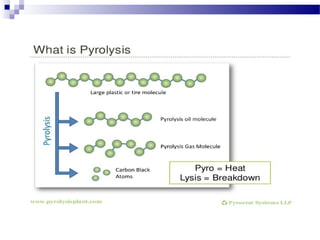
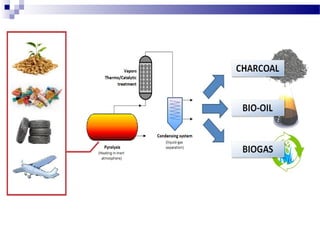
The document discusses waste polymer recovery through pyrolysis. Pyrolysis involves thermally decomposing waste plastics and tires at high temperatures without oxygen to produce pyrolysis oil, carbon black, and hydrocarbon gas. These products have various uses - pyrolysis oil can be used as fuel, carbon black can substitute for industrial coal, and gas can provide heat for the pyrolysis reactor. Pyrolysis is economically viable as the costs of raw plastic waste are decreasing while prices for pyrolysis oil are increasing.