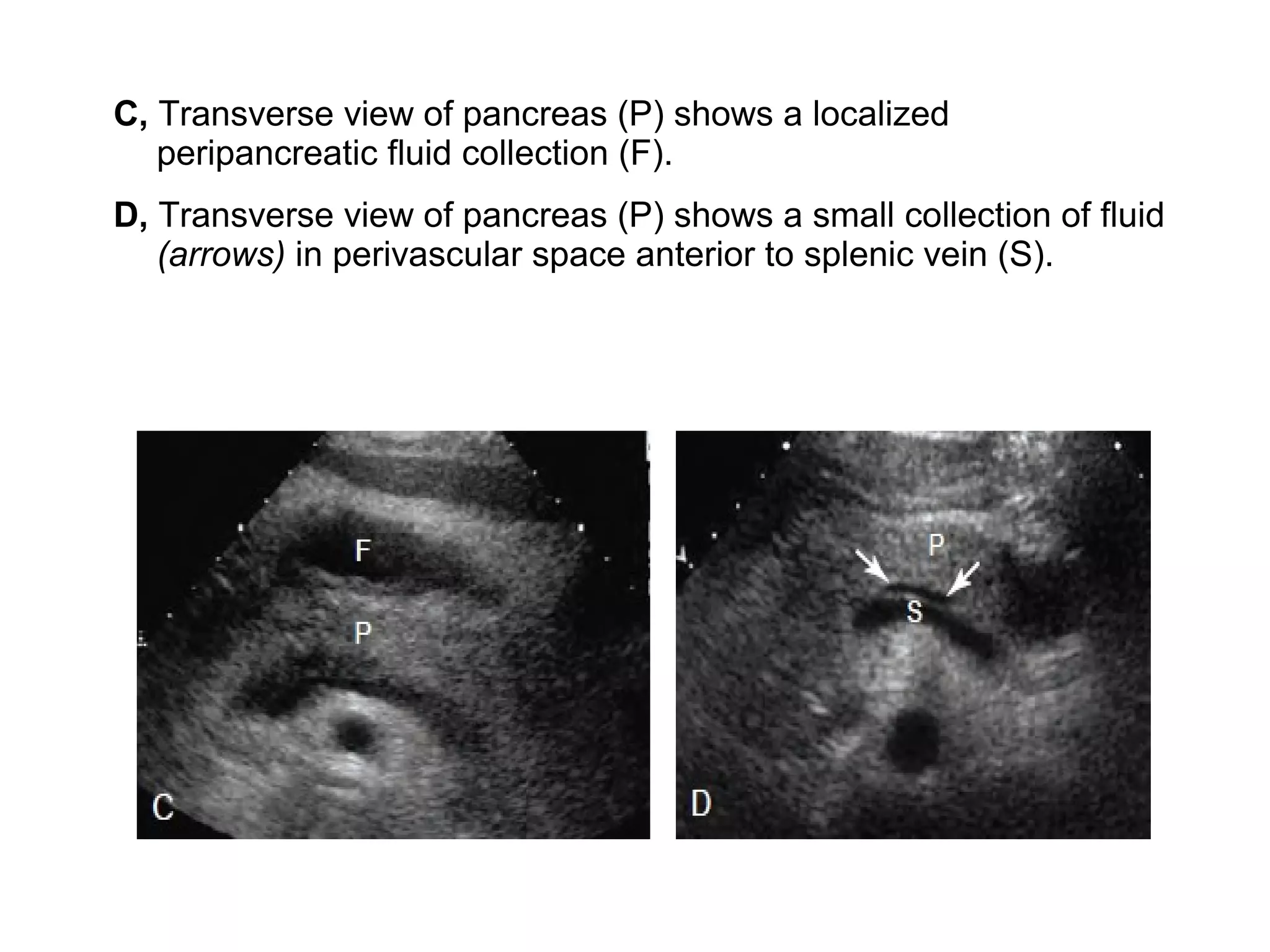
The pancreas normally has a head, body, tail, and uncinate process. It develops from two anlagen that fuse during embryological development. The pancreatic duct typically drains the entire pancreas. Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed based on abdominal pain, elevated pancreatic enzymes, and imaging findings of pancreatic swelling, decreased echogenicity, and heterogeneity. Sonography can detect pancreatic enlargement, duct dilation, peripancreatic fluid collections, and decreased echogenicity in acute pancreatitis.