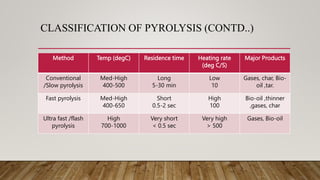
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process used to convert organic materials, like plastic waste and biomass, into fuel products in the absence of oxygen at varying temperatures. The process yields three main types of products: liquid (bio-oil), solid (char), and gas, with different pyrolysis methods (slow, fast, ultra-fast) affecting the output composition. Advantages include waste management and energy generation, but it comes with high operational costs and requires careful gas treatment.