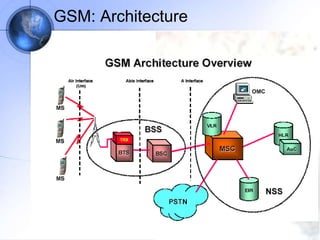
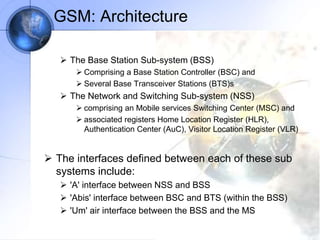
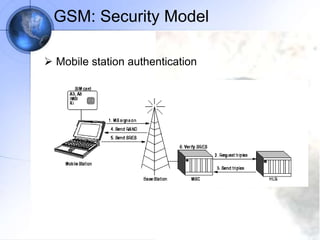
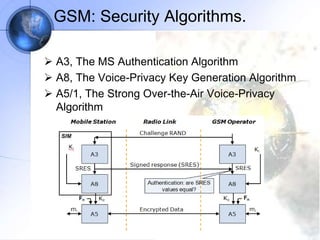
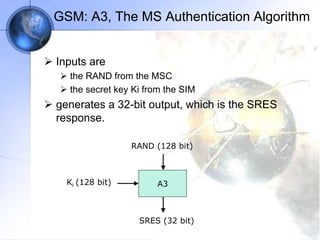
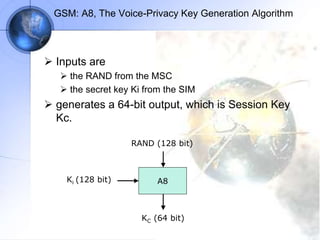
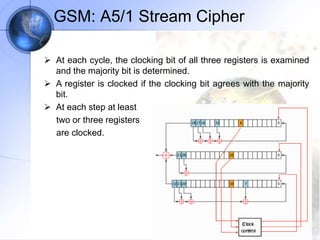
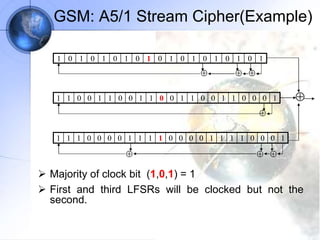
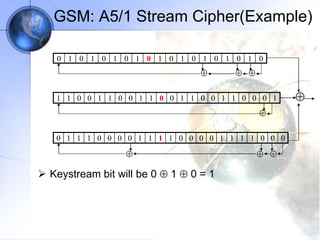
The document discusses security in GSM networks. It describes the GSM architecture including mobile stations, base stations, and network switching systems. It then explains the security concerns with GSM and the features used to address them, including subscriber authentication using algorithms A3 and A8, and voice encryption with algorithm A5/1. The document provides details on how these algorithms work to authenticate users and encrypt communications in GSM networks.