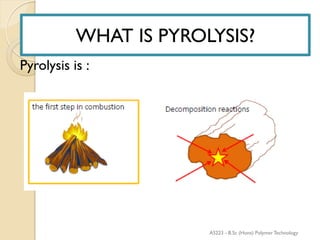
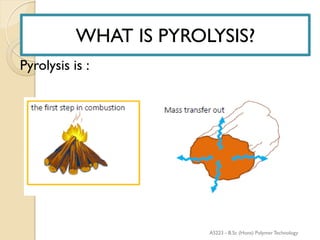
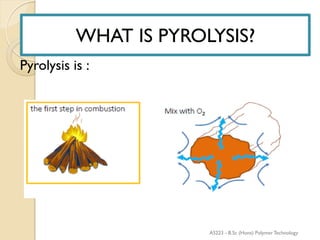
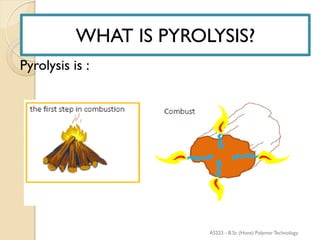
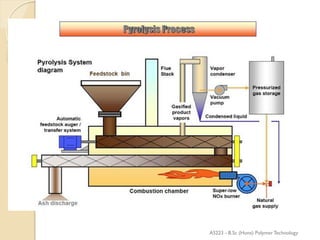
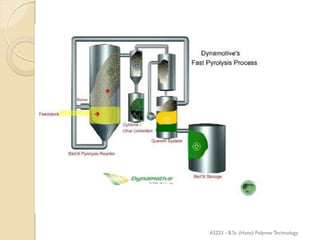
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures in an oxygen-free environment. It involves chemical changes and phase changes to the material. Pyrolysis of biomass produces bio-oil, char, and syngas. It occurs above 430°C without direct contact with oxygen or other reagents. Common pyrolysis types are dry pyrolysis, which occurs at various temperatures to produce different products, and oxidizing pyrolysis, where a small amount of oxidation takes place despite attempts at an oxygen-free environment.